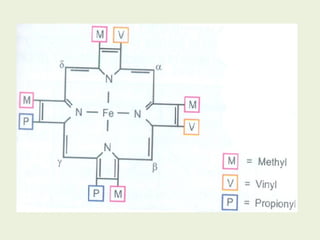
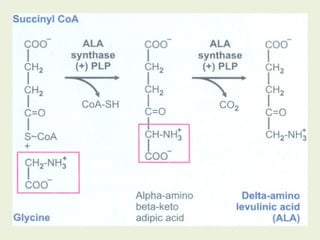
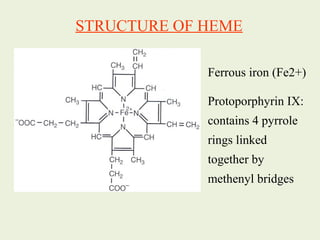
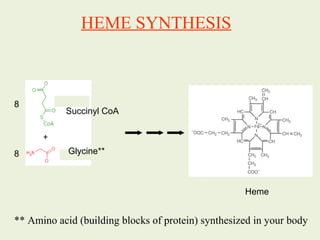
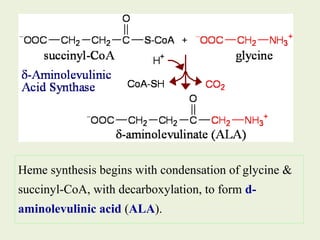
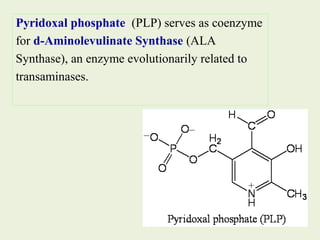
1. Heme is synthesized through a series of enzymatic reactions beginning with the condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA to form delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA).
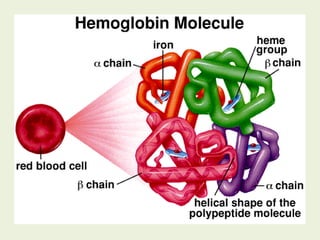
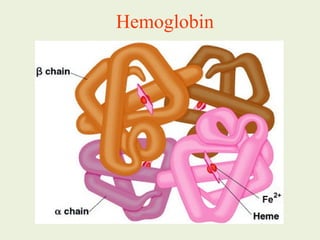
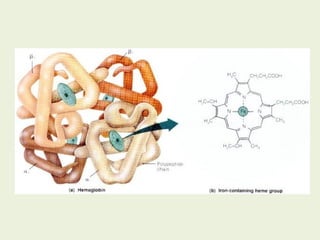
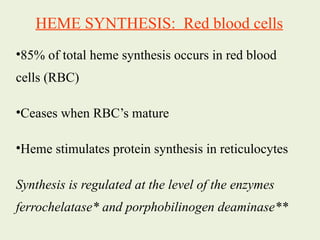
2. The liver and bone marrow are the major sites of heme synthesis. In the liver, heme is used to synthesize cytochromes while in bone marrow it is used in hemoglobin synthesis.
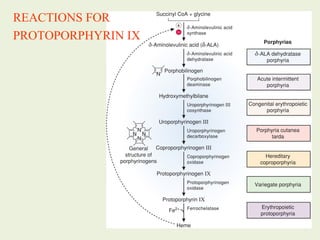
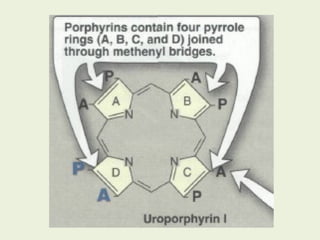
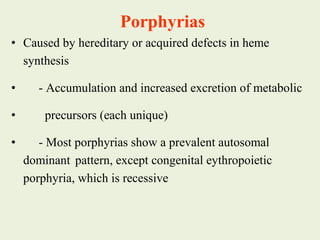
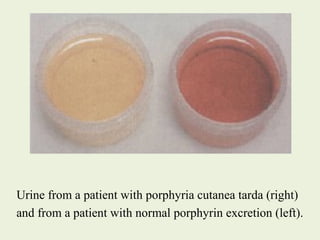
3. Defects in heme synthesis can cause porphyrias, characterized by accumulation of heme precursors and acute attacks triggered by certain drugs and chemicals.

















































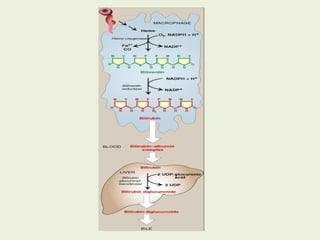
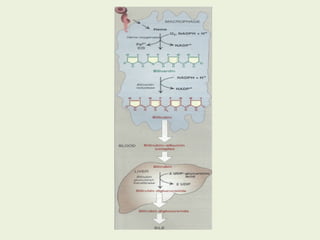
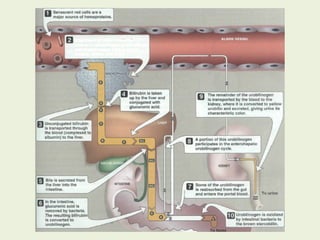
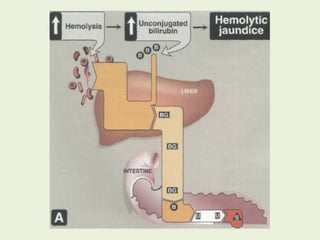
![Most heme from RBCs (85%) - rest from
turnover of cytochromes, p450s, immature
erythrocytes.
RBCs last 120 days, degraded by
reticuloendothelial (RE) system [liver and
spleen].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/istyearfj-140519091937-phpapp01/85/HEMOGLOBIN-SYNTHESIS-64-320.jpg)