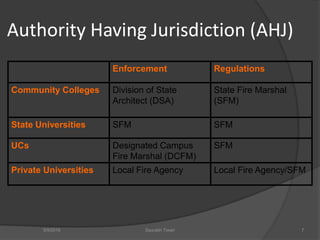
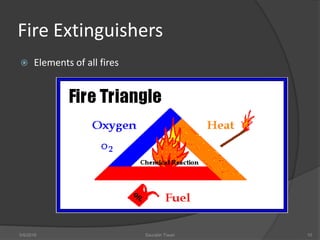
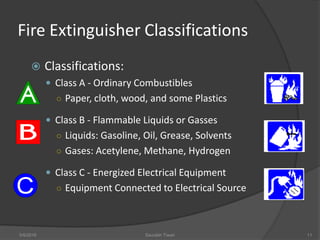
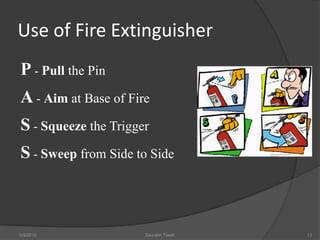
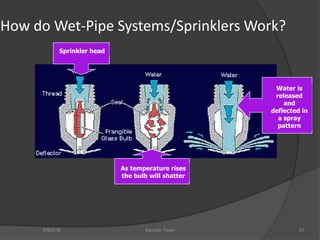
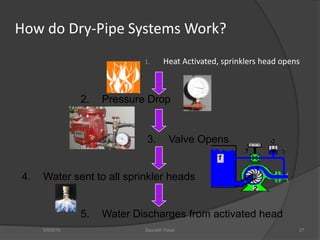
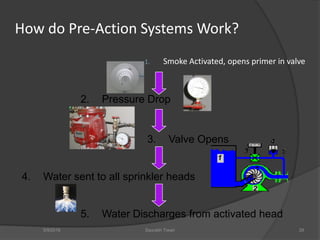
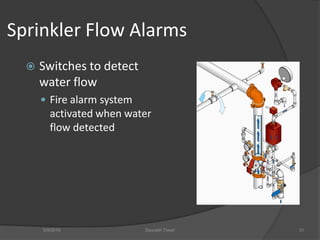
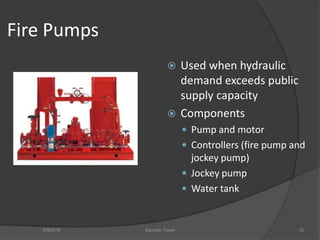
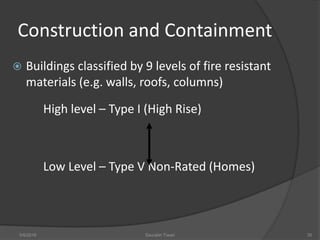
This document discusses fire safety systems and codes. It covers awareness of fire hazards, fire codes established by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), fire extinguishers, fire alarm systems, fire suppression systems like sprinklers, and fire construction requirements. The document provides an overview of each topic with examples and emphasizes the importance of code compliance, system maintenance, and hazard awareness for fire safety.