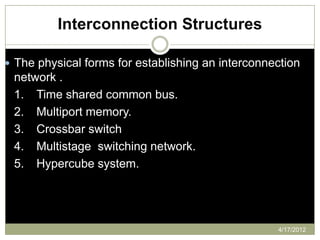
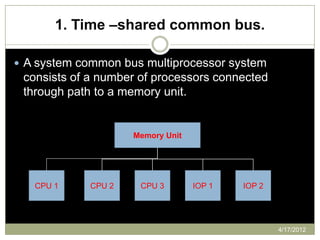
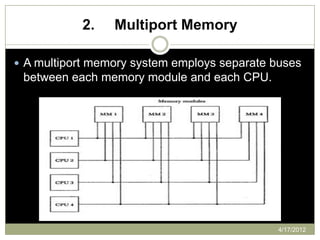
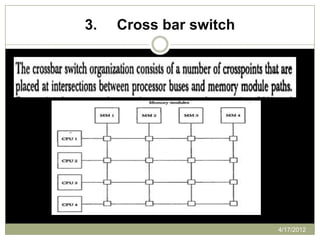
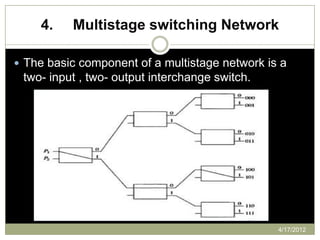
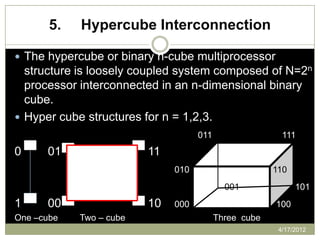
The document provides an overview of multiprocessor systems, defining them as interconnections of multiple CPUs that enhance performance through features like multitasking and responsiveness. It categorizes multiprocessors into tightly coupled and loosely coupled systems, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Additionally, the document outlines various interconnection structures used in multiprocessor configurations.