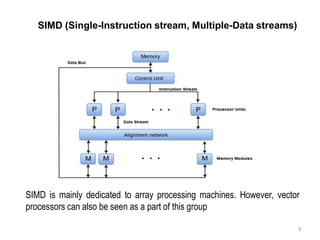
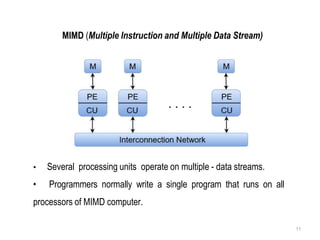
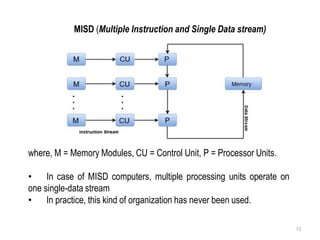
Flynn's Classification categorizes computer architectures based on the number of concurrent instruction streams and data streams. There are four categories:
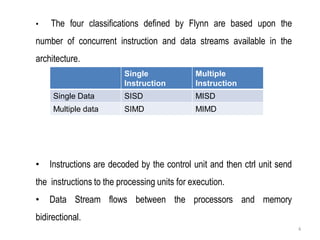
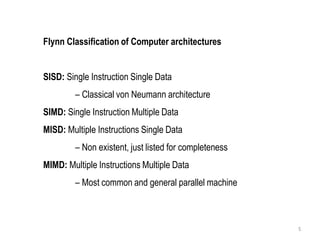
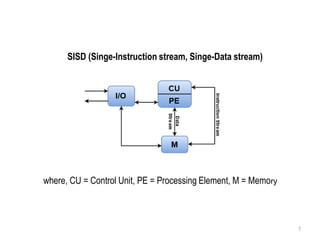
SISD refers to a traditional von Neumann architecture with a single instruction stream and single data stream. SIMD uses a single instruction stream to process multiple data streams, as seen in vector processors. MIMD allows multiple instruction streams and data streams, as in most parallel computers today. MISD, with multiple instructions operating on a single data stream, is theoretically possible but no systems have been built this way.