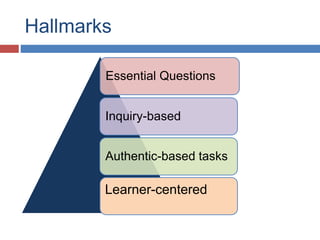
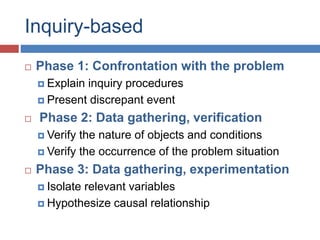
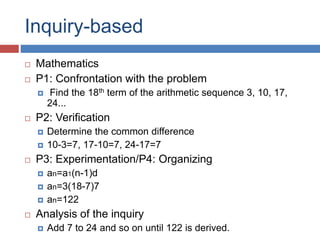
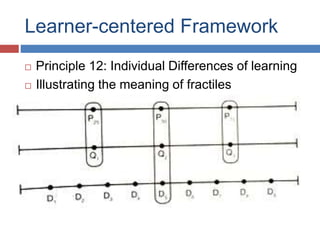
The document outlines the hallmarks of Vibal textbooks and emphasizes a learner-centered approach to education that incorporates inquiry-based and authentic tasks. It stresses the importance of engaging learners in active, constructive, and cumulative processes while promoting higher-order thinking skills and self-regulated learning. Additionally, it discusses the need for teachers to adapt to individual differences and develop positive relationships with students to support their educational journey.