The document summarizes the history and workings of a diesel engine. It discusses:
1. Otto invented the four-stroke engine in 1876, using a gas-air mixture. This became known as the Otto cycle.
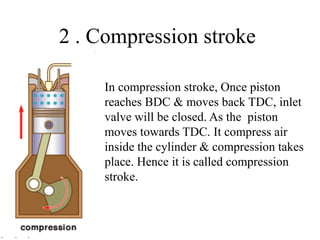
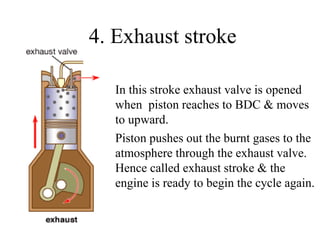
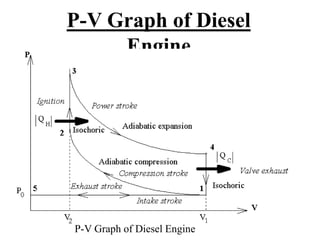
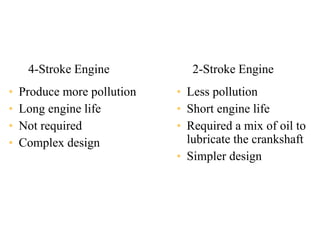
2. A four-stroke diesel engine completes one cycle over four strokes - intake, compression, power, and exhaust - within two revolutions of the crankshaft.
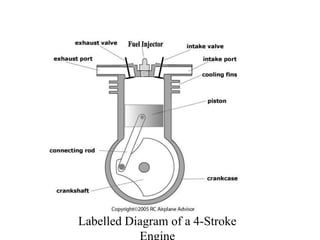
3. It provides labeled diagrams of the engine and describes the processes that occur in each stroke of the four-stroke cycle.