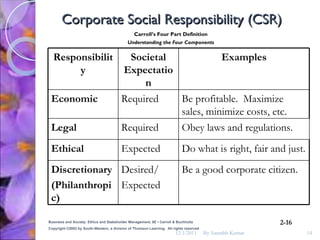
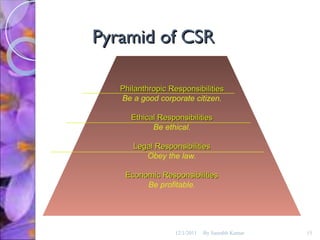
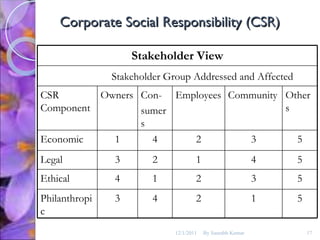
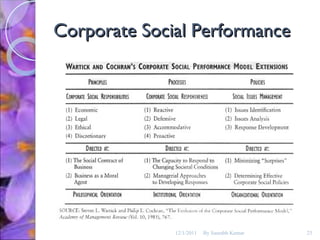
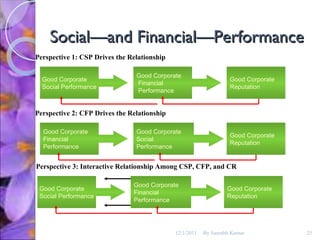
The document discusses the concepts of corporate social responsibility (CSR), social responsiveness, and social performance. It provides definitions and frameworks for understanding a company's responsibilities and obligations to society beyond profit and legal compliance. Carroll's four-part definition of CSR as encompassing economic, legal, ethical, and discretionary expectations is discussed.