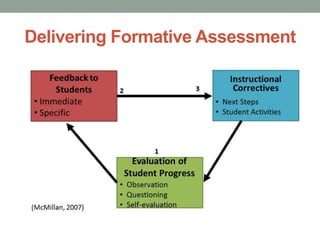
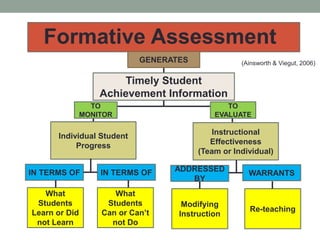
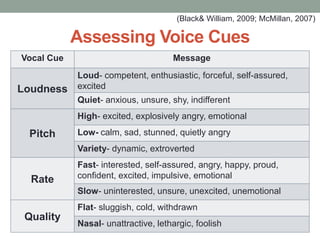
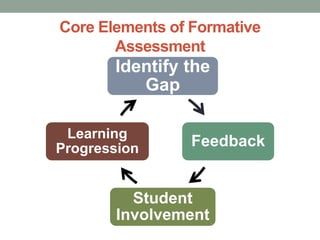
The document provides a comprehensive overview of formative assessment, aiming to improve student learning through ongoing feedback and instructional adjustments. It discusses the negative perceptions associated with traditional assessment methods and emphasizes the importance of understanding both the concept and practical applications of formative assessment in the classroom. Key techniques include gathering evidence from student interactions and promoting self-assessment to empower students in their learning journey.