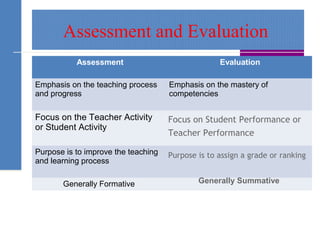
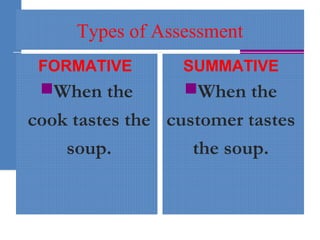
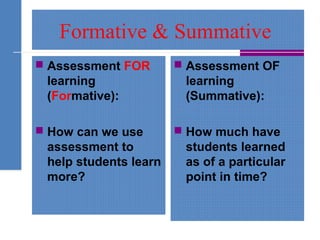
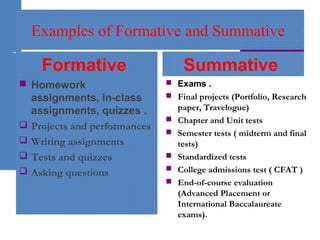
The document discusses assessment strategies in education, emphasizing the definition, types, and important qualities of effective assessments. It distinguishes between formative and summative assessments and provides examples and simple strategies to enhance student understanding. Additionally, it highlights the importance of feedback in the learning process and suggests various methods for evaluating student comprehension.