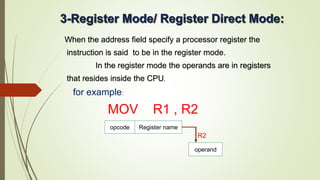
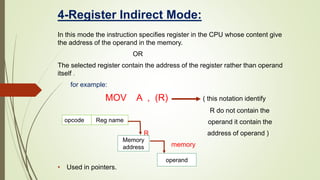
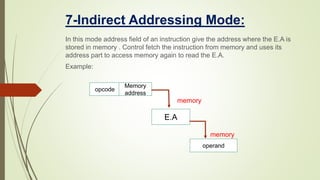
The document discusses addressing modes in computers. There are 10 common addressing modes: implied, immediate, register, register indirect, autoincrement/autodecrement, direct, indirect, relative, indexed, and base register. Addressing modes specify the location of operands in instructions and allow versatility in programming through pointers, loop counters, data indexing, program relocation, and reducing instruction size. The control unit fetches, decodes, and executes instructions based on the program counter, which tracks the next instruction address.








![5-Autoincrement/Autodecrement Mode:
In this mode E.A of the operand is the content of register specified in
instruction , after / before accessing the operand the content of the
register are automatically incremented/decremented to the step size
d.
This mode is similar to the register indirect mode except that the
register is incre /decr after it’s value is used.
For example: ADD R1,(R2)+ memory
E.A=[R] 1000
E.A=[R]+d R 1001
E.A=[R]+2d 1002
• This mode is used in loop counter. 1003
opcode R
E.A(1003)
operand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a-m-170612064653/85/addressing-modes-11-320.jpg)
![6-Direct Addressing Mode:
In this mode E.A / address of operand directly given I n
instruction.
In this mode the effective address is equal to the address
part of the instruction the operand resides in memory and its
address is given directly by the address field of the instruction.
for example: ADD R , 2000 E.A
r r+[2000]
opcode E.A
Operand
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a-m-170612064653/85/addressing-modes-12-320.jpg)




![Example:
Instruction IR
1000
1000 1001 1002 1003 1004
[A]
0 1 2 3 4
E.A=1000+3
This type of address mode used to access array element.
opcode
Memory add /base
address
3
operand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a-m-170612064653/85/addressing-modes-18-320.jpg)



