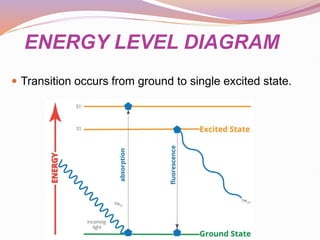
The document discusses photoluminescence, focusing on fluorescence and phosphorescence, outlining their principles, applications, and examples of fluorescent materials. Fluorescence occurs when a substance absorbs energy and re-emits it almost immediately, while phosphorescence involves a delayed light emission after the energy source is removed. Practical applications include uses in biology, mineralogy, and various consumer products like lamps and safety signs.