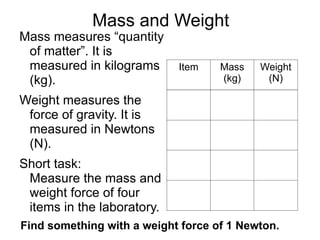
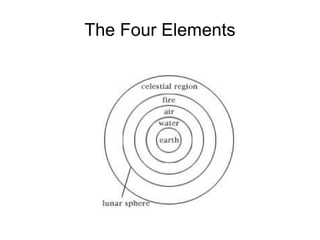
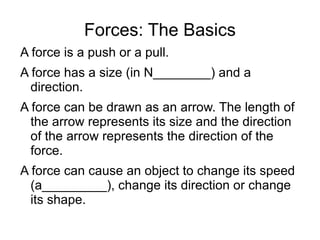
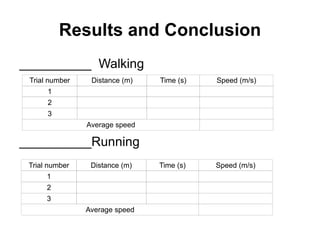
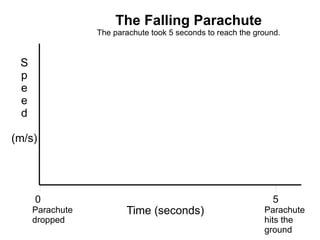
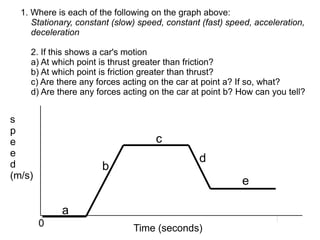
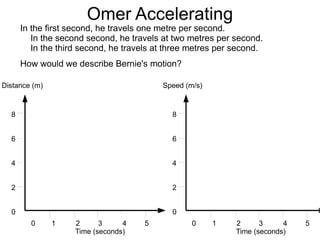
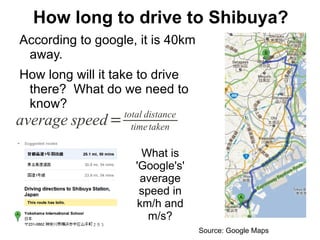
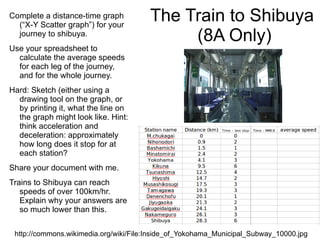
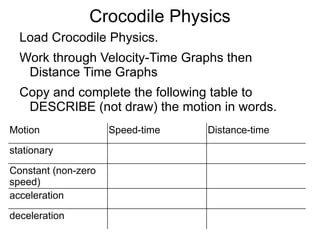
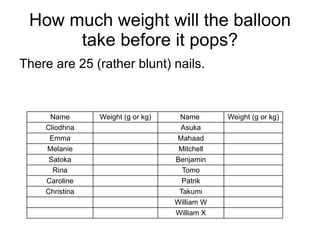
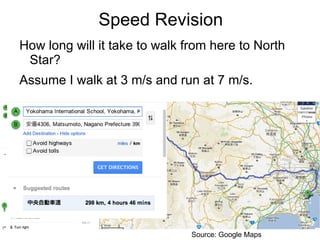
The document summarizes key concepts about forces and motion from a grade 8 science textbook. It discusses Aristotle's early theories of motion, which proposed that objects naturally move in circles and at constant speeds. It then covers Galileo and Newton's discoveries that disproved Aristotle, including that all objects accelerate at the same rate when falling and that forces cause accelerations described by Newton's Three Laws of Motion. The document also explains the difference between mass and weight, and how to calculate weight on different planets using gravitational acceleration.