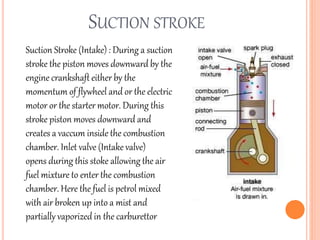
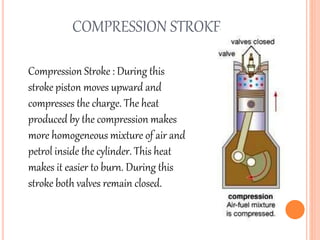
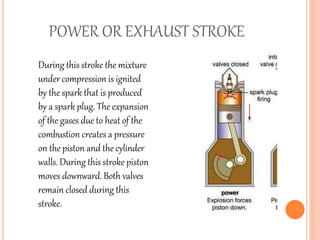
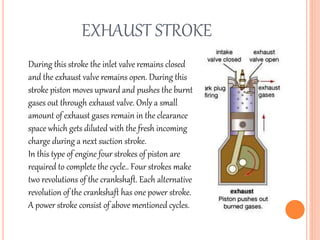
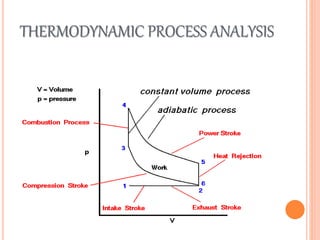
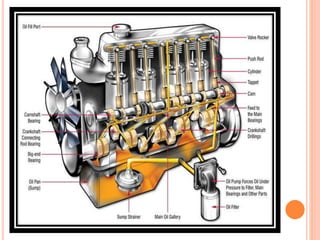
This document discusses the four stroke petrol engine. It describes the four strokes of the engine cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. During intake, the piston moves down and air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber. In compression, the piston moves up and compresses the mixture. In power stroke, ignition occurs and the expanding gases push the piston down. Finally, in exhaust stroke, the piston moves up to push out the exhaust gases. The four strokes complete one cycle requiring two revolutions of the crankshaft.