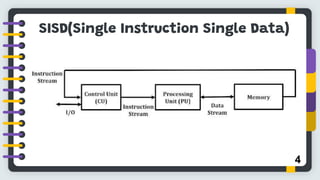
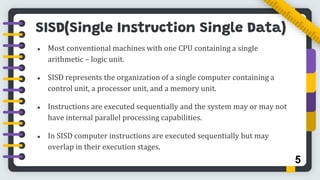
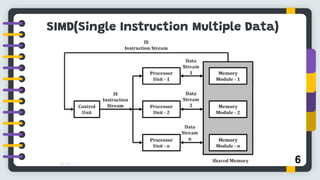
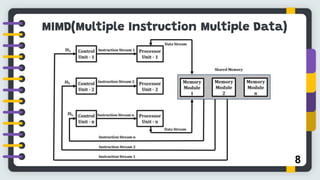
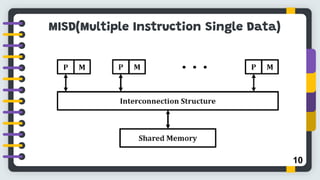
Flynn's classification, proposed by Michael J. Flynn in 1966, categorizes computer architectures based on instruction and data streams into four types: SISD, SIMD, MIMD, and MISD. Each type represents different organization structures and processing capabilities, with SISD being the most conventional and MIMD commonly used in multiprocessor systems. The conclusion highlights the limitations of this classification in addressing the complexity of modern parallel computing architectures.