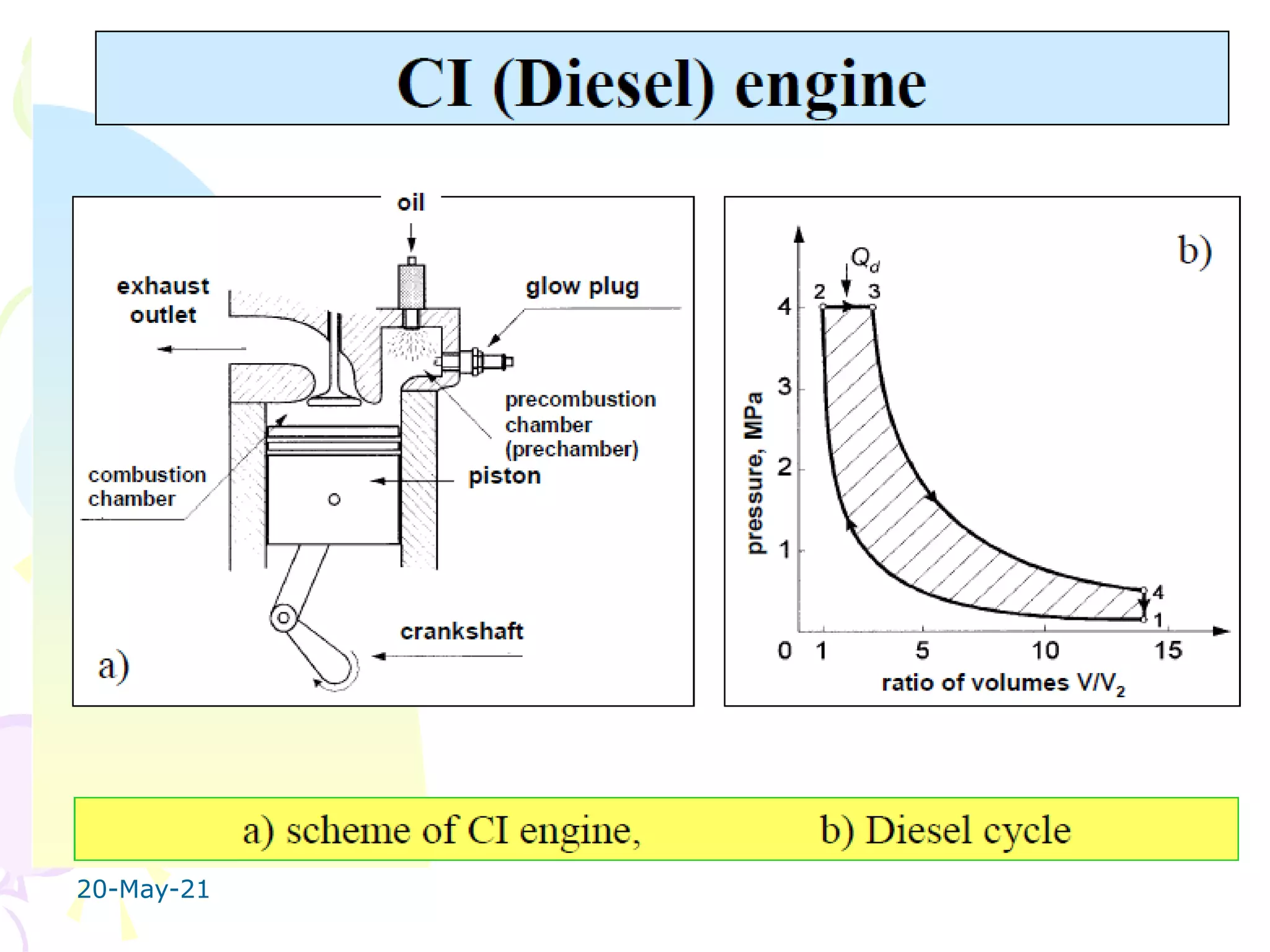
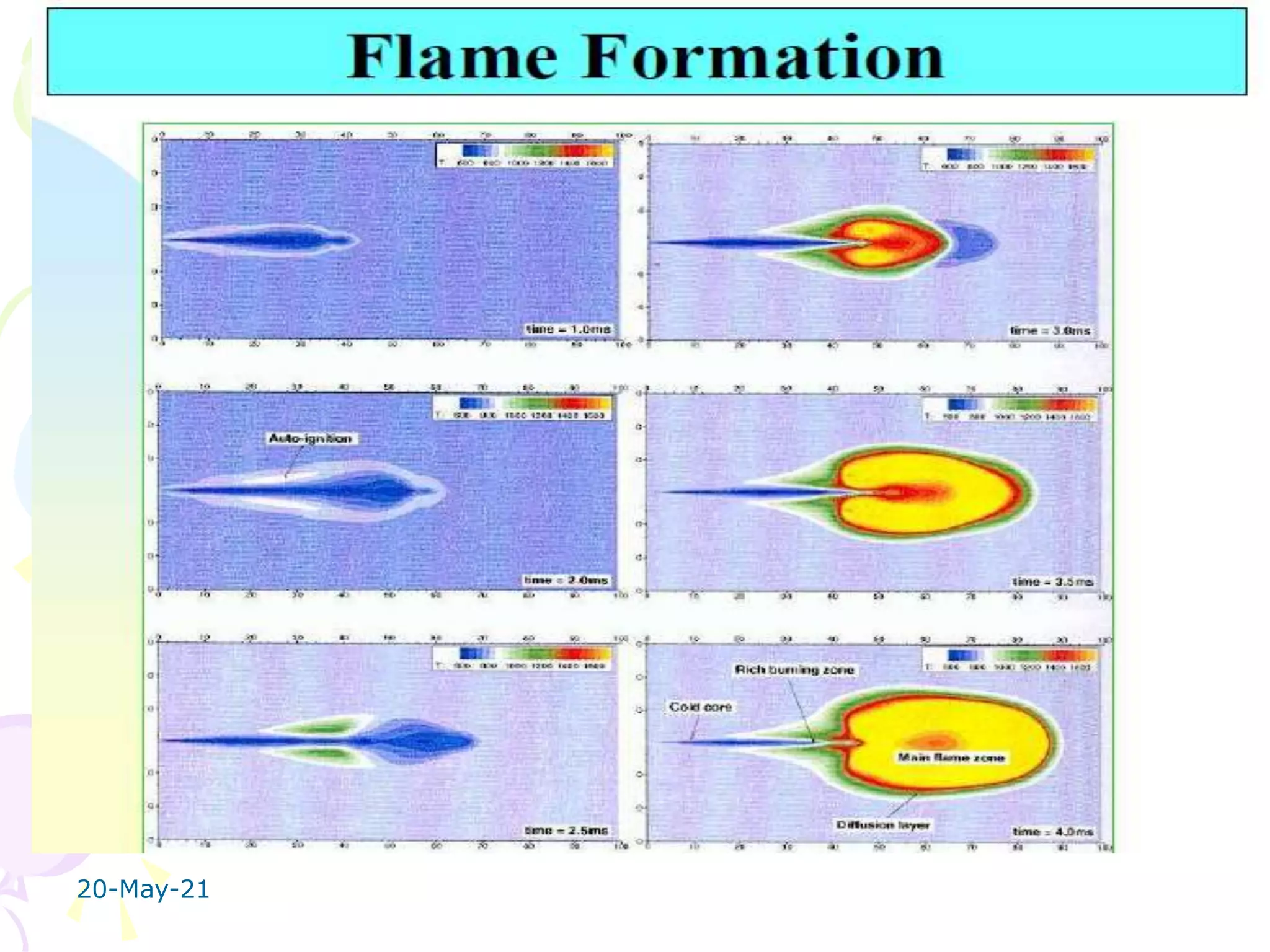
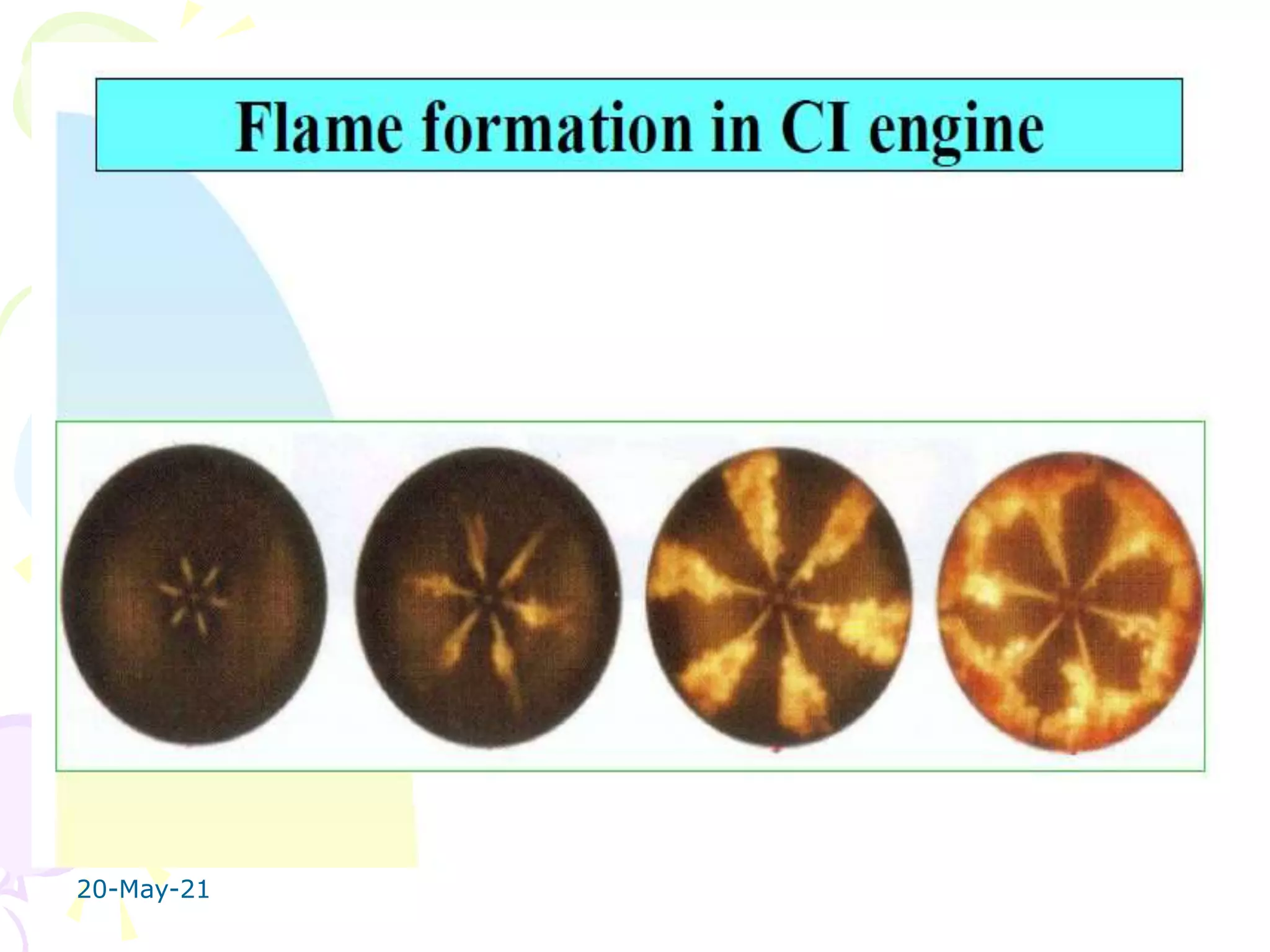
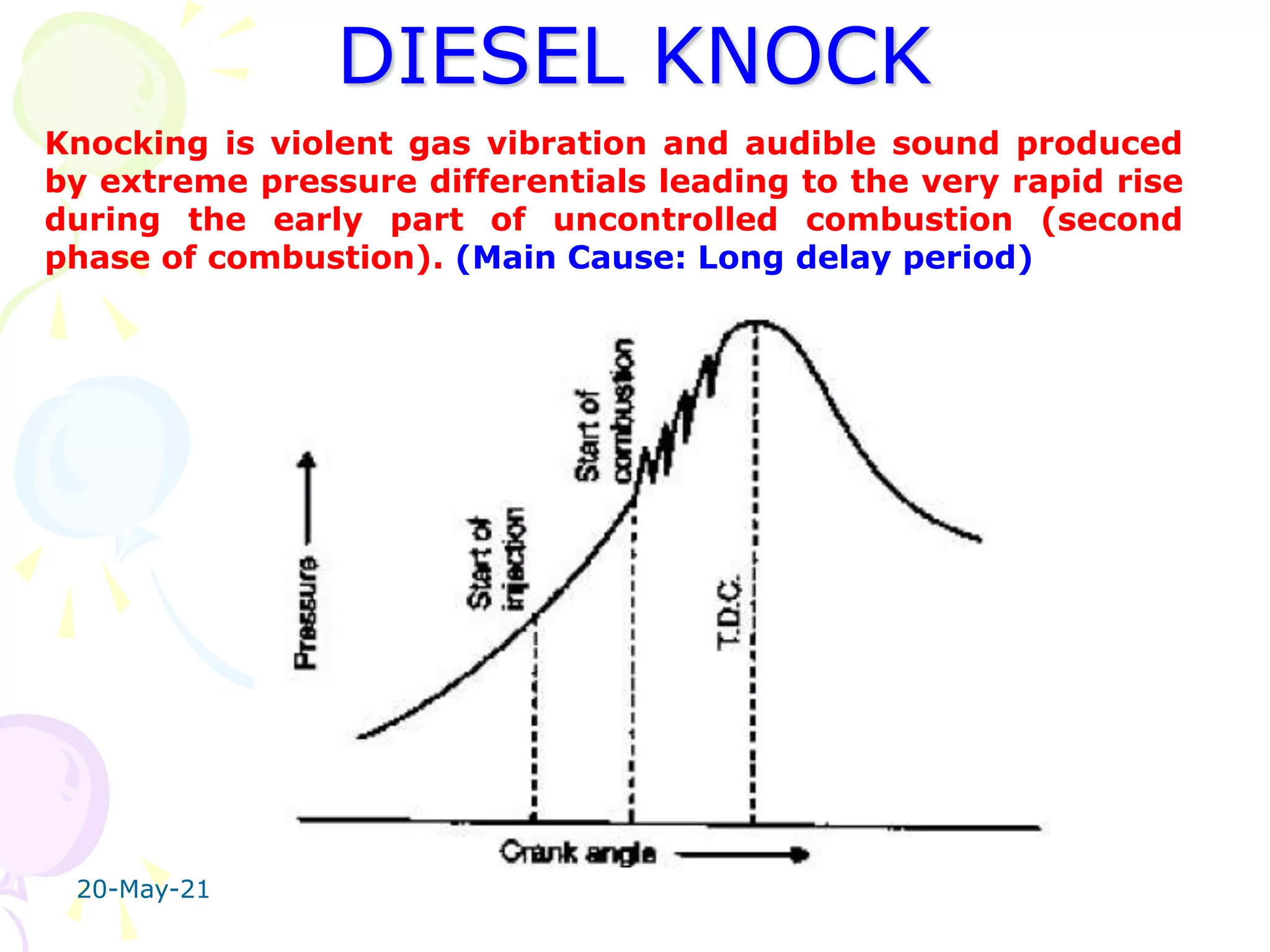
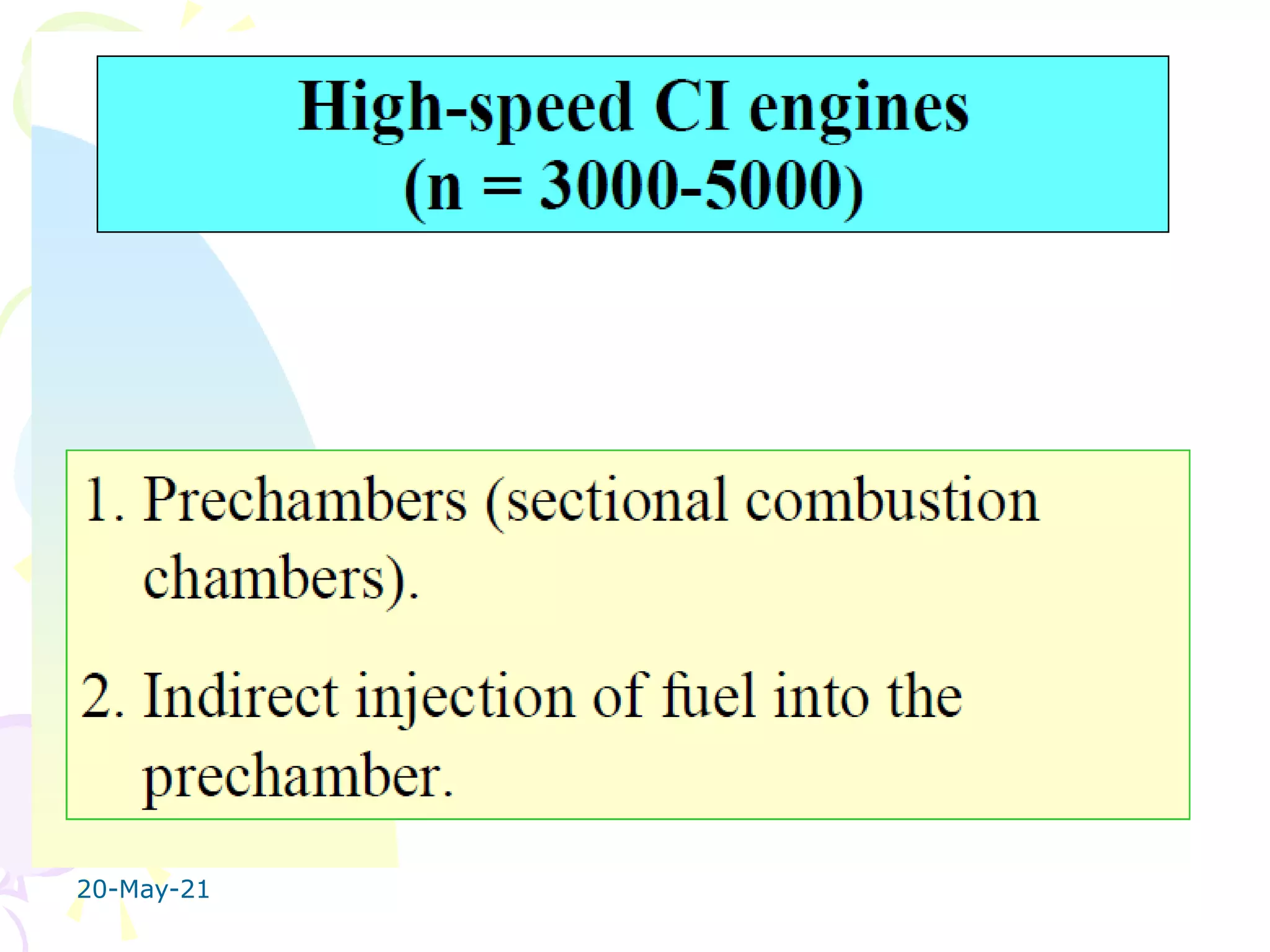
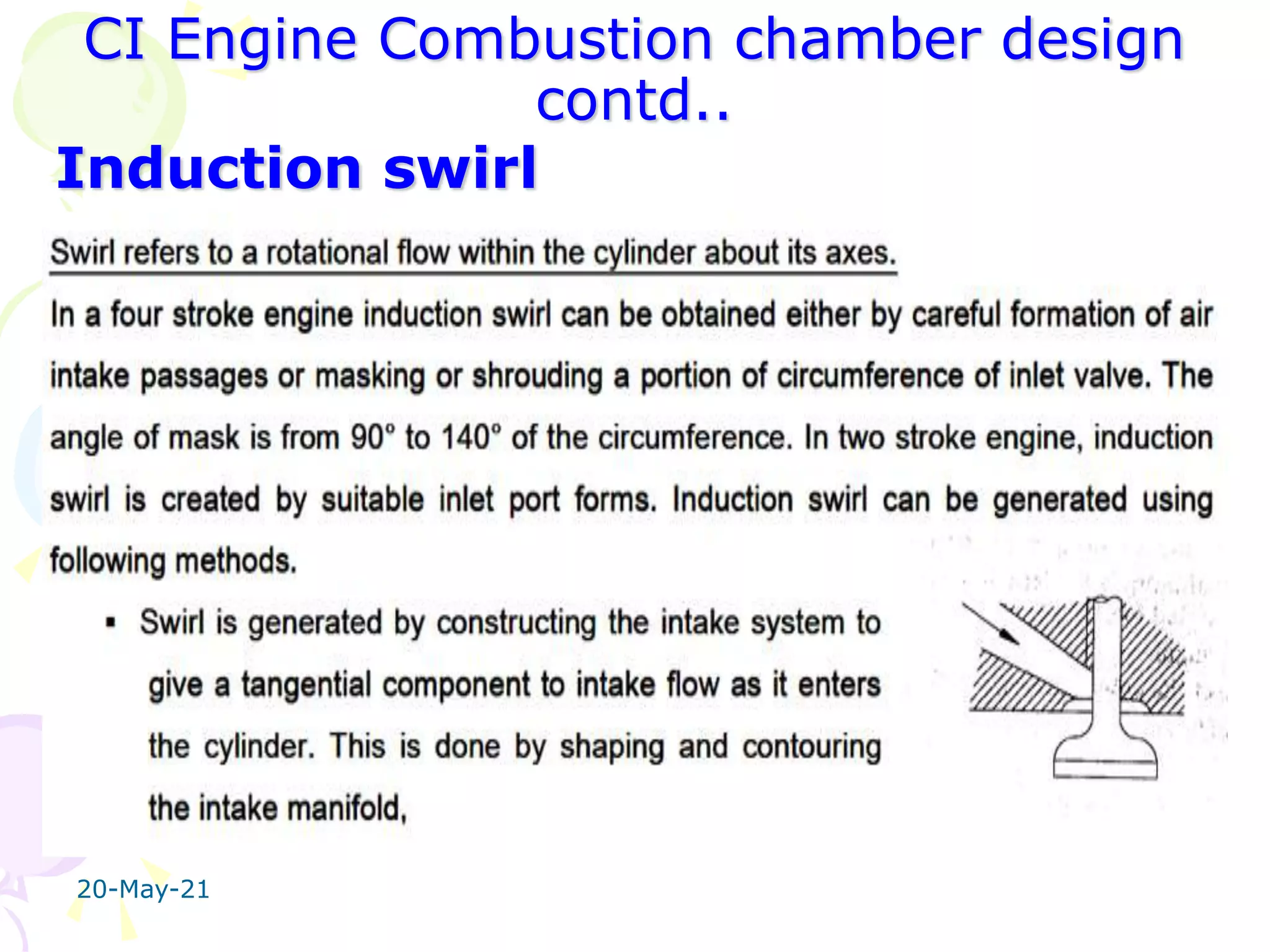
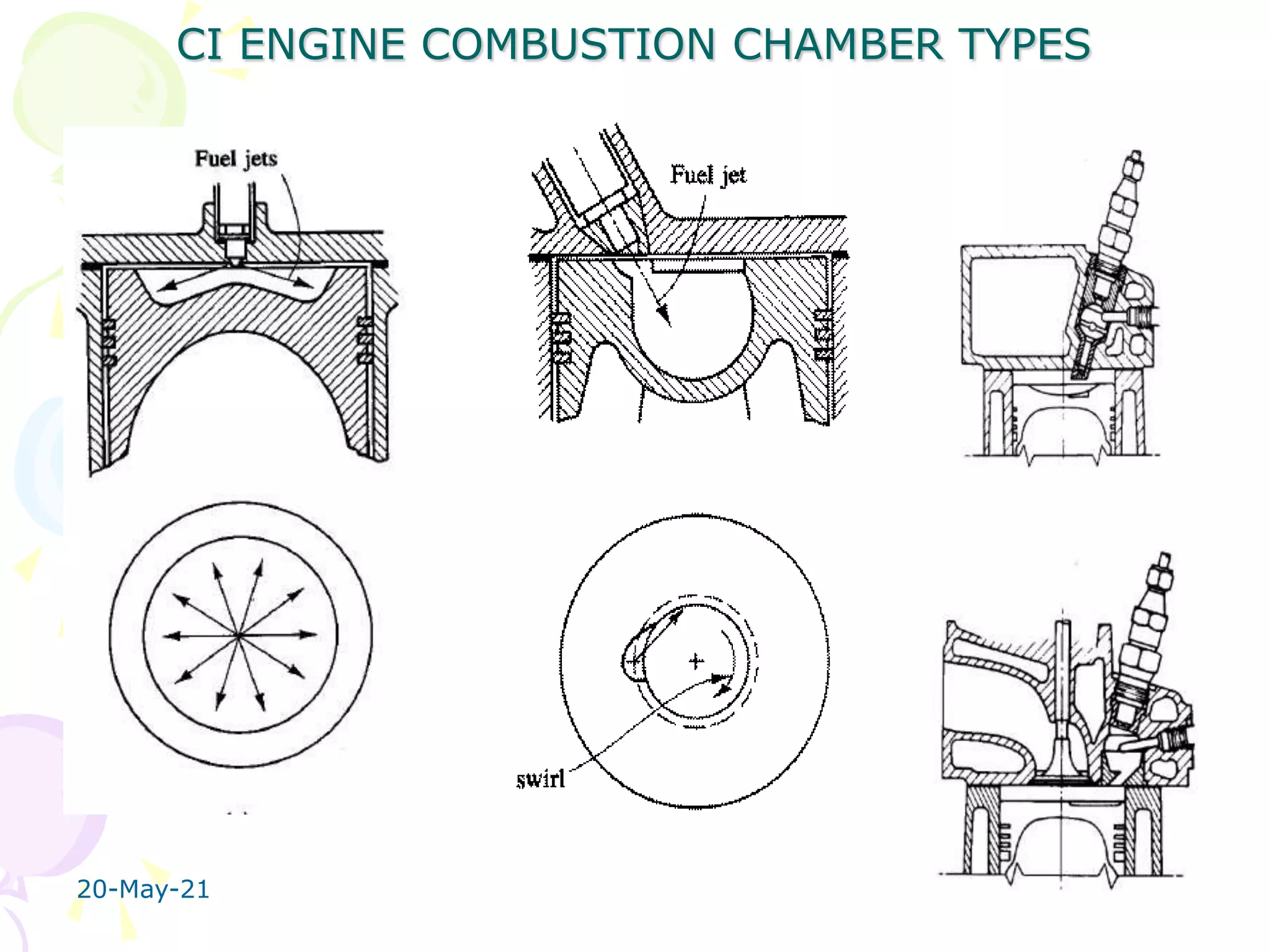
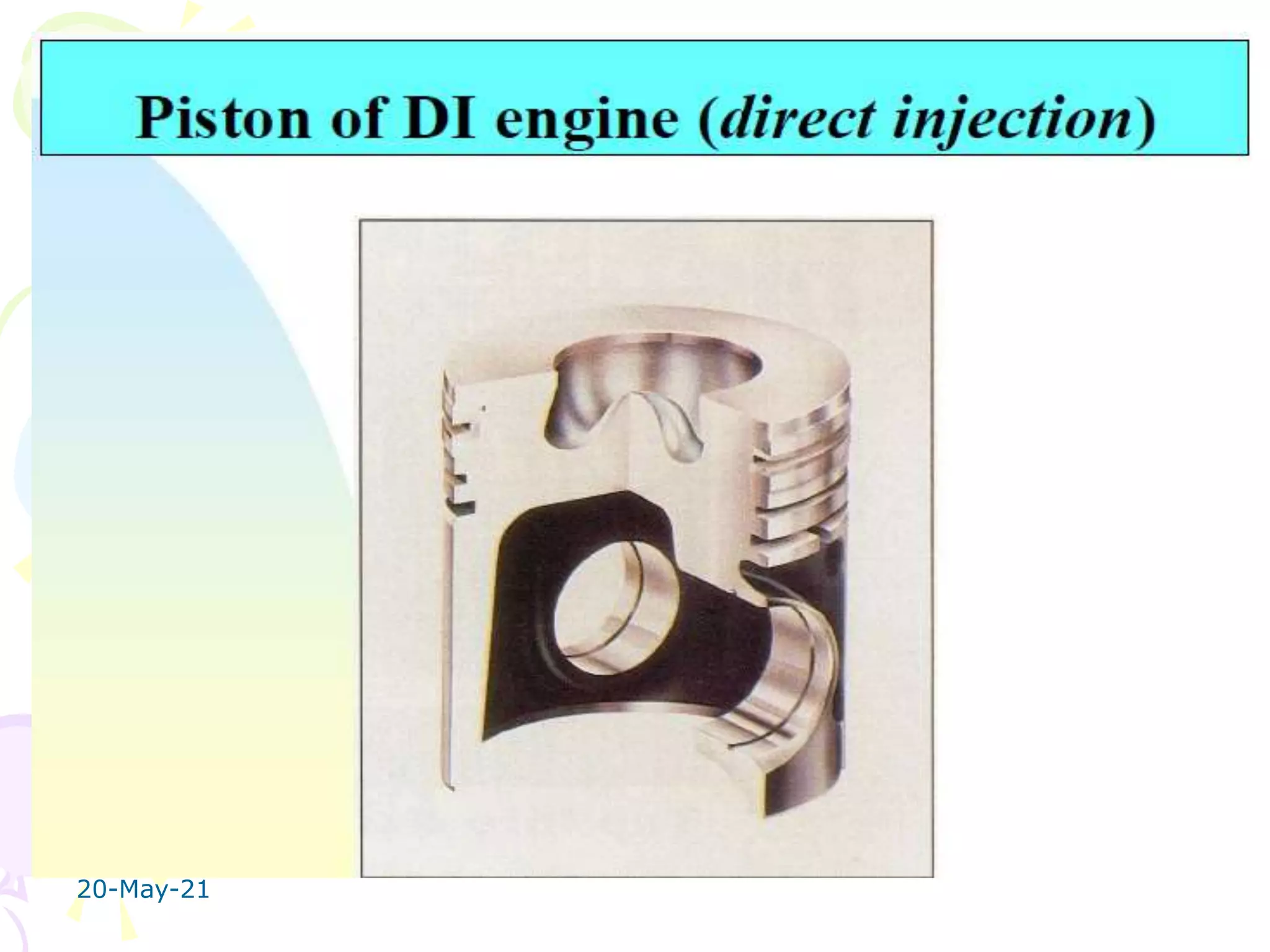
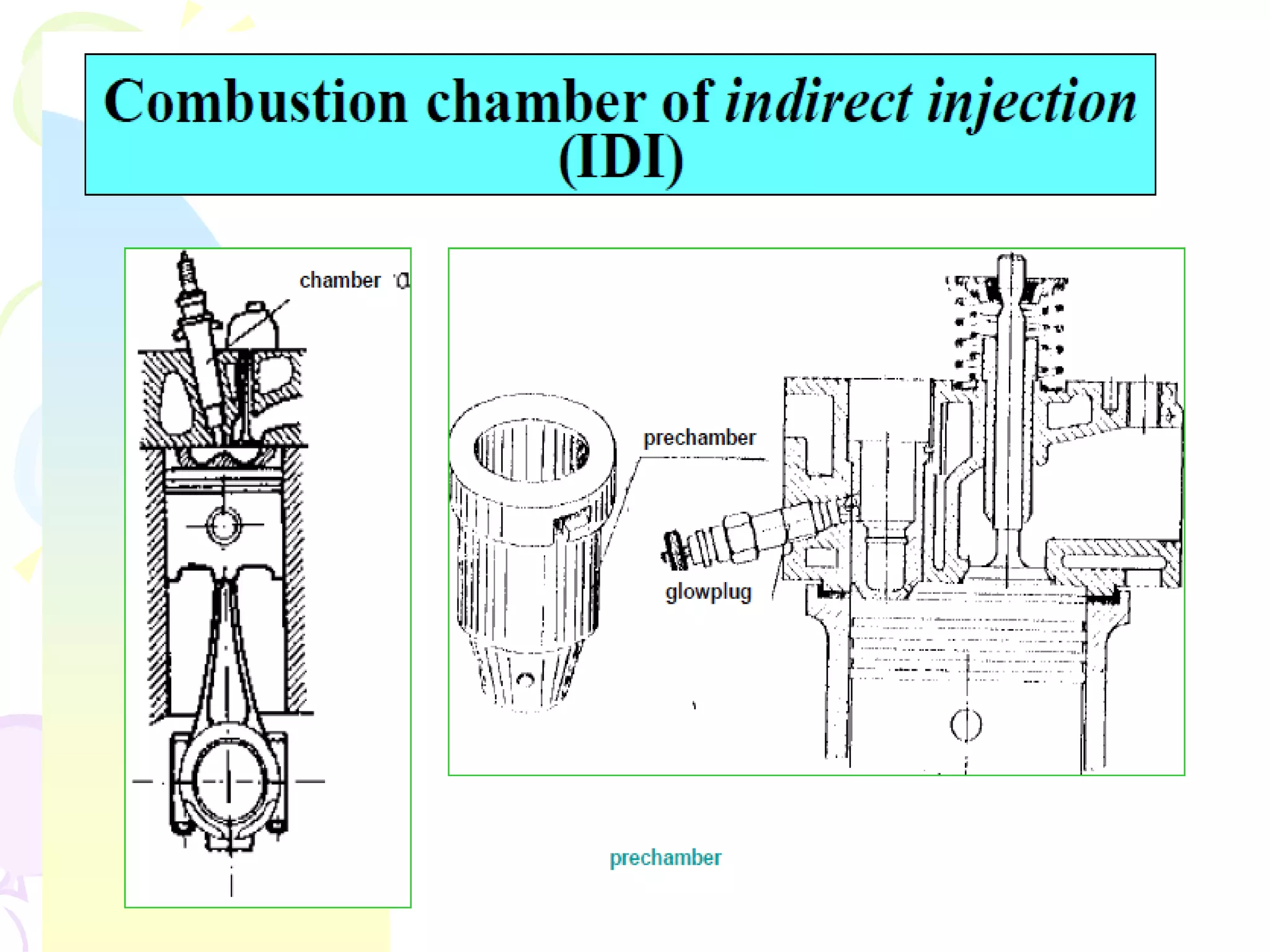
The document discusses the combustion stages in a compression ignition (CI) engine:
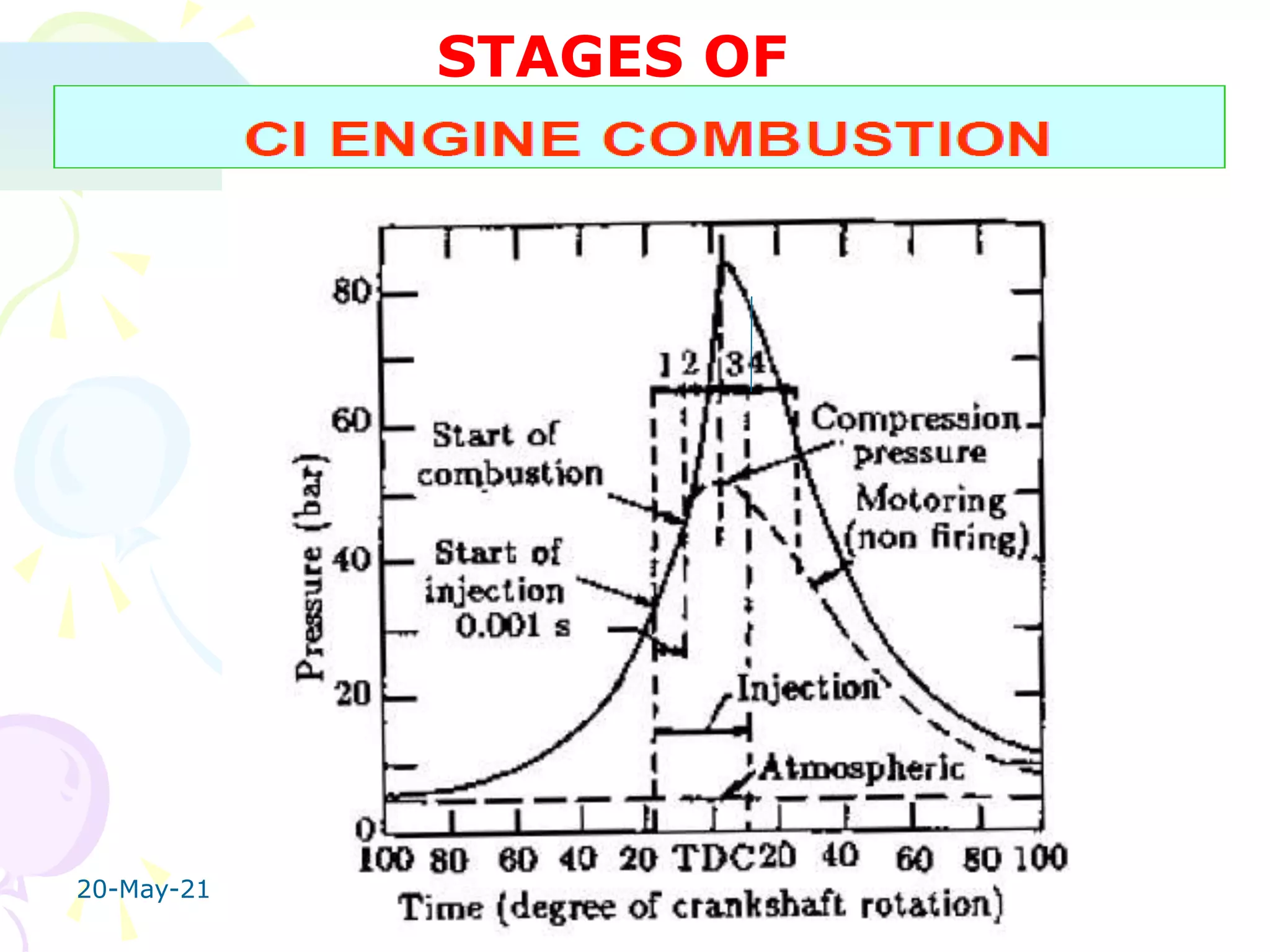
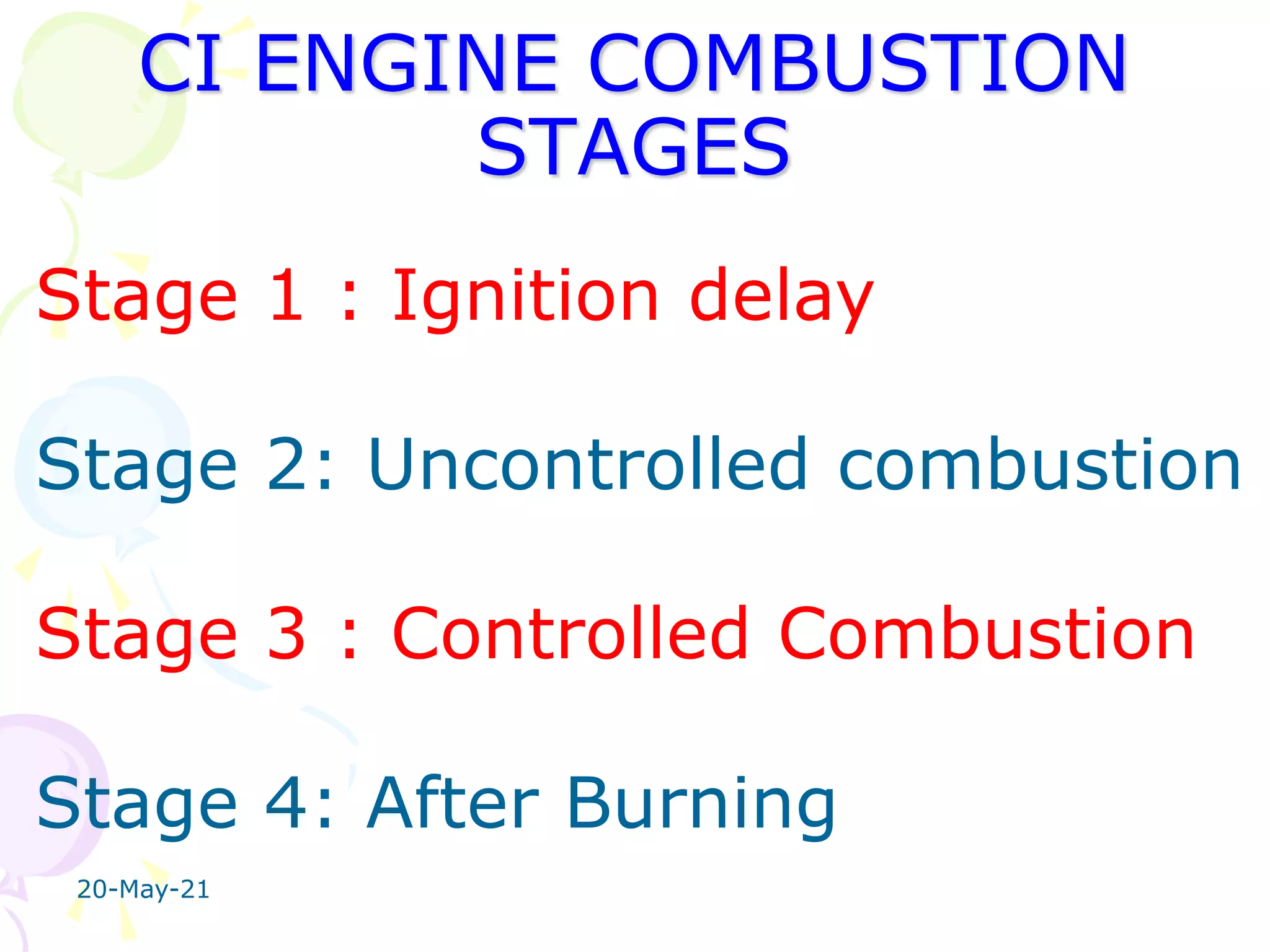
1. Ignition delay stage where fuel does not ignite immediately upon injection.
2. Uncontrolled combustion stage where rapid combustion occurs causing a steep pressure rise.
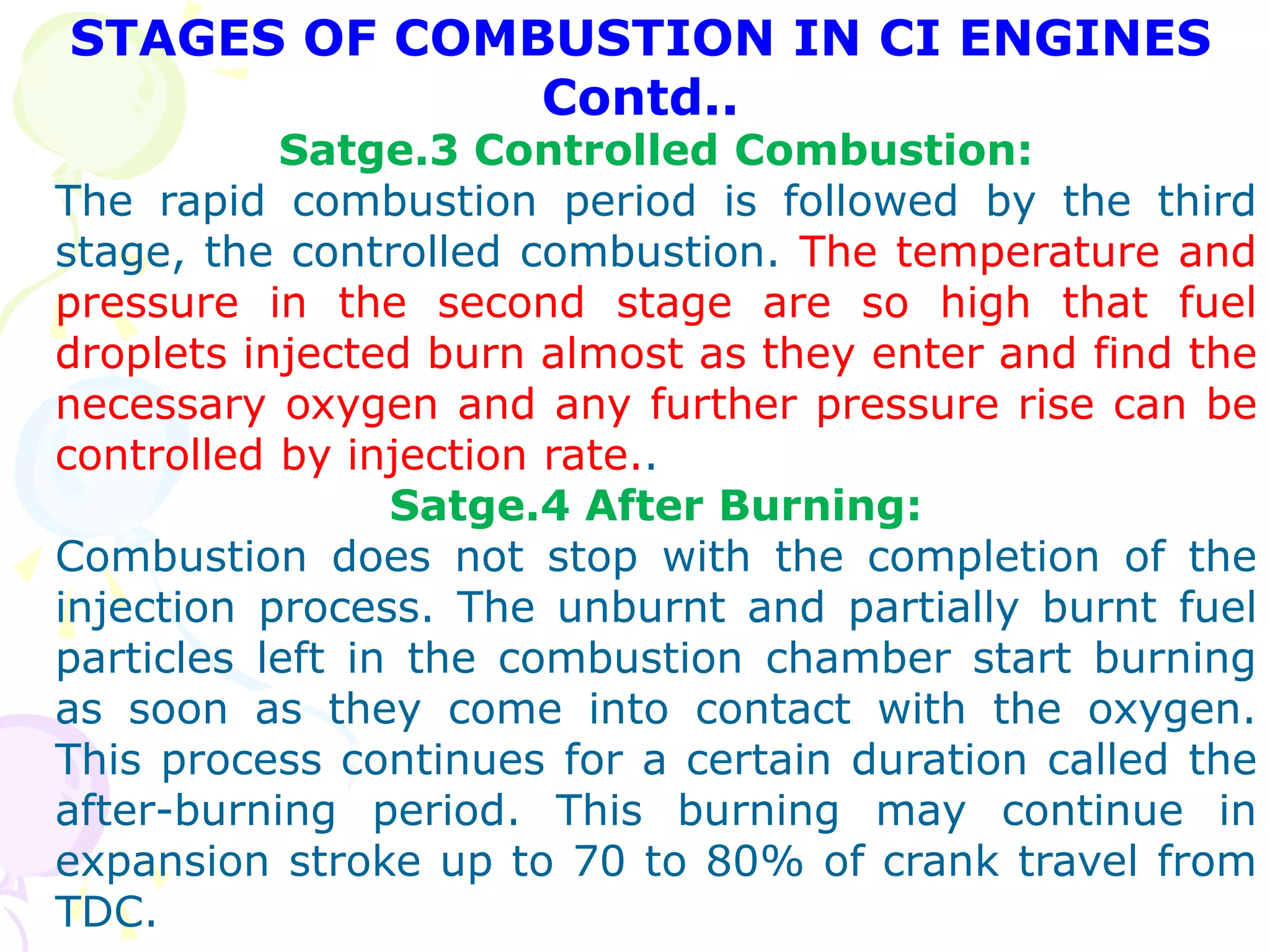
3. Controlled combustion stage where further pressure rise is controlled by injection rate.
4. Afterburning stage where unburnt fuel particles continue burning in the expansion stroke.
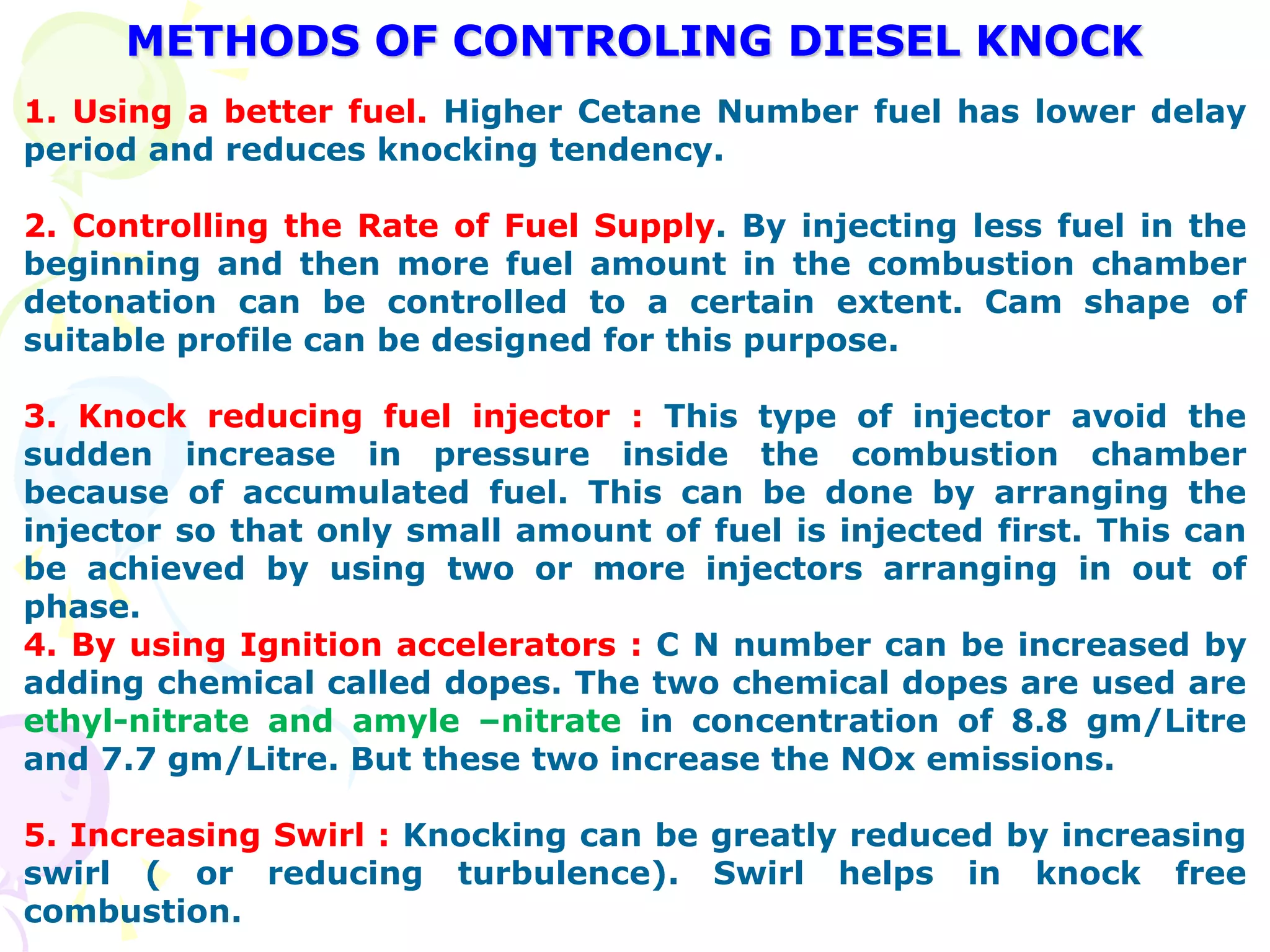
Diesel knock can occur if the ignition delay is long, allowing too much fuel to accumulate and cause an excessively rapid pressure rise when combustion begins. Methods to control knocking include using higher cetane fuel or modifying the combustion chamber design.