Embed presentation
Download to read offline





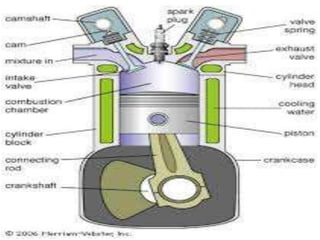



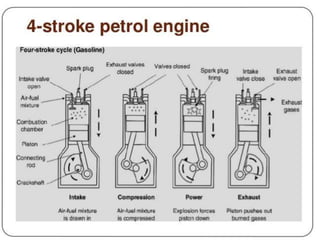


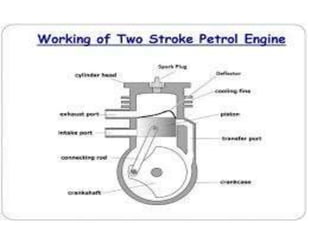



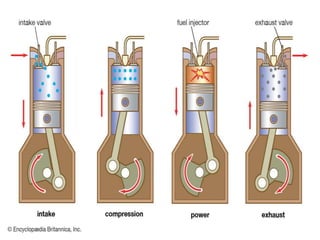




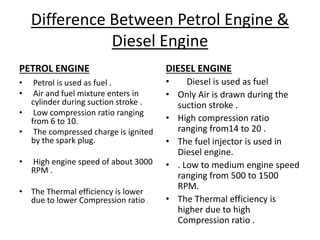
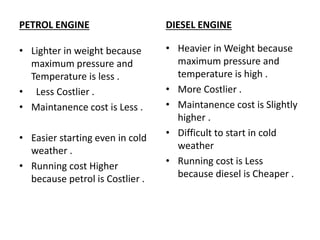

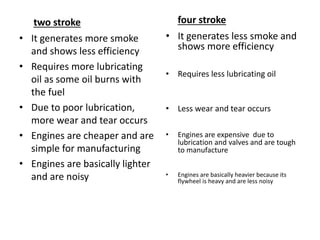

The document provides an overview of internal combustion engines. It defines internal combustion engines as devices that convert the chemical energy of fuel into heat energy and then into mechanical work. It classifies internal combustion engines based on the type of fuel used, thermodynamic cycle, number of strokes, ignition method, cooling method, cylinder arrangement, and engine speed. The document then describes the basic components and functioning of 4-stroke petrol engines, 2-stroke petrol engines, 4-stroke diesel engines, and 2-stroke diesel engines. It highlights the differences between petrol and diesel engines as well as 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines.

























