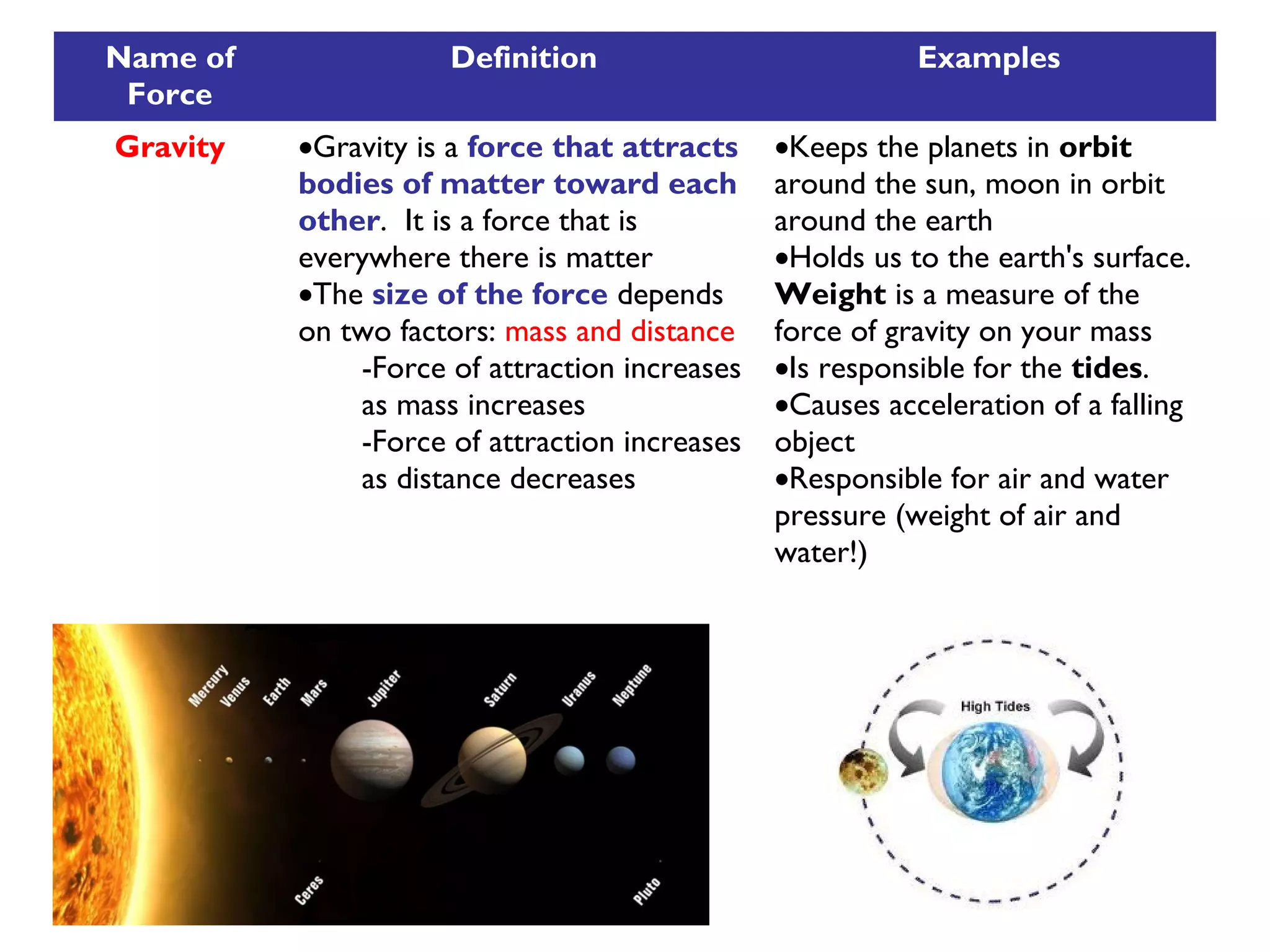
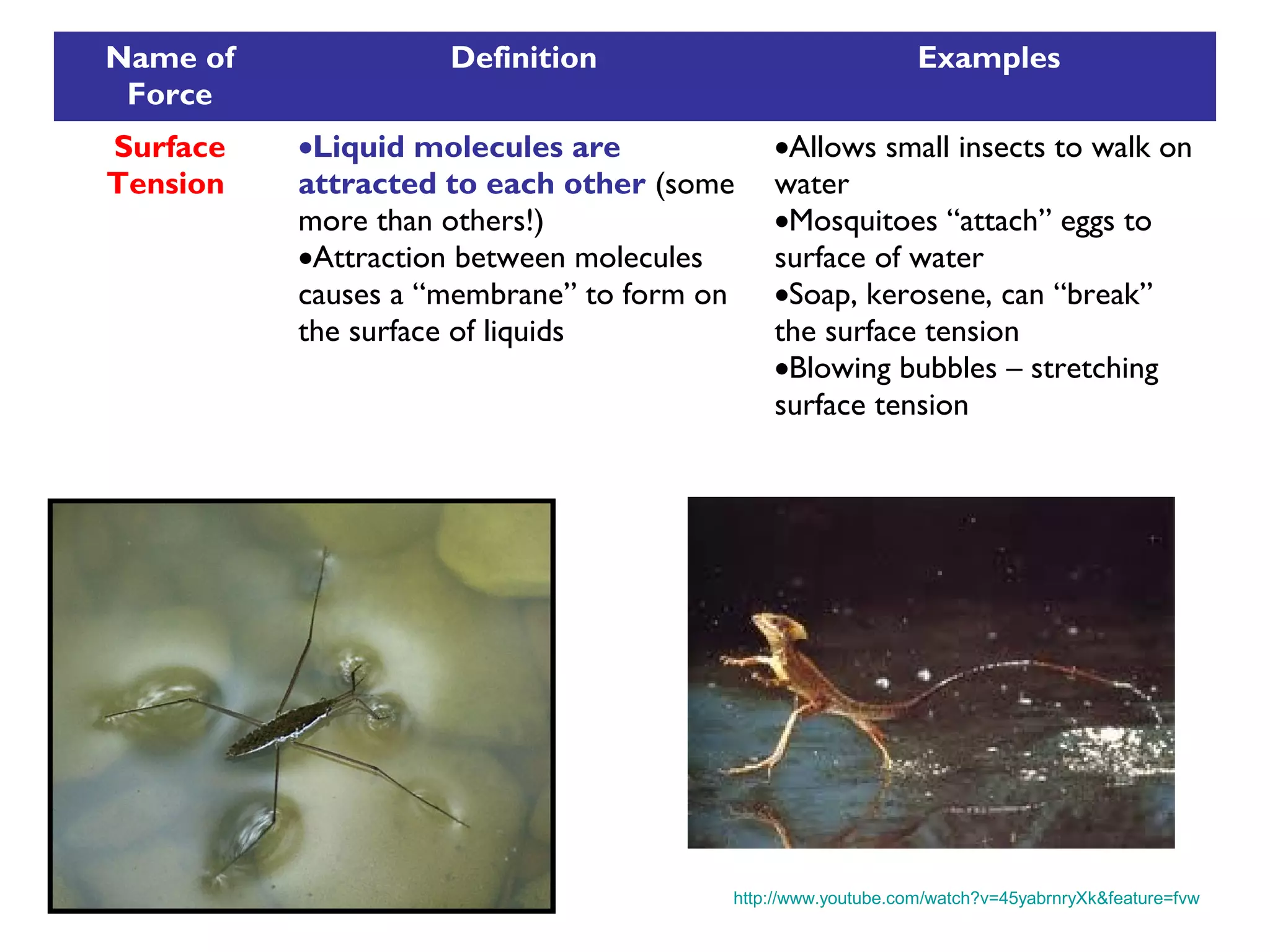
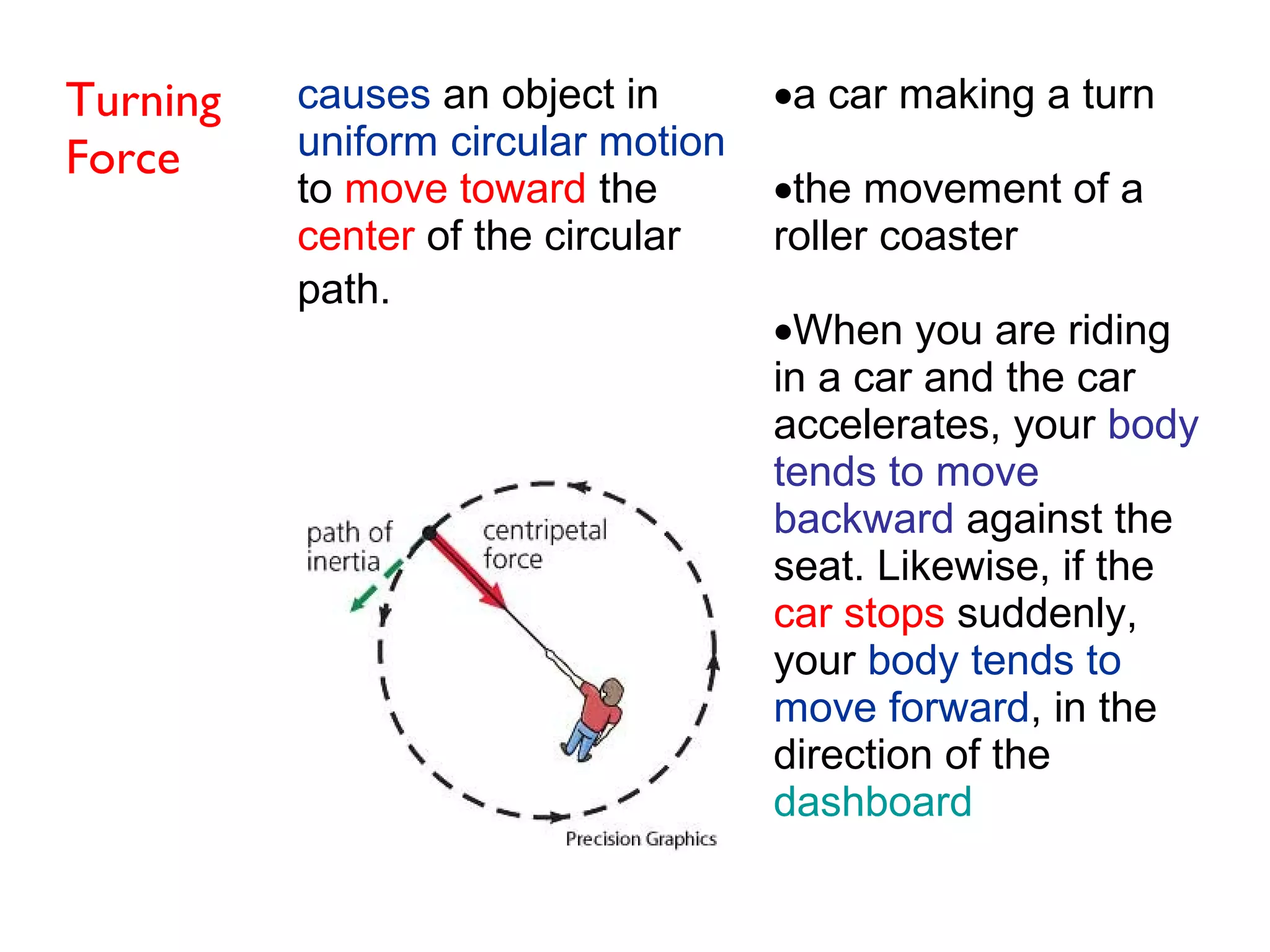
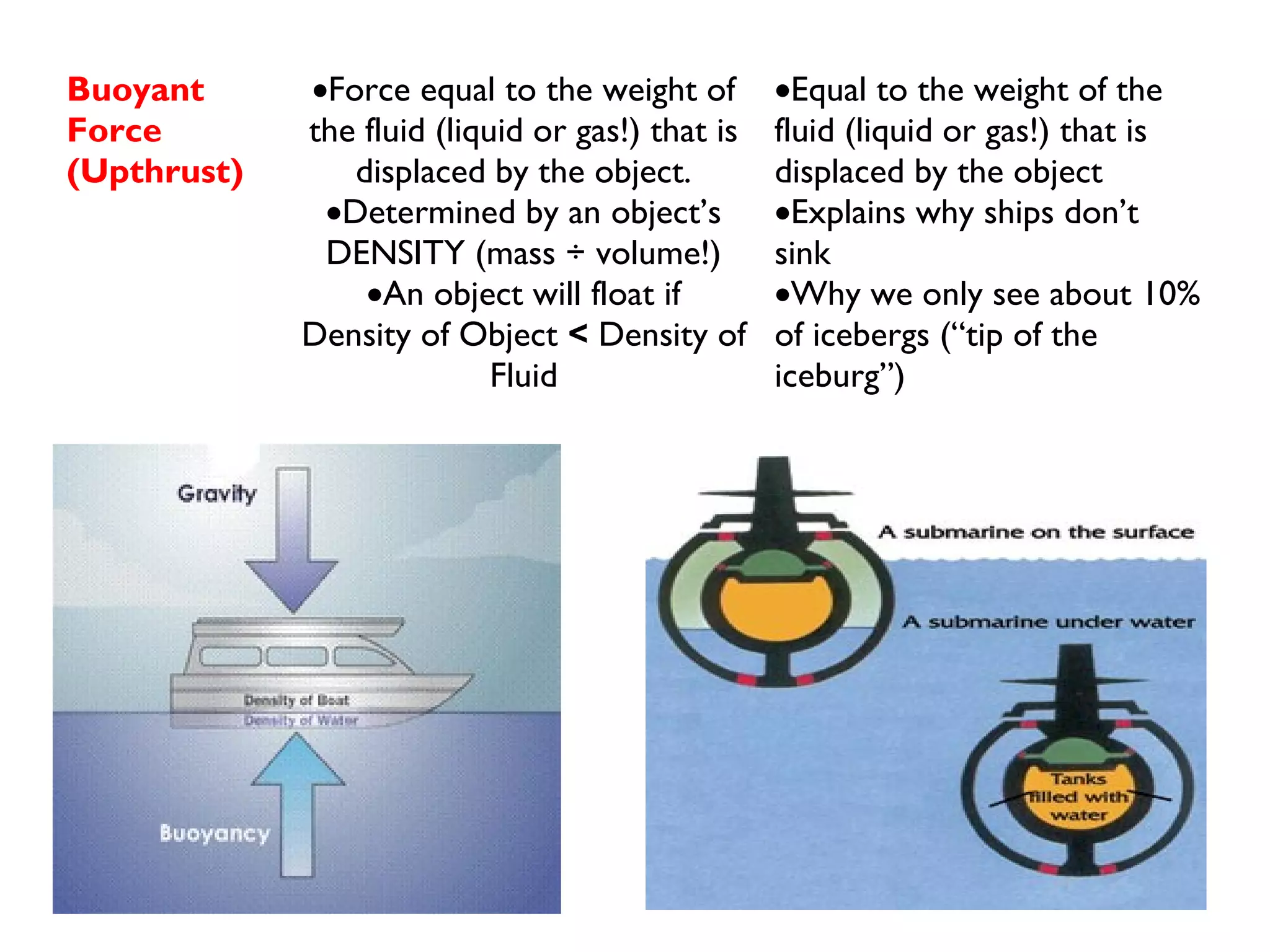
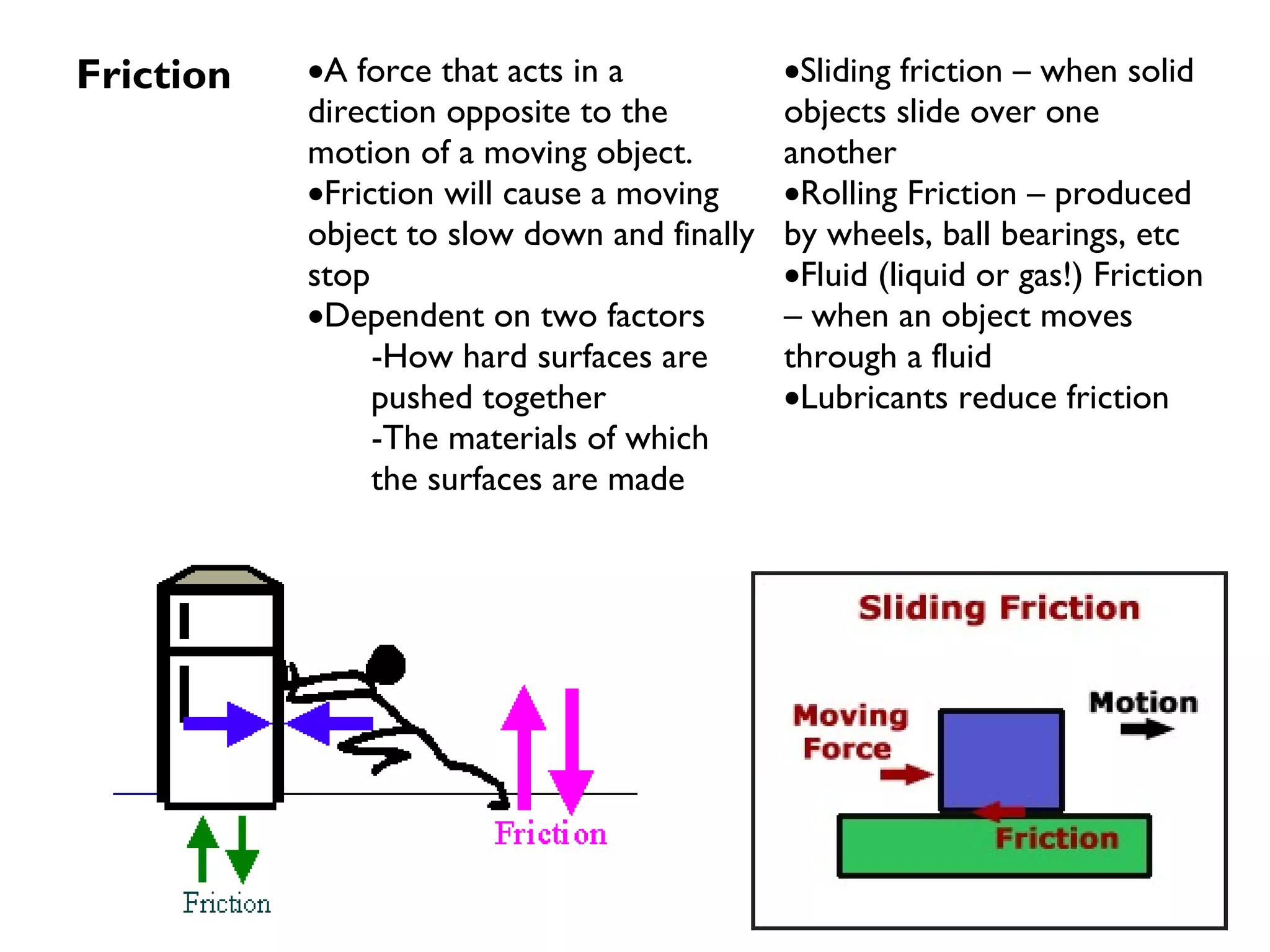
Friction is a force that resists motion between objects in contact with each other. It causes a moving object to slow down and stop. The size of the frictional force depends on how hard the surfaces are pressed together and the types of materials. Sliding friction occurs when surfaces slide over each other, while rolling friction involves wheels or bearings. Lubricants can reduce frictional forces.