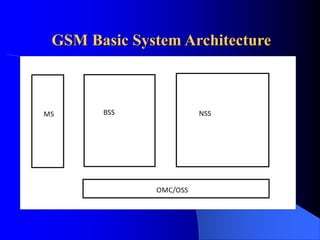
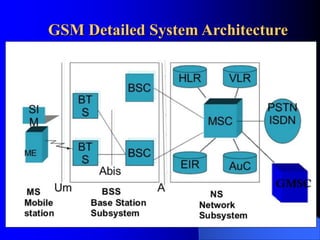
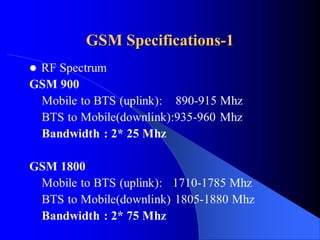
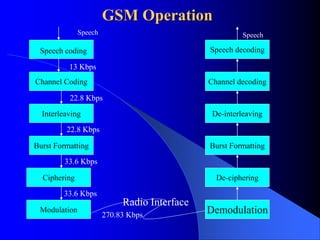
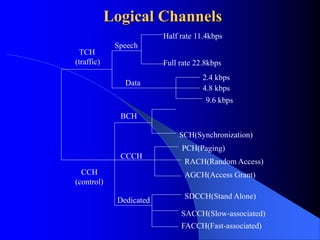
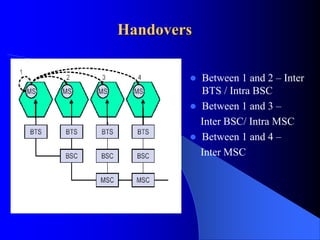
The document provides an overview of the GSM network, including its architecture and technical specifications. It discusses (1) the basic GSM system architecture consisting of mobile stations, the base station subsystem, and the network switching subsystem; (2) GSM specifications including channels, handovers between base stations, and a maximum data rate of 33.6 kbps; and (3) characteristics and features such as digital modulation, security, and advantages over analog networks.