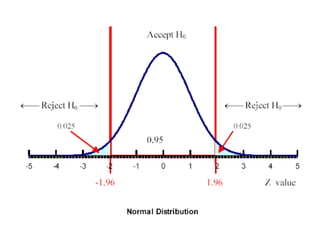
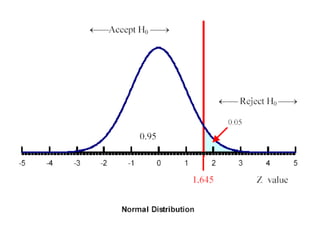
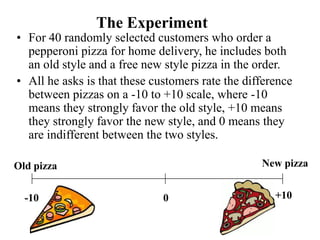
This document discusses one-tailed and two-tailed hypothesis tests. A one-tailed test has rejection regions in only one tail, while a two-tailed test splits rejection regions equally between both tails. The key difference is how the null and alternative hypotheses are expressed. A one-tailed alternative hypothesis uses "<" or ">" to specify the direction of the expected difference, while a two-tailed alternative uses "≠" to allow for differences in either direction. The appropriate type of test depends on what the researcher aims to prove.