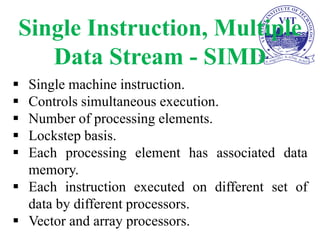
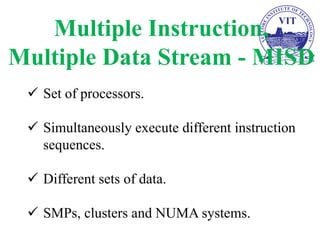
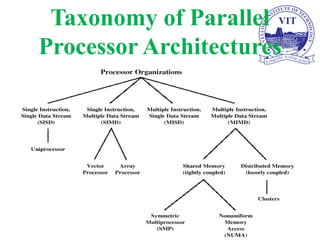
The document discusses computer organization and architecture with a focus on processor-level parallelism and multiprocessors. It covers Flynn's taxonomy of computer architectures, including SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD classifications, as well as the challenges and benefits of parallel processing in improving computational speed. Key concepts include memory organization for multiprocessor systems and cache coherence protocols.