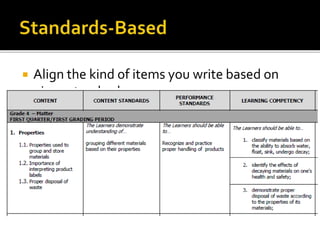
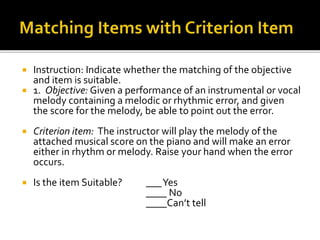
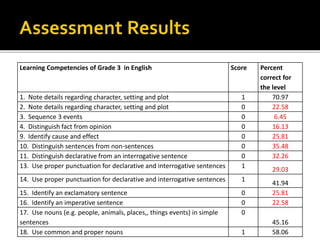
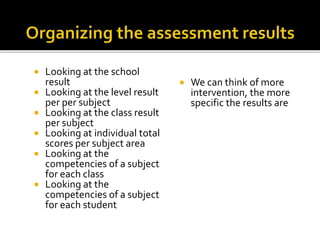
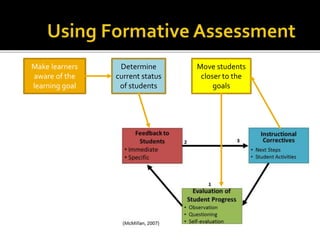
The document discusses the key role of school principals in improving student achievement. It emphasizes that principals should prioritize academics and quality instruction. They should ensure curriculum, instruction, and assessments are well-aligned. Principals also play an important role in analyzing student data and using it to inform instructional decisions. They must provide guidance to teachers on administering and using assessments effectively. Principals should also monitor instruction to guarantee changes are implemented based on data. Creating a culture of collaboration where teachers learn from each other is important. The document stresses the principal's responsibility for continuous learning in the school.