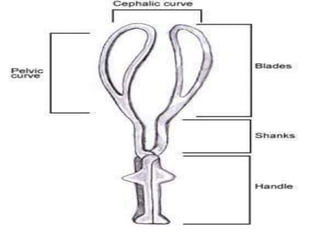
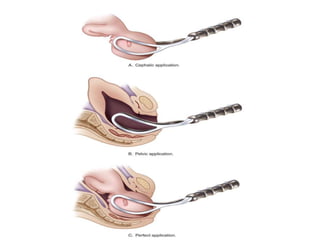
Obstetric forceps are metal instruments used to extract the fetal head during delivery, with various applications based on fetal position and maternal conditions. Indications for use include prolonged labor, maternal distress, and specific fetal conditions, while contraindications include prematurity and unengaged heads. Forceps delivery carries risks for both mother and child, including potential lacerations and fetal injuries, necessitating proper prerequisites such as anesthesia and engaged fetal head.