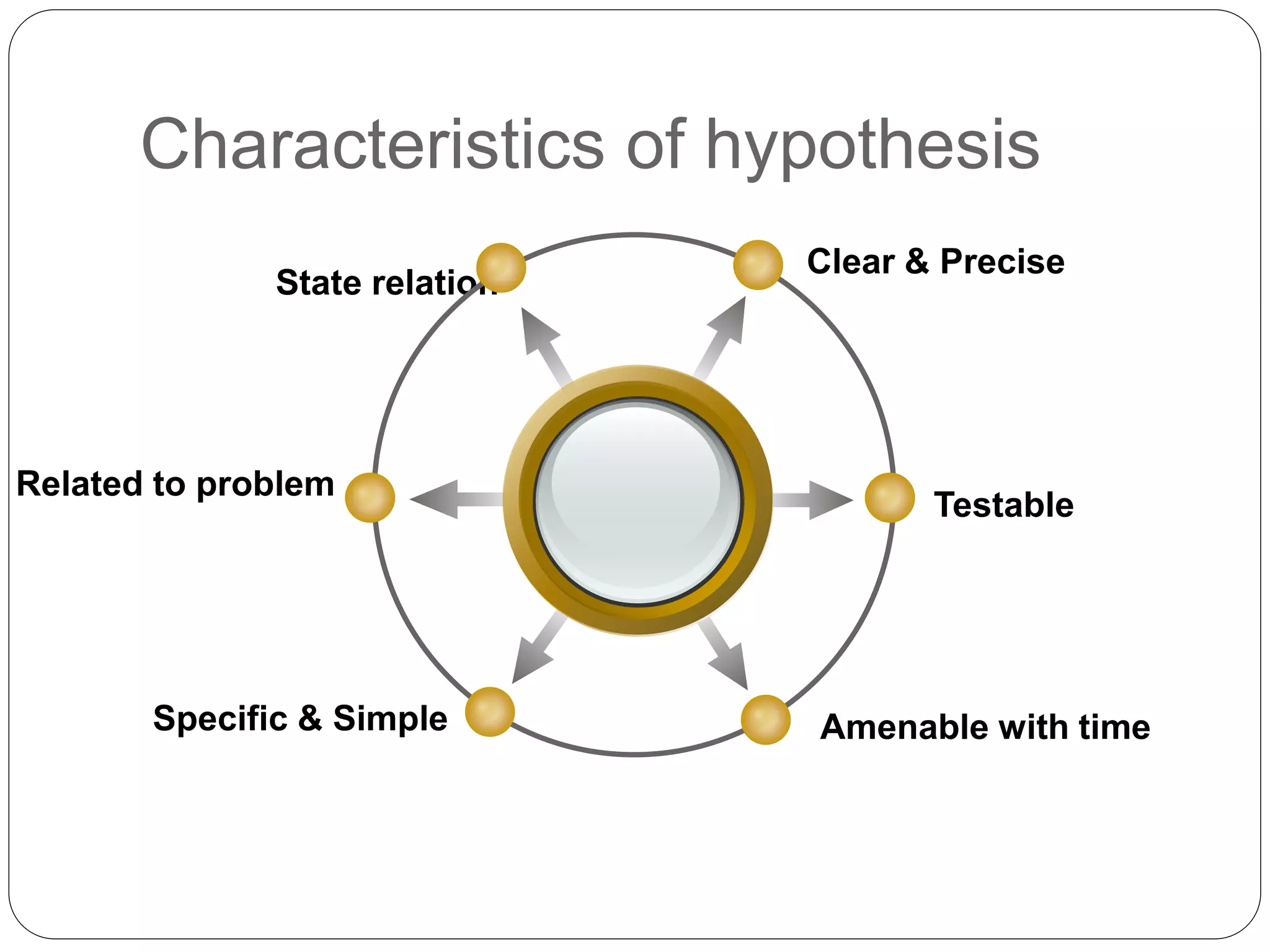
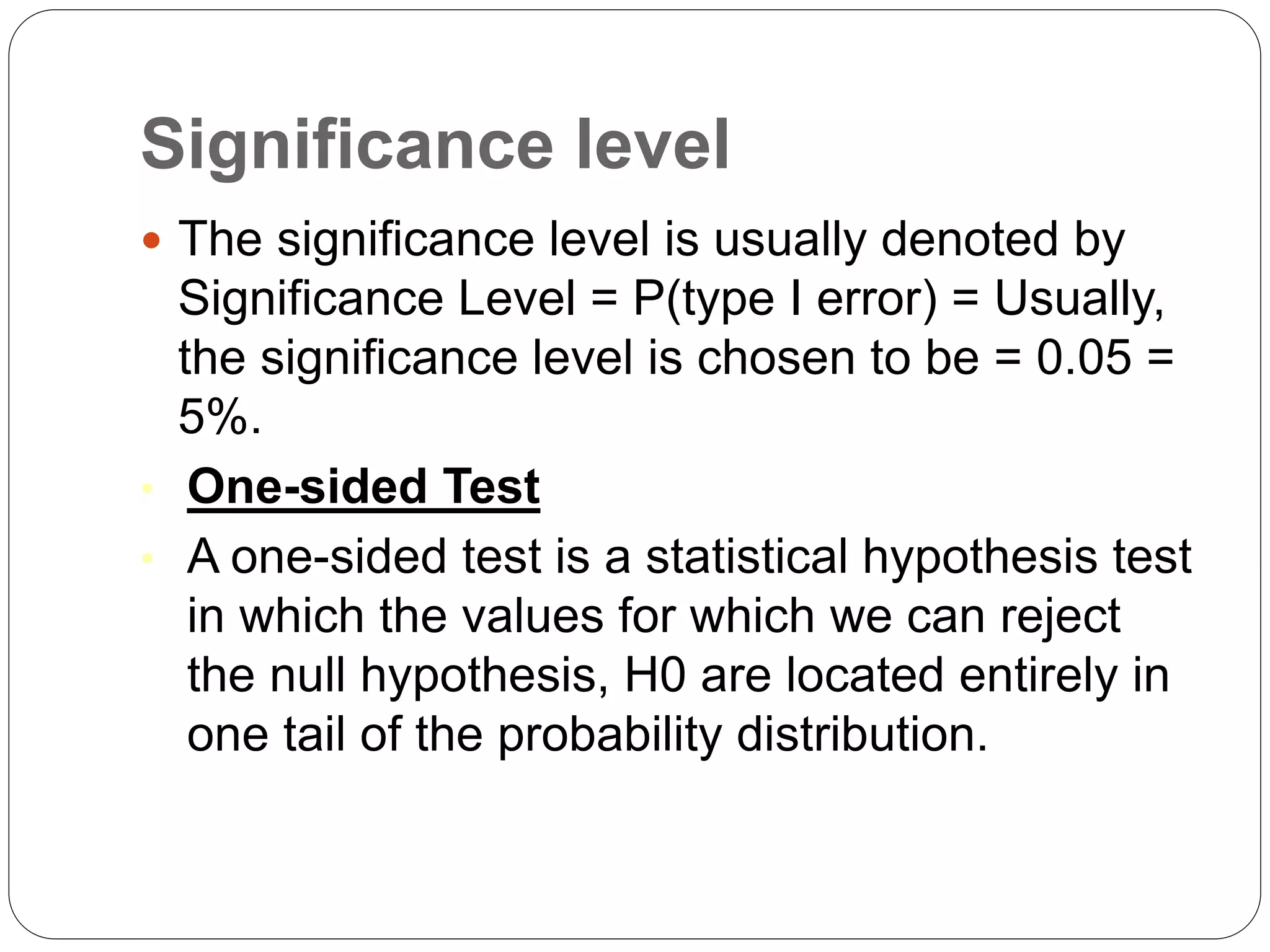
This document discusses key concepts related to testing hypotheses. It defines a hypothesis as a statement that can be tested scientifically to determine if it is true. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or relationship, while the alternative hypothesis specifies what the test is designed to detect. Type I and Type II errors occur when the null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected or accepted. The level of significance refers to the probability of a Type I error. One-sided and two-sided tests determine whether the critical values are in one or both tails of the probability distribution. Finally, a decision rule establishes the criteria for rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis based on the sample results.