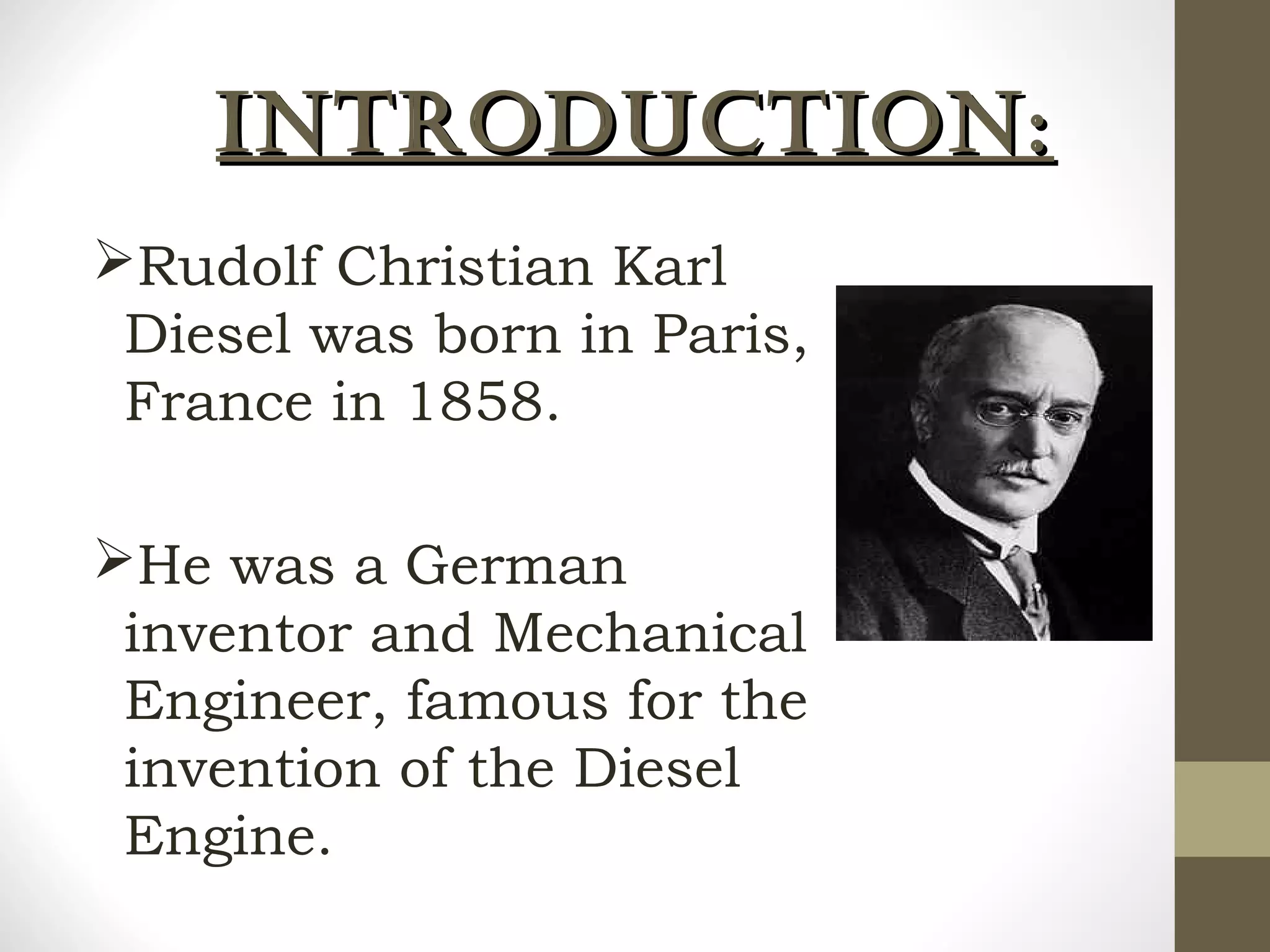
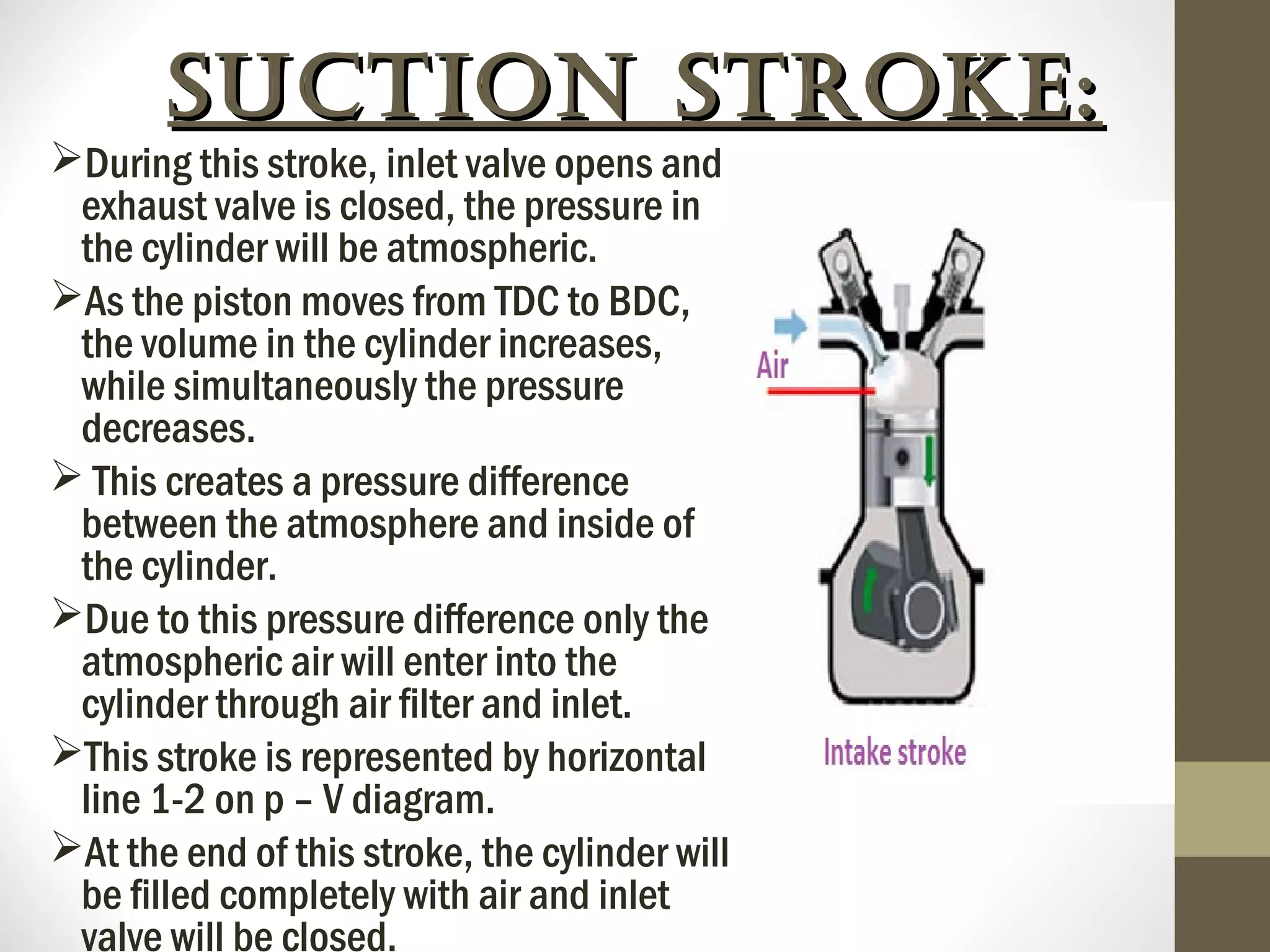
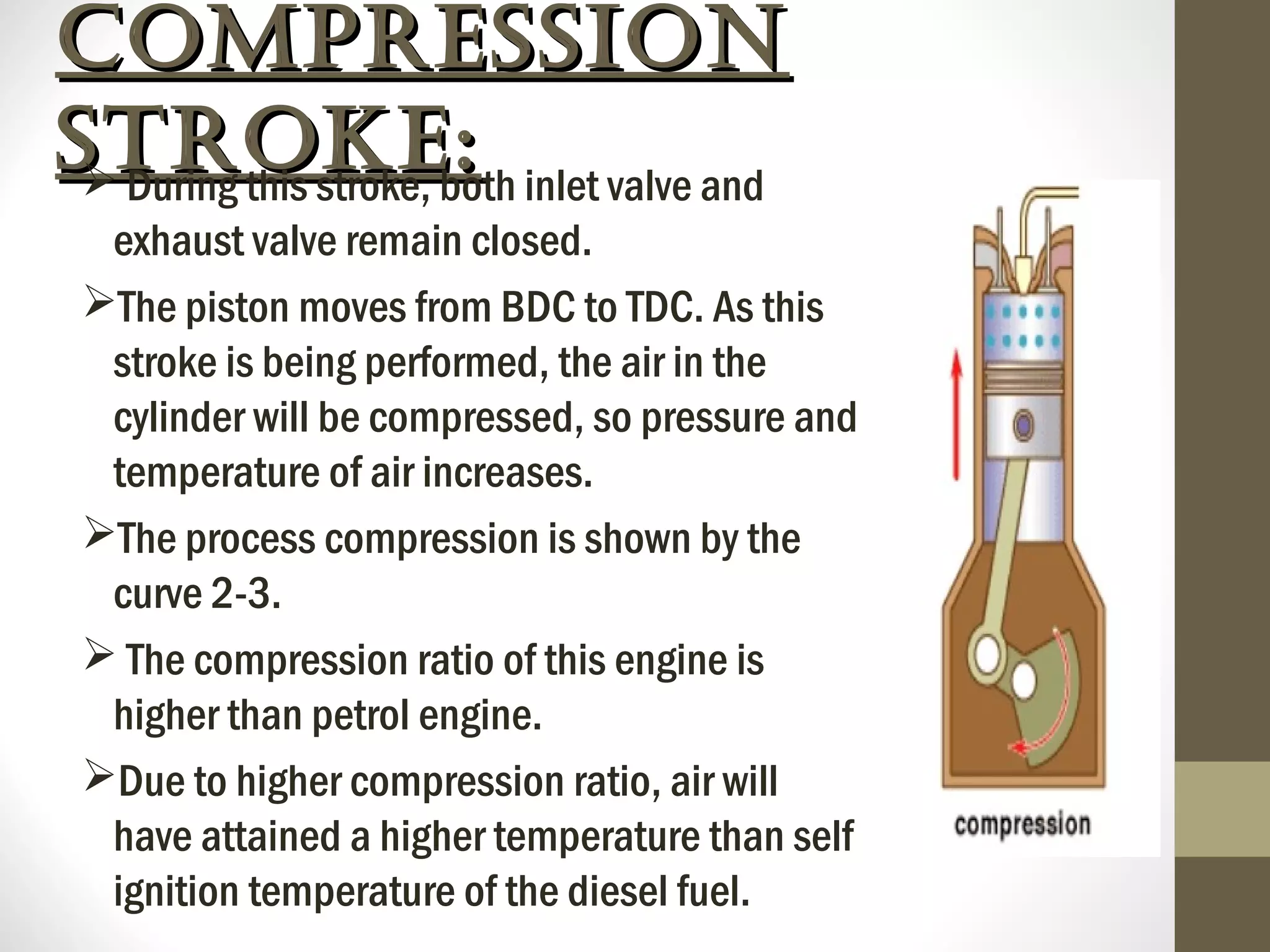
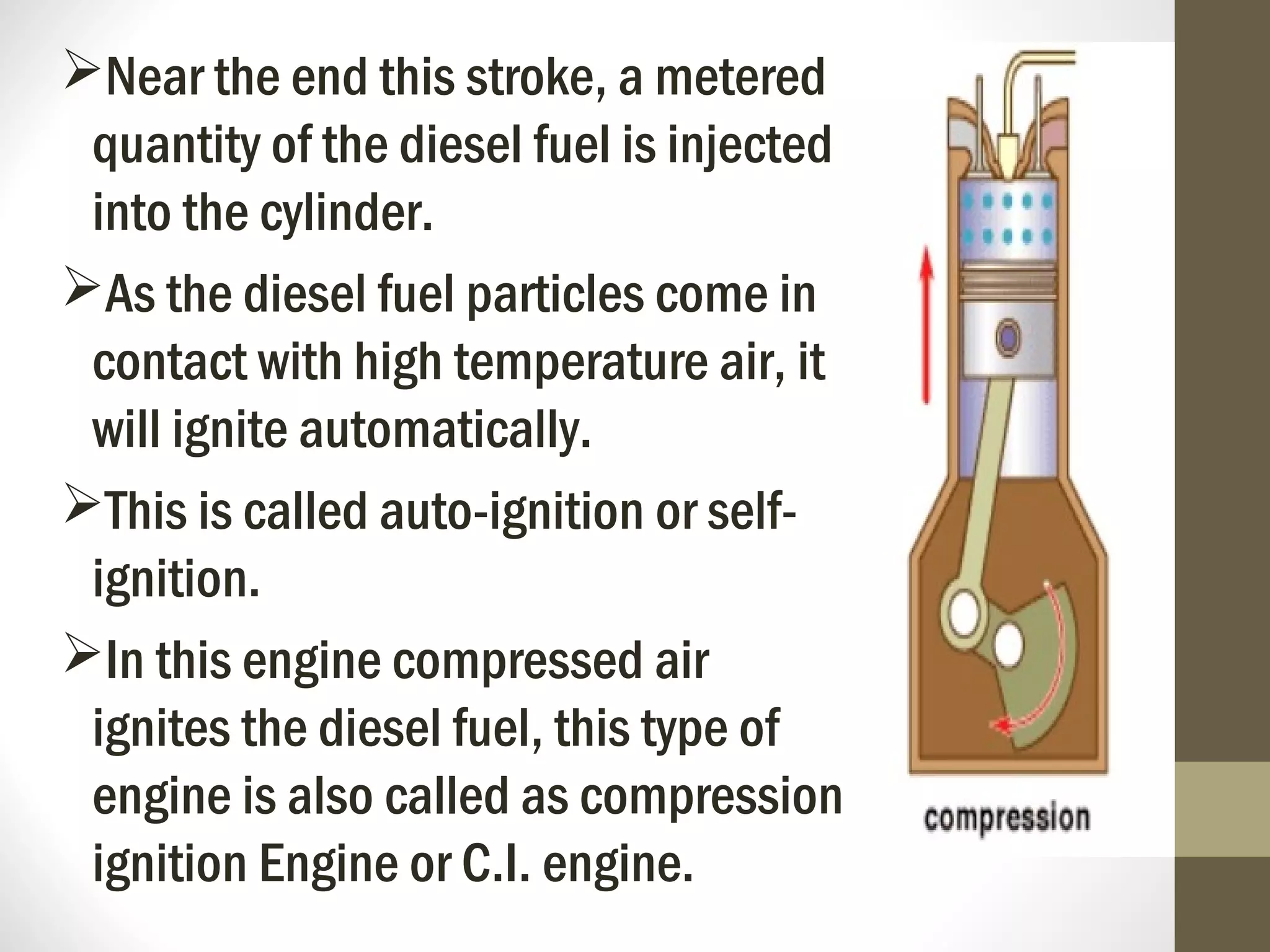
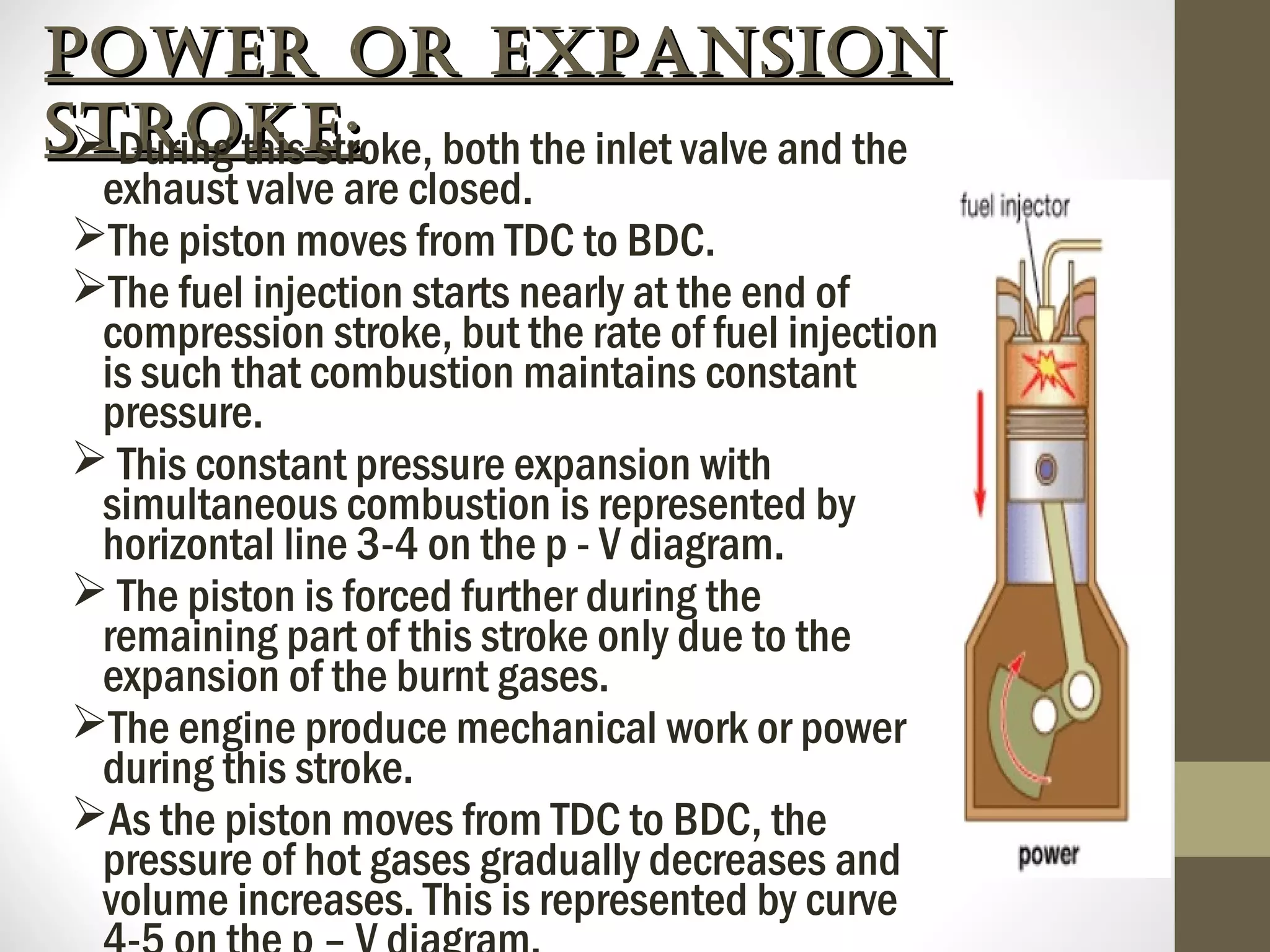
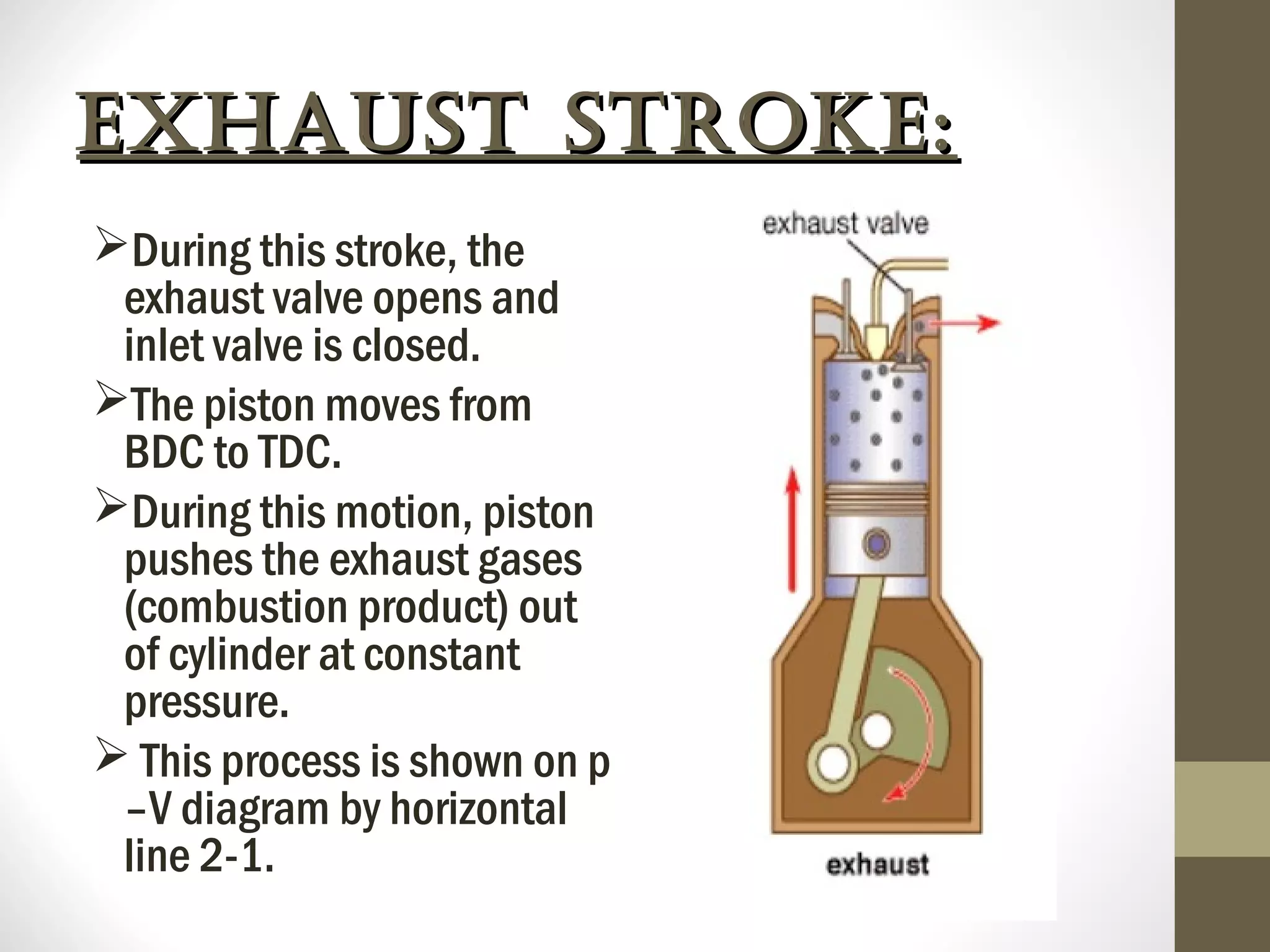
The document summarizes the working of a four-stroke diesel engine. It describes the four strokes of the diesel cycle: 1) Suction stroke where air enters the cylinder, 2) Compression stroke where the air is compressed, 3) Power or expansion stroke where fuel is injected and burned at constant pressure to push the piston, and 4) Exhaust stroke where burned gases are pushed out. Rudolf Diesel invented the diesel engine, which ignites fuel not with a spark but from the high heat of compressed air in the compression ignition cycle.