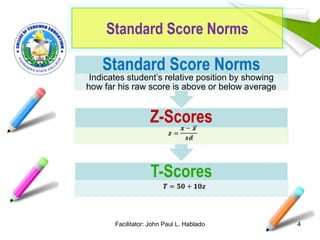
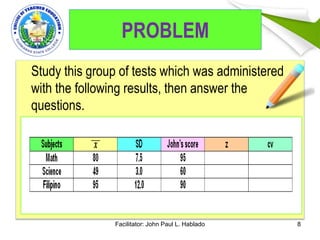
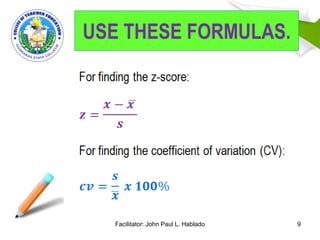
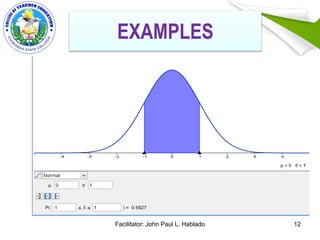
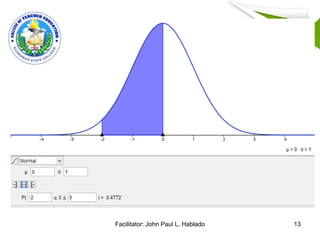
This document discusses two methods of interpreting test scores: norm-referenced and criterion-referenced. It also covers standard score norms like T-scores and Z-scores, which indicate a student's position relative to the average. The document uses an example to show how to calculate a Z-score and T-score. It also discusses the normal curve distribution and areas under the curve. Finally, it lists guidelines for properly interpreting test results, such as considering the test items, a student's background, and purpose of evaluation.