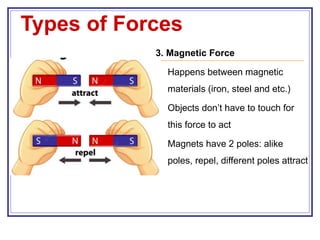
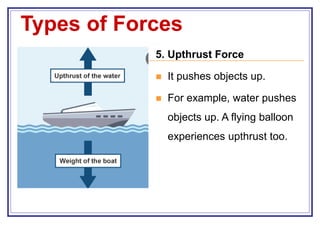
This document introduces forces and describes the different types of forces. It explains that a force is a push or pull that can cause motion or change motion. There are several main types of forces including gravitational, electrostatic, magnetic, friction, air resistance, upthrust, and tension forces. The document provides examples of how each of these forces works and notes that forces are involved in almost all movement and can be measured in Newtons.