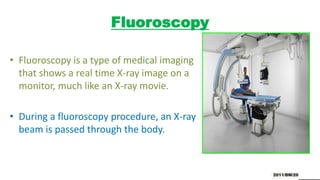
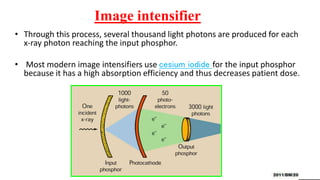
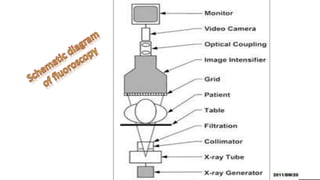
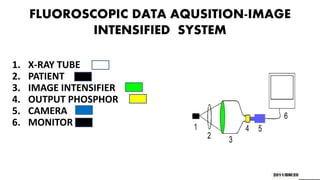
Fluoroscopy uses X-rays to produce real-time moving images and is displayed on a monitor. It works by passing an X-ray beam through the body. The image intensifier converts the X-ray image into a brighter visible light image. It contains a photocathode that emits electrons when hit by X-rays, and an output phosphor that converts the electrons back into a magnified visible light image. This process amplifies and multiplies the number of photons. Fluoroscopy provides brighter images than older techniques and allows examinations to be done without complete darkness. It is used in procedures like cardiac catheterization, joint imaging, and IV catheter placement.