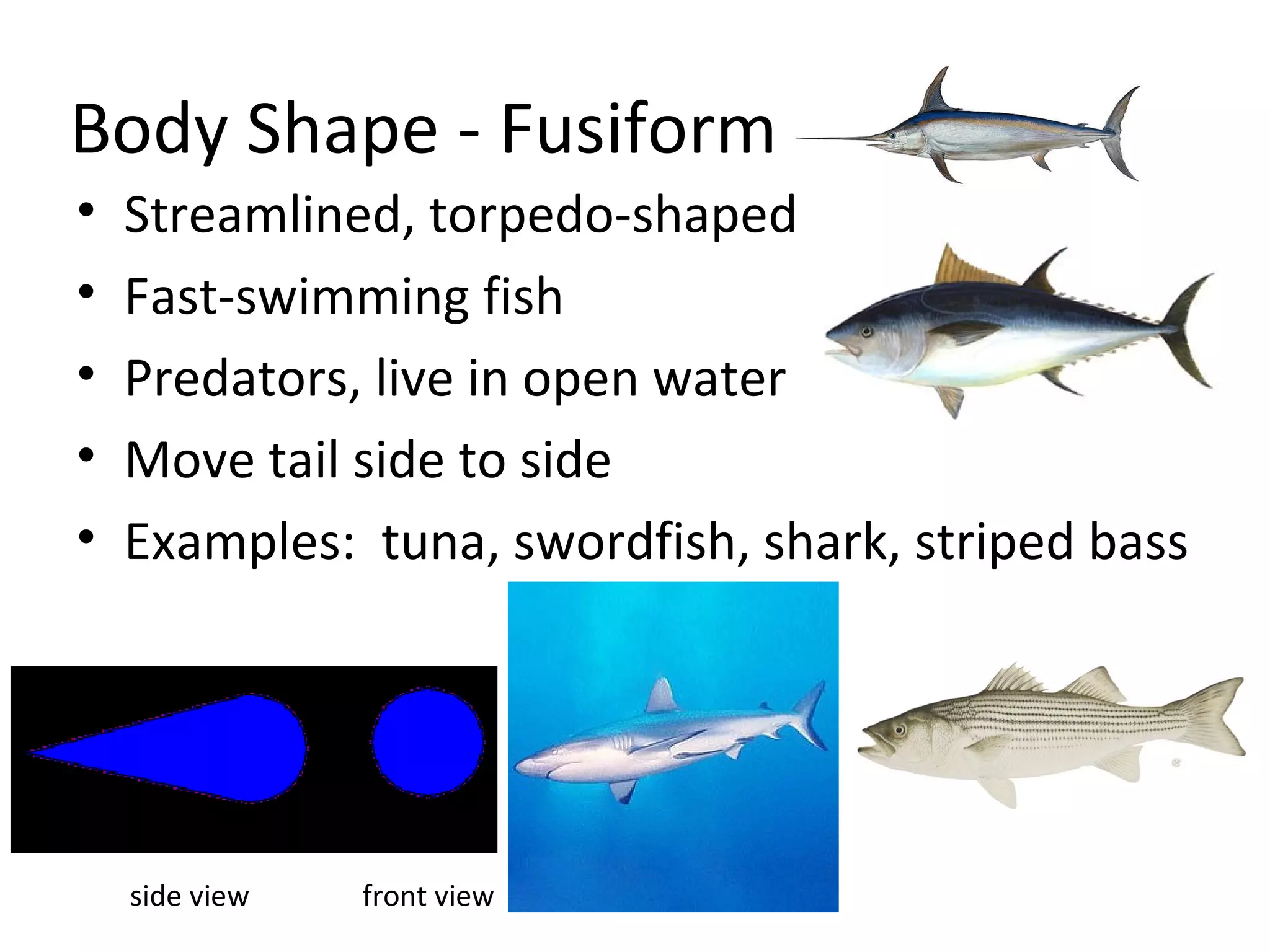
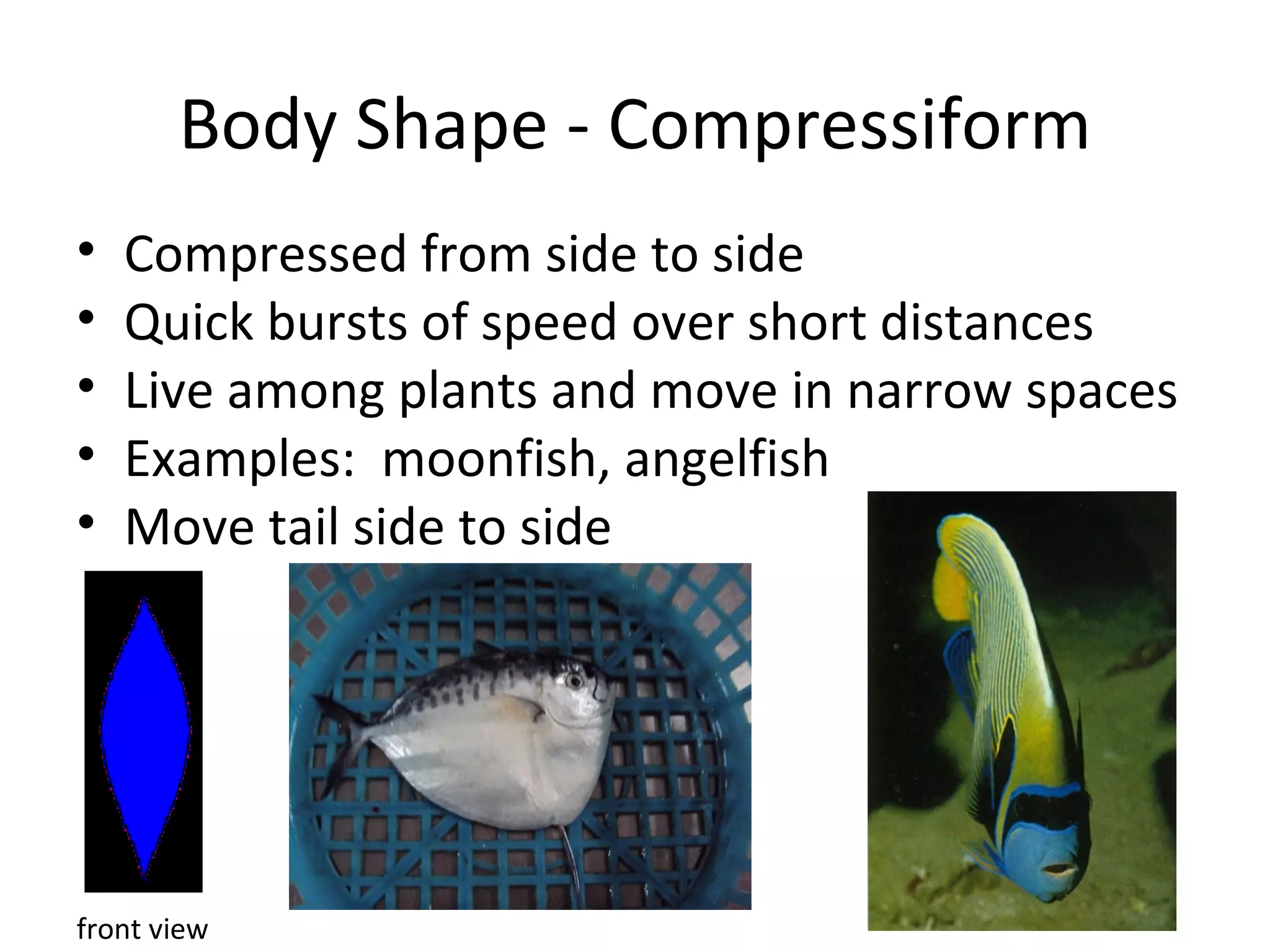
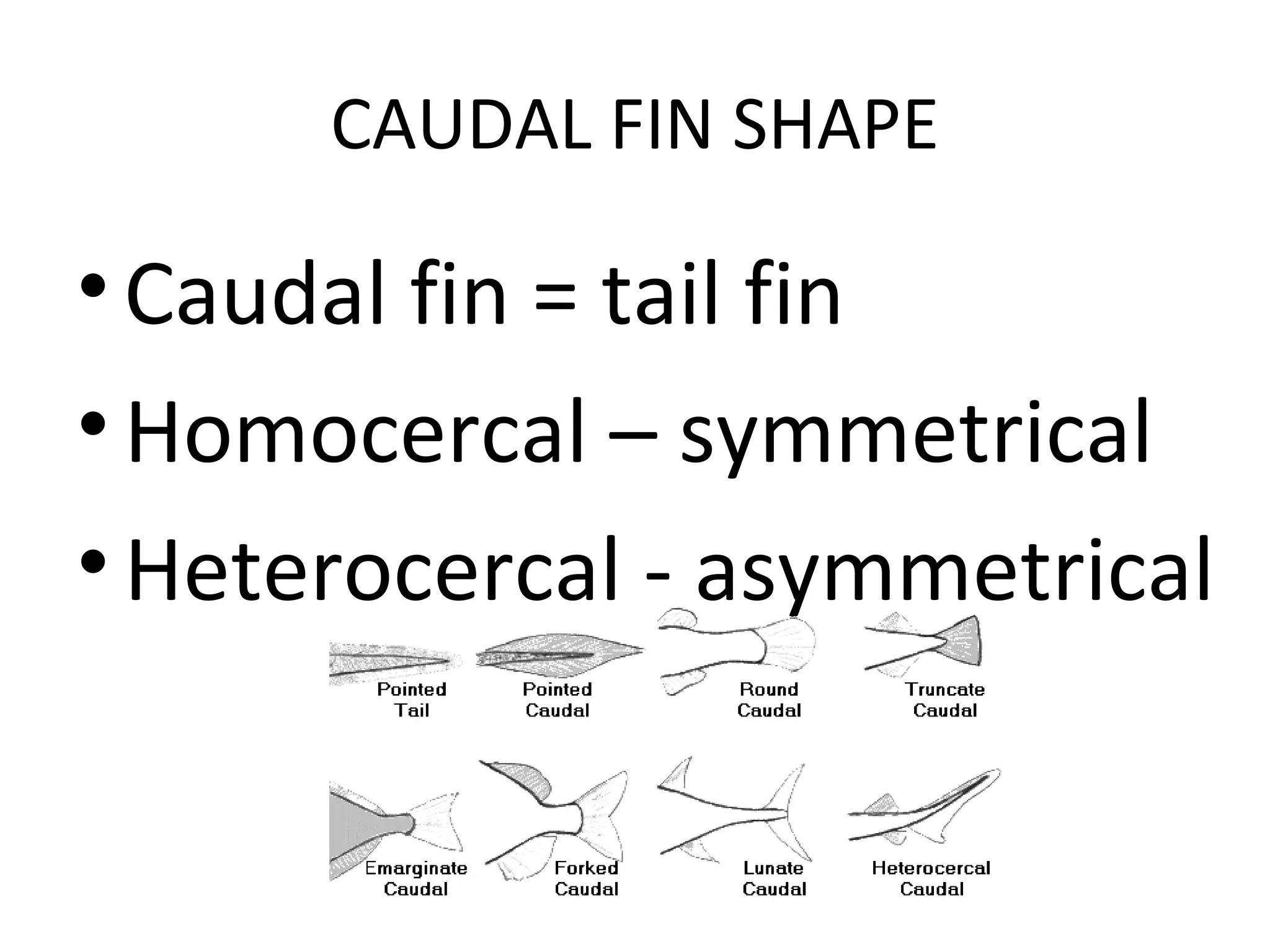
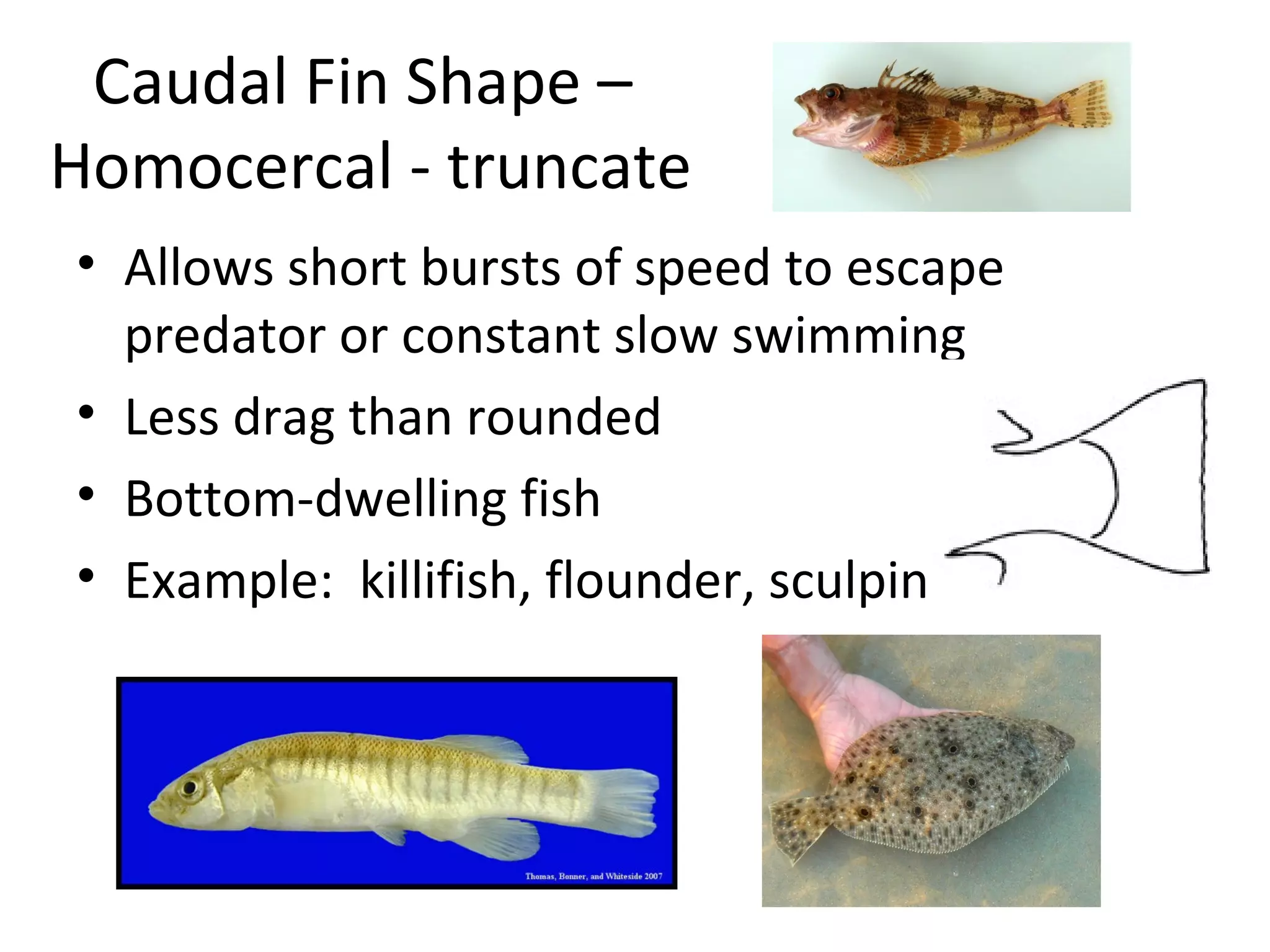
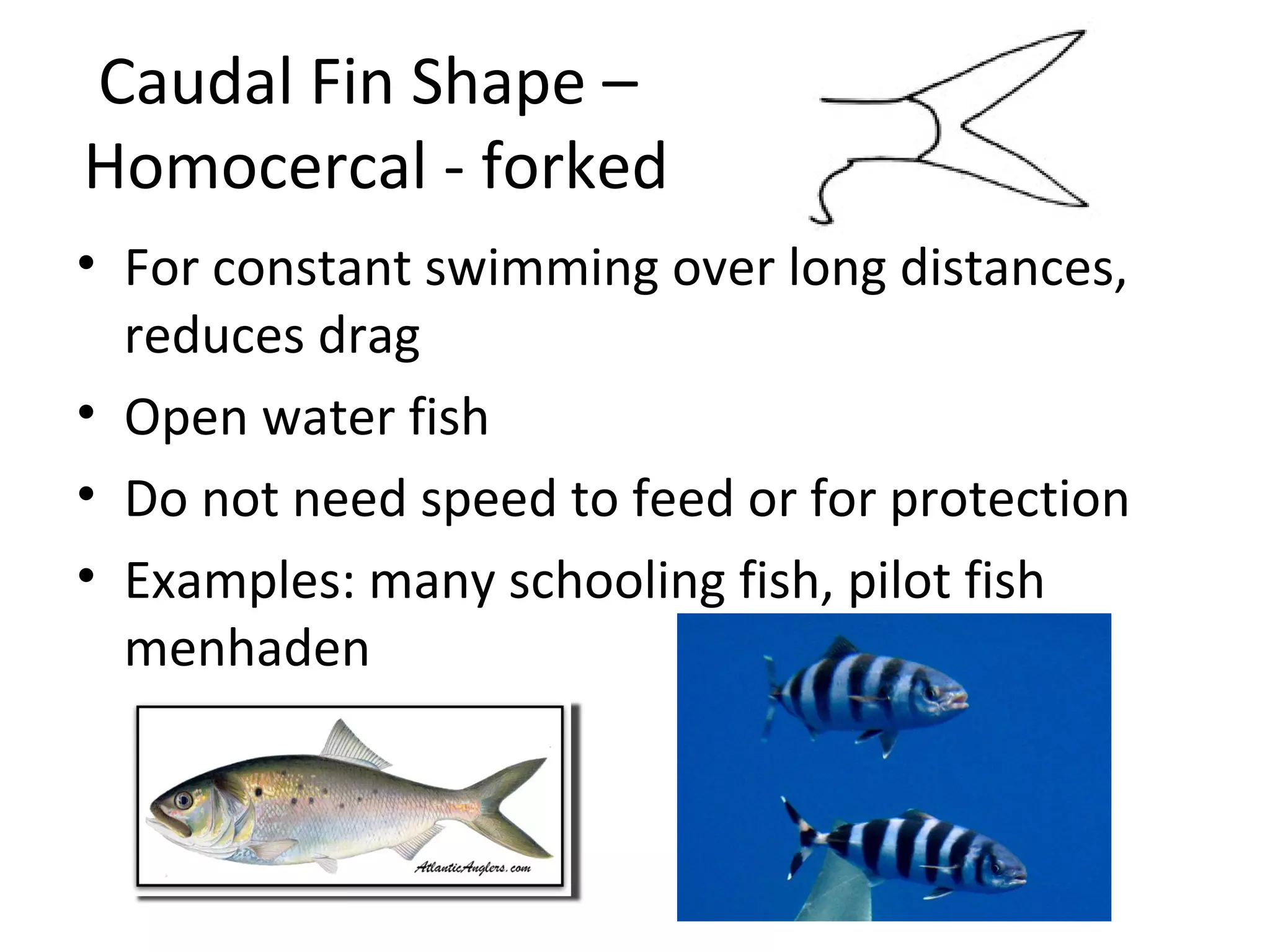
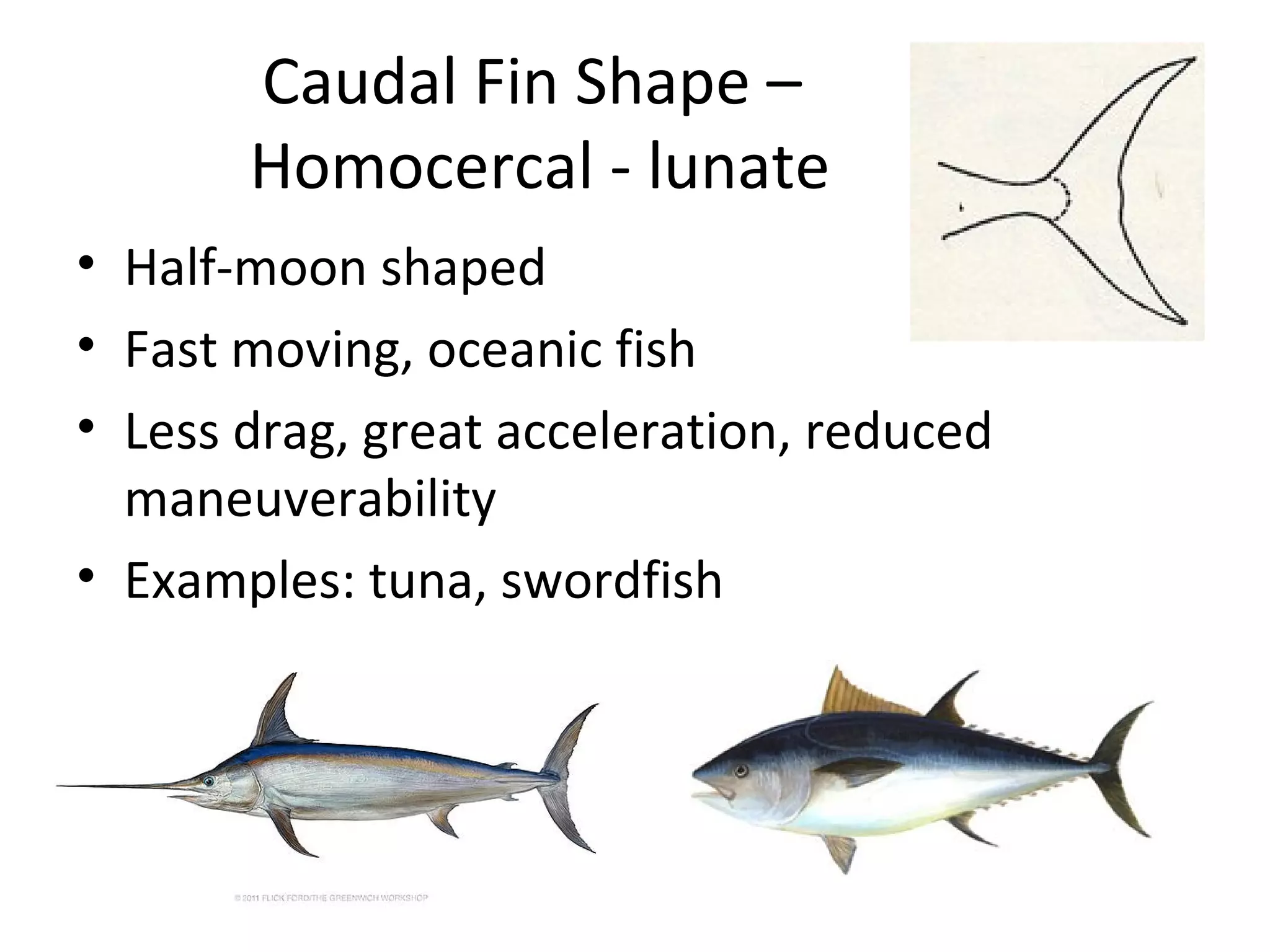
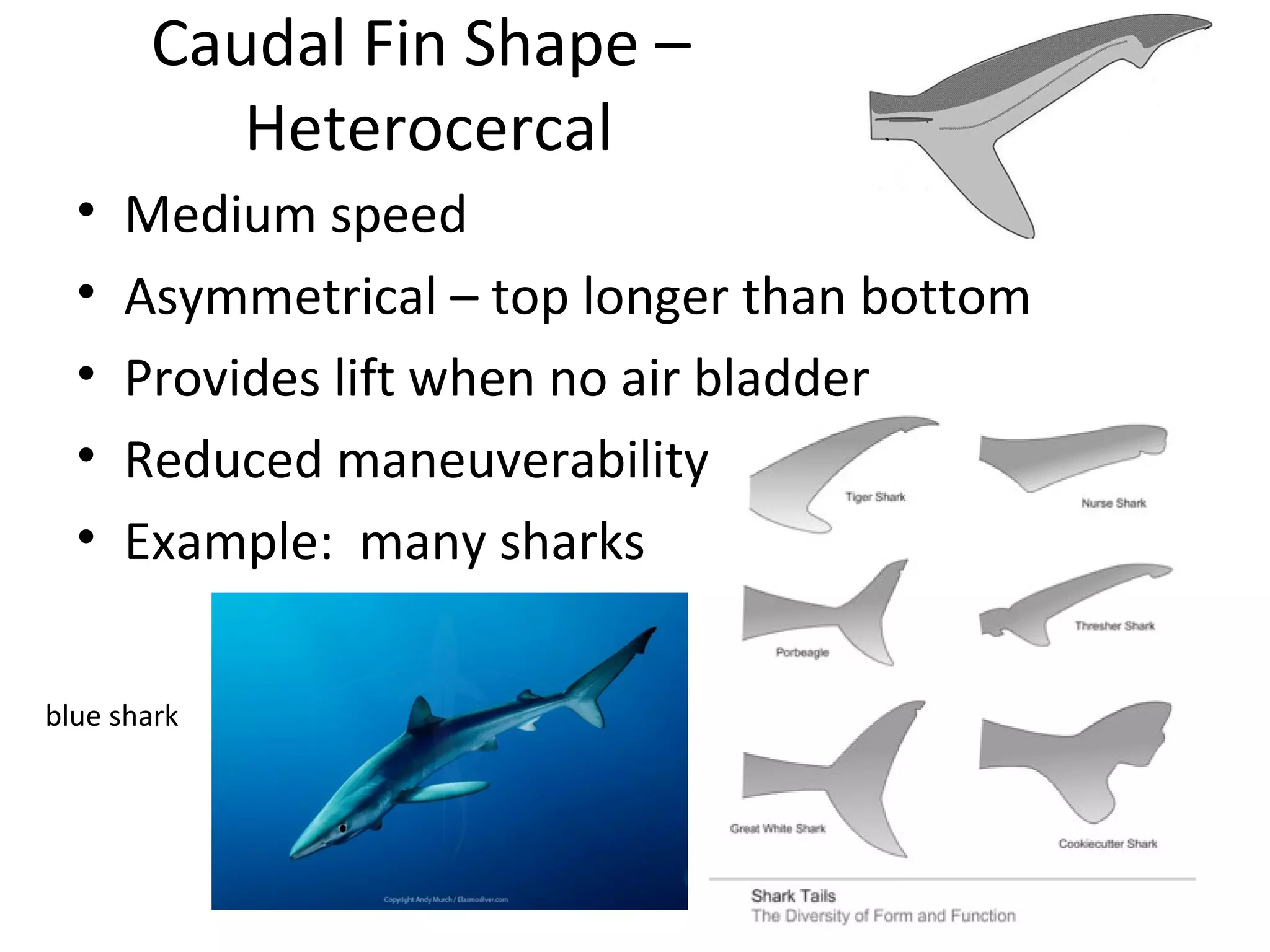
The document discusses fish morphology and how the shapes of fishes and their body parts are adaptations to their environments and behaviors. It describes four main body shapes - fusiform for fast-swimming predators, compressiform for quick bursts of speed, depressiform for bottom-dwelling fish, and filiform for elongated fish. It also outlines different caudal fin shapes including homocercal and heterocercal, and provides examples of fish that exhibit each shape.