Embed presentation
Download to read offline










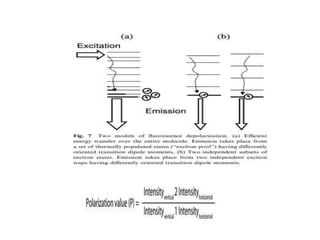
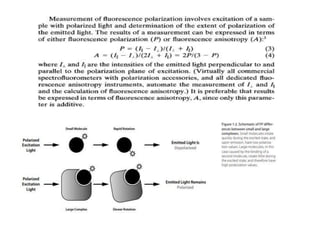
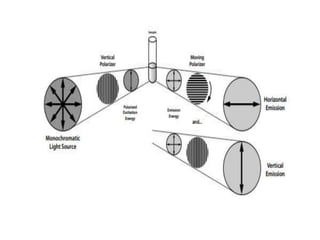
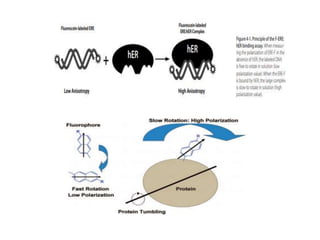

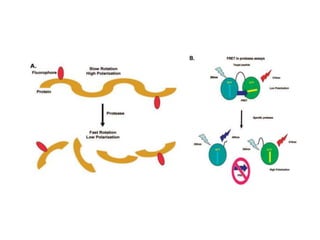
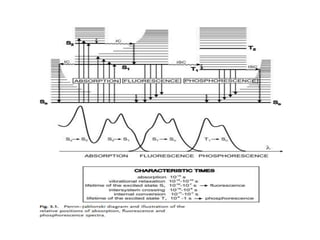
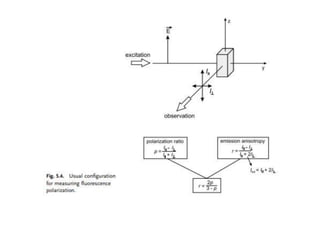
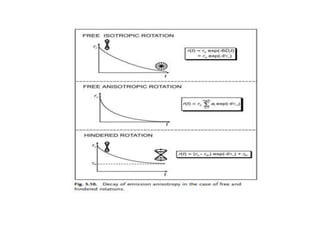

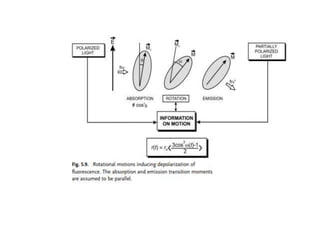
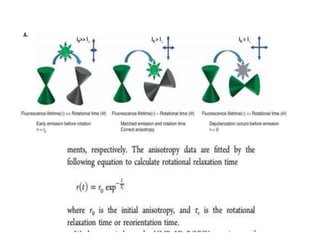
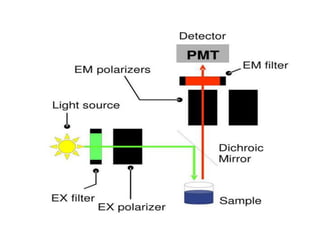

1. Fluorescence anisotropy measures the polarization of emitted light from fluorophores and can be used to study molecular interactions and rotational motions. 2. When fluorophores are excited with polarized light, their subsequent emission is depolarized by rotational diffusion. Larger molecules rotate more slowly, preserving more polarization. 3. Fluorescence anisotropy can be used to measure binding constants and kinetics by detecting changes in rotational diffusion upon molecular interactions like antibody-antigen binding. This provides information about molecular size, shape, and microenvironment.


























