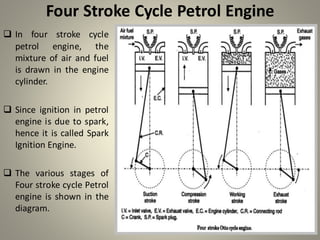
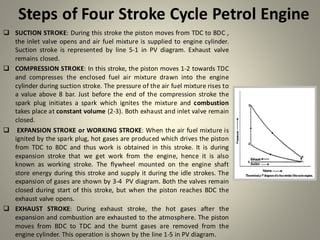
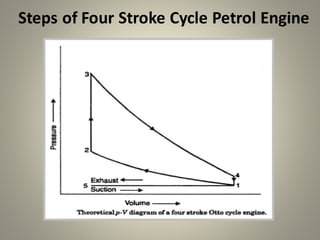
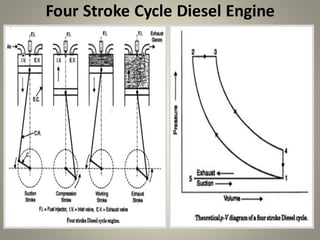
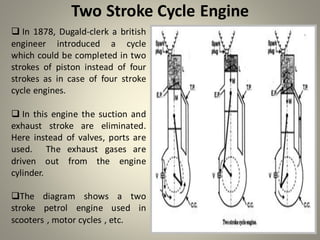
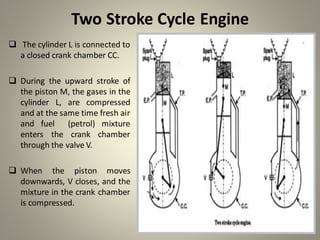
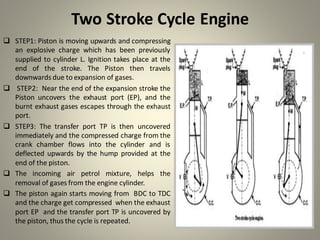
Internal combustion engines can operate on four main cycles: Otto, Diesel, dual combustion, and Atkinson. The Otto cycle uses spark ignition of a premixed fuel-air mixture at constant volume. Diesel engines ignite fuel injected into compressed hot air at constant pressure. Dual combustion engines combine aspects of Otto and Diesel cycles. Two-stroke engines complete the combustion cycle in two strokes while four-stroke engines take four strokes - intake, compression, power, and exhaust. The document then provides detailed explanations and diagrams of the operating cycles and processes within four-stroke petrol and diesel engines and two-stroke engines.