The document discusses the concept of force. Some key points:
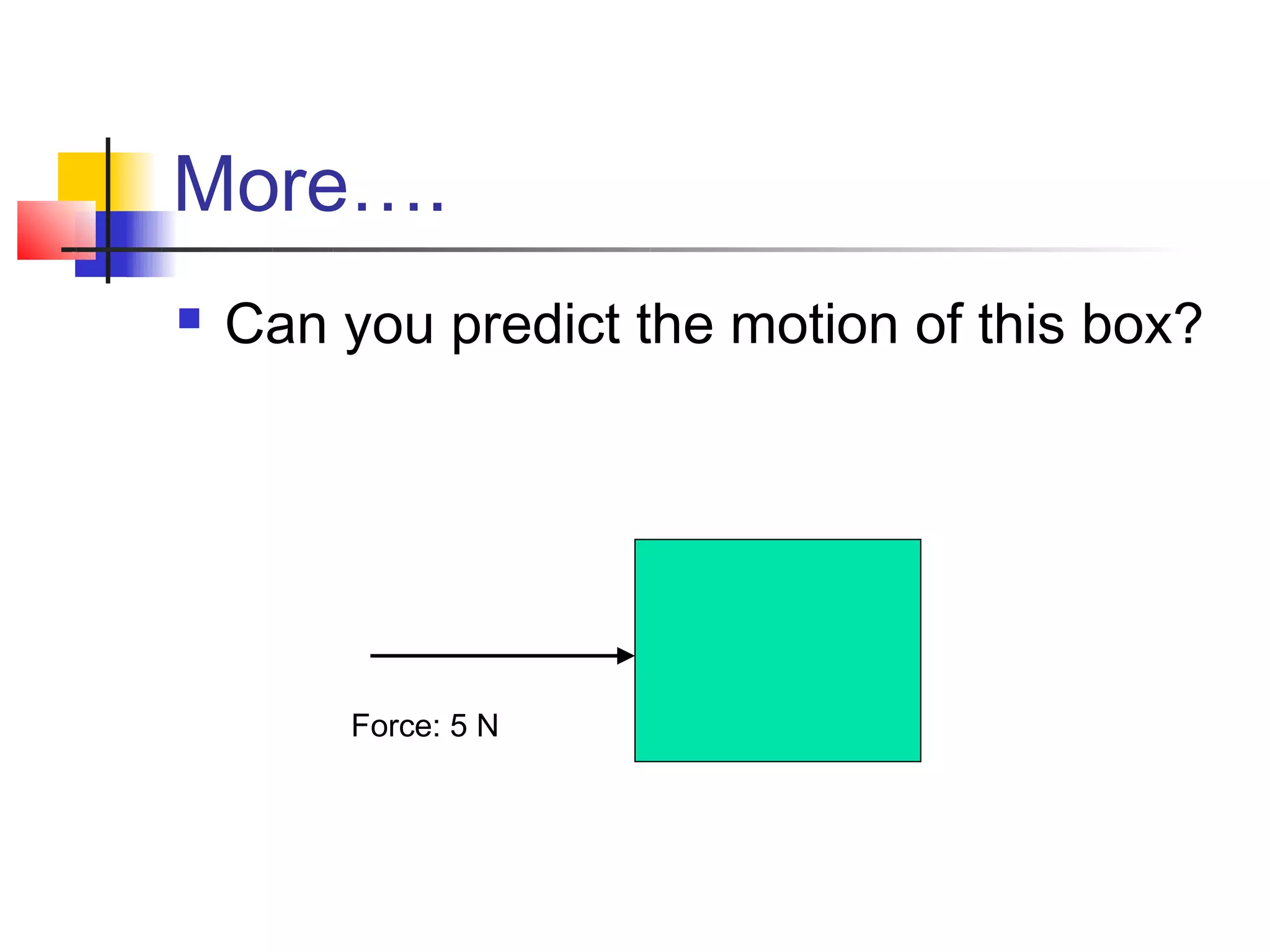
1) A force is any push or pull on an object and can cause acceleration, slowing down, or a change in direction. Forces do not need to come from living or moving things.
2) Balanced forces occur when forces cancel each other out, resulting in no acceleration. Unbalanced forces add together to cause acceleration.
3) Forces are measured in Newtons in the metric system. Weight is also a force, equal to an object's mass multiplied by the acceleration of gravity.