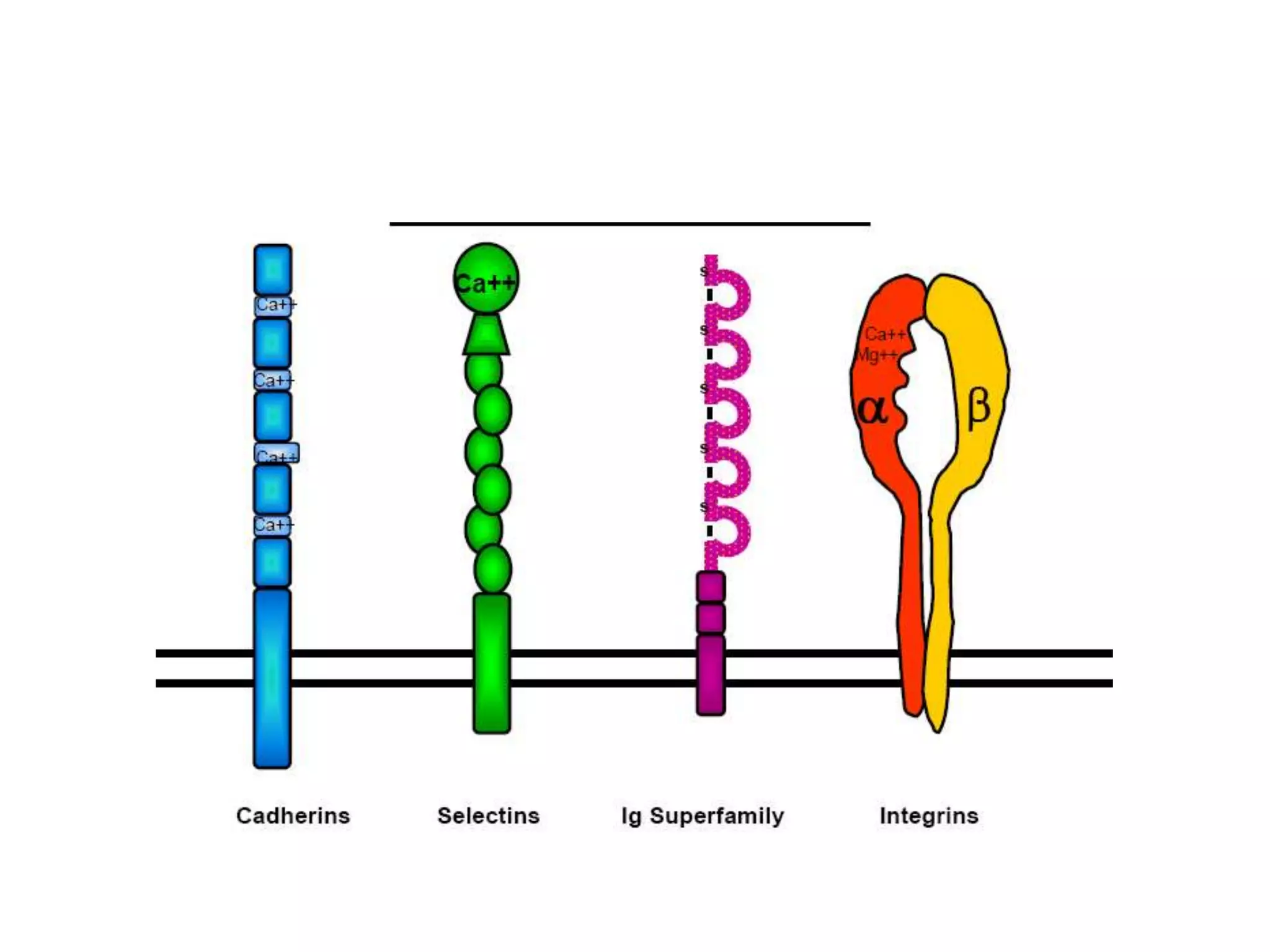
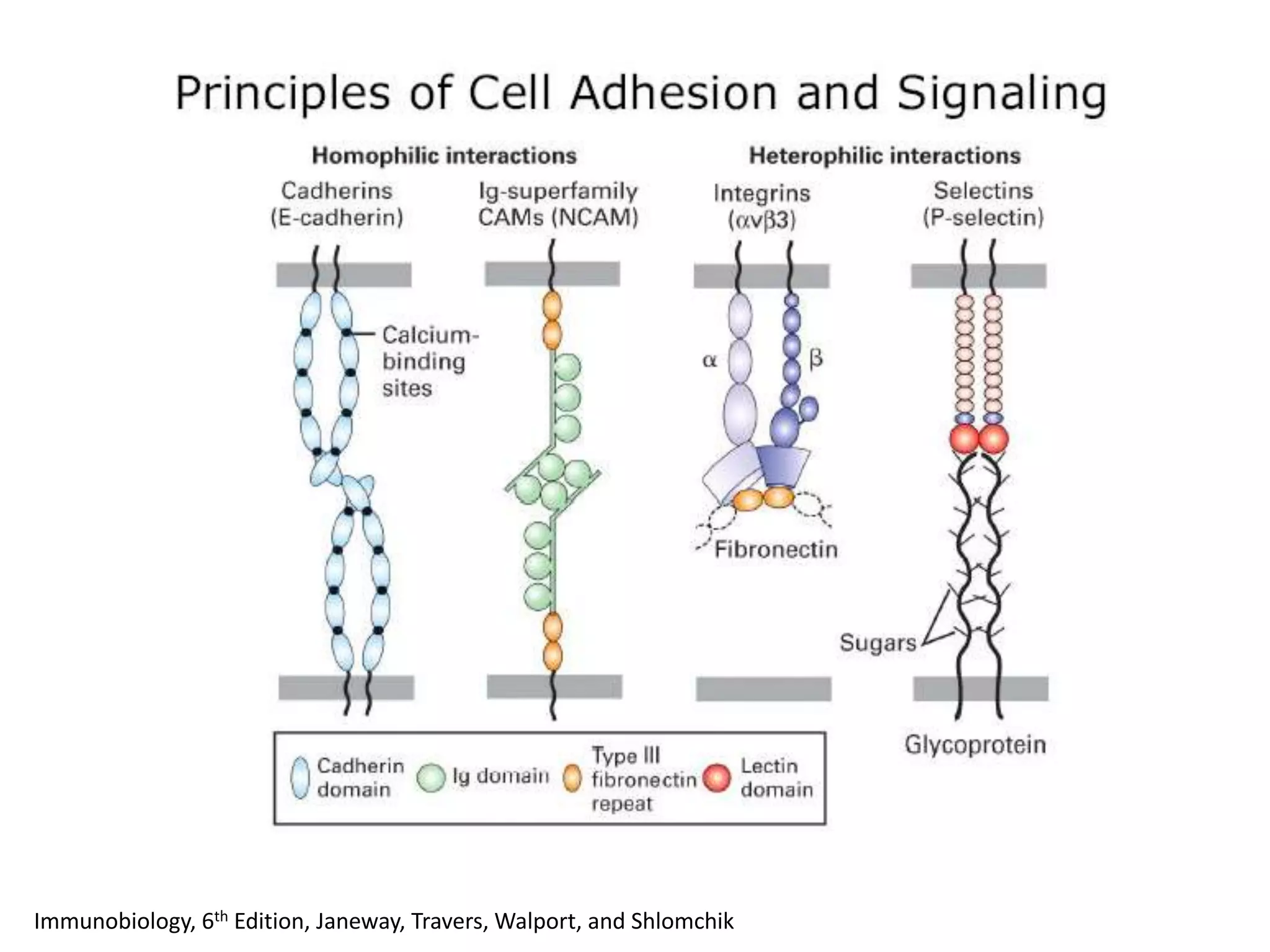
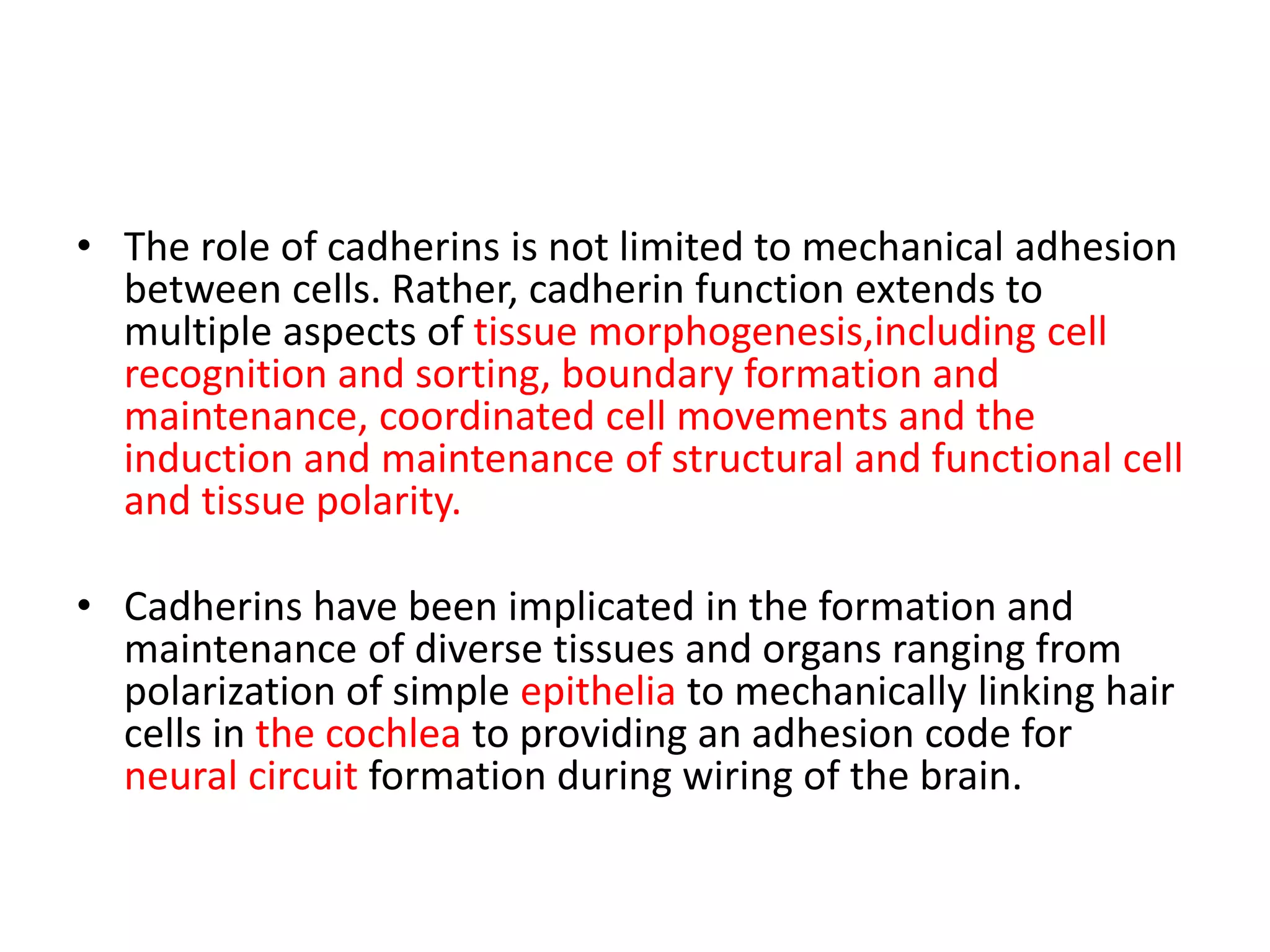
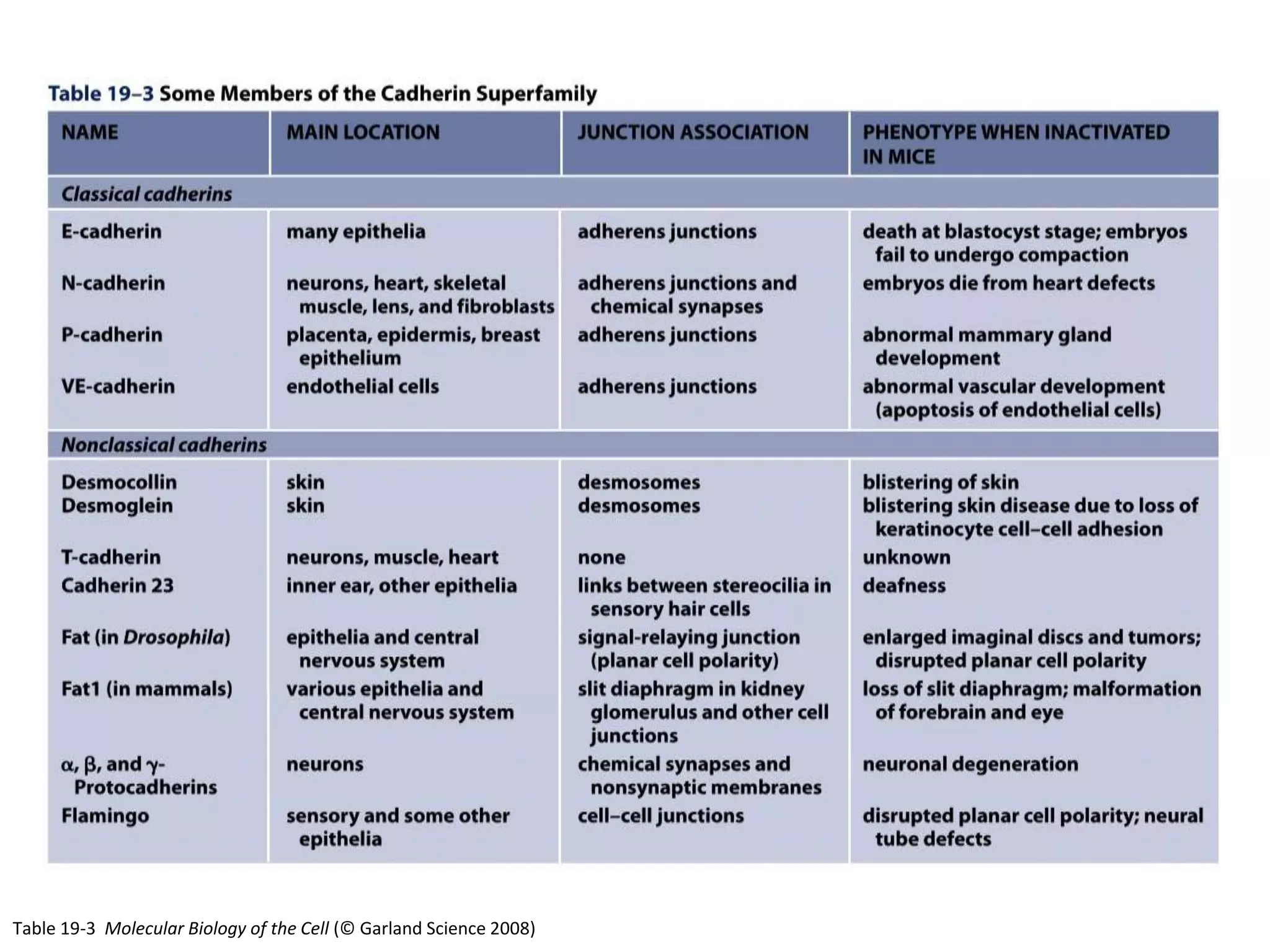
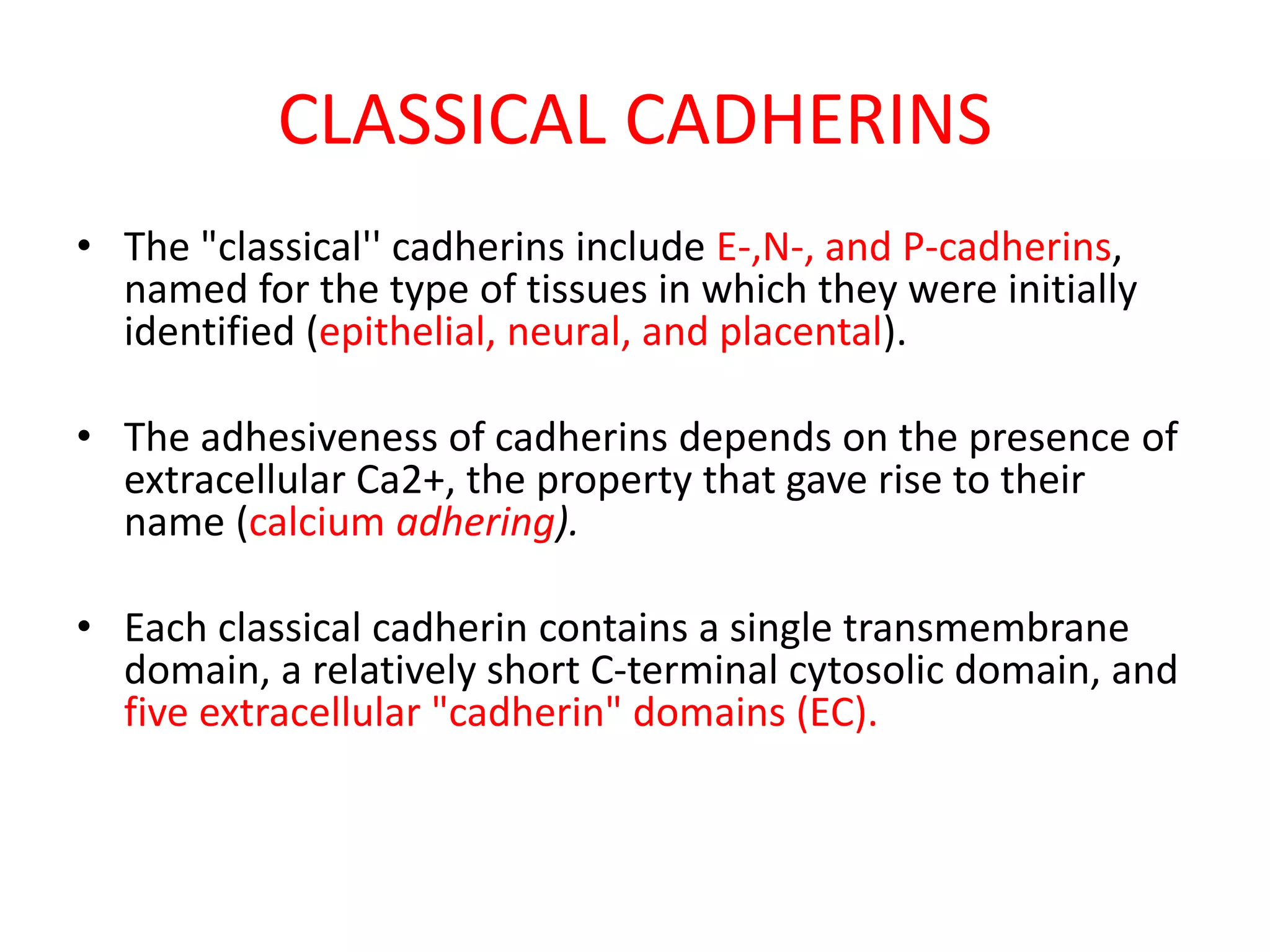
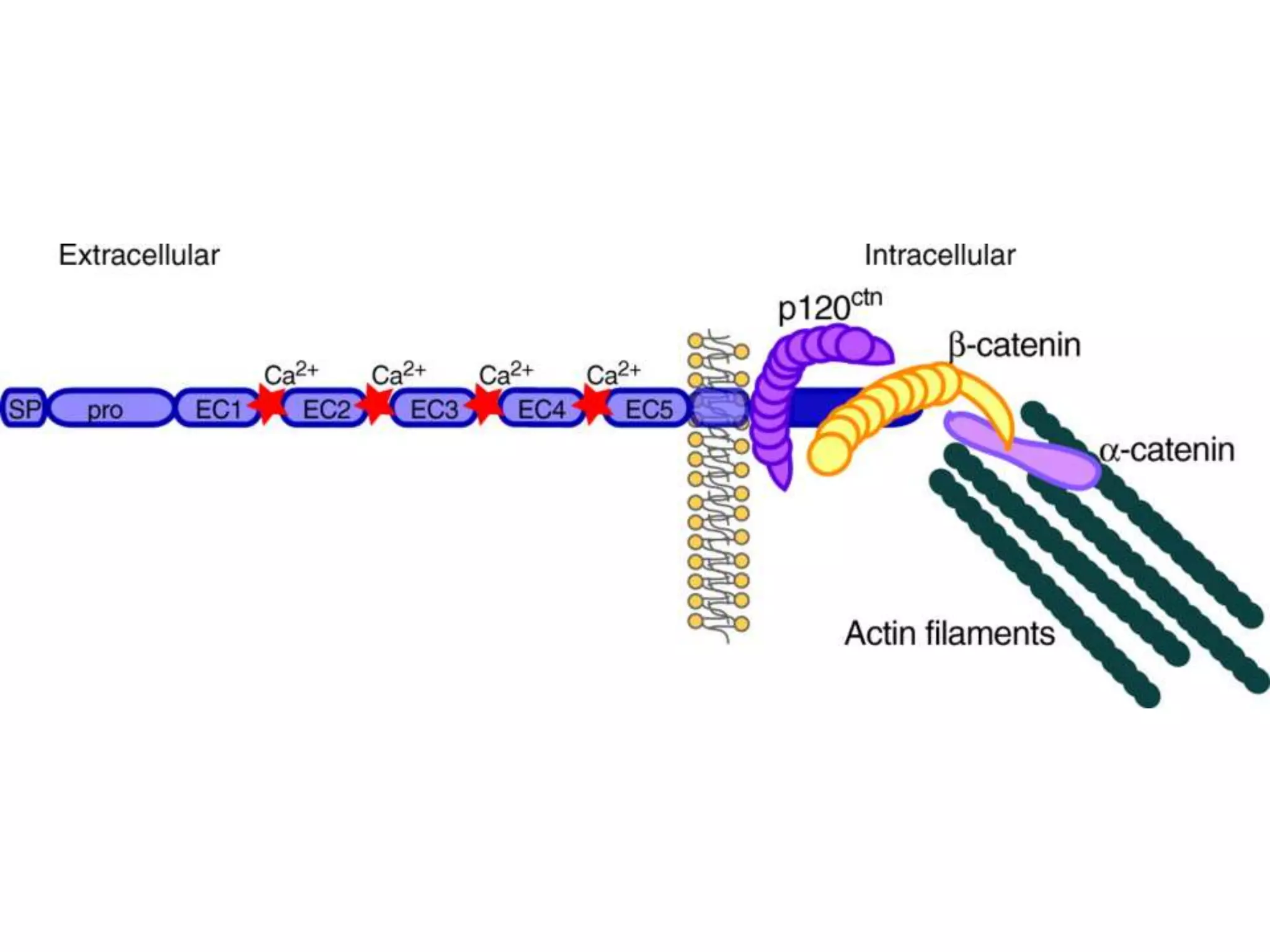
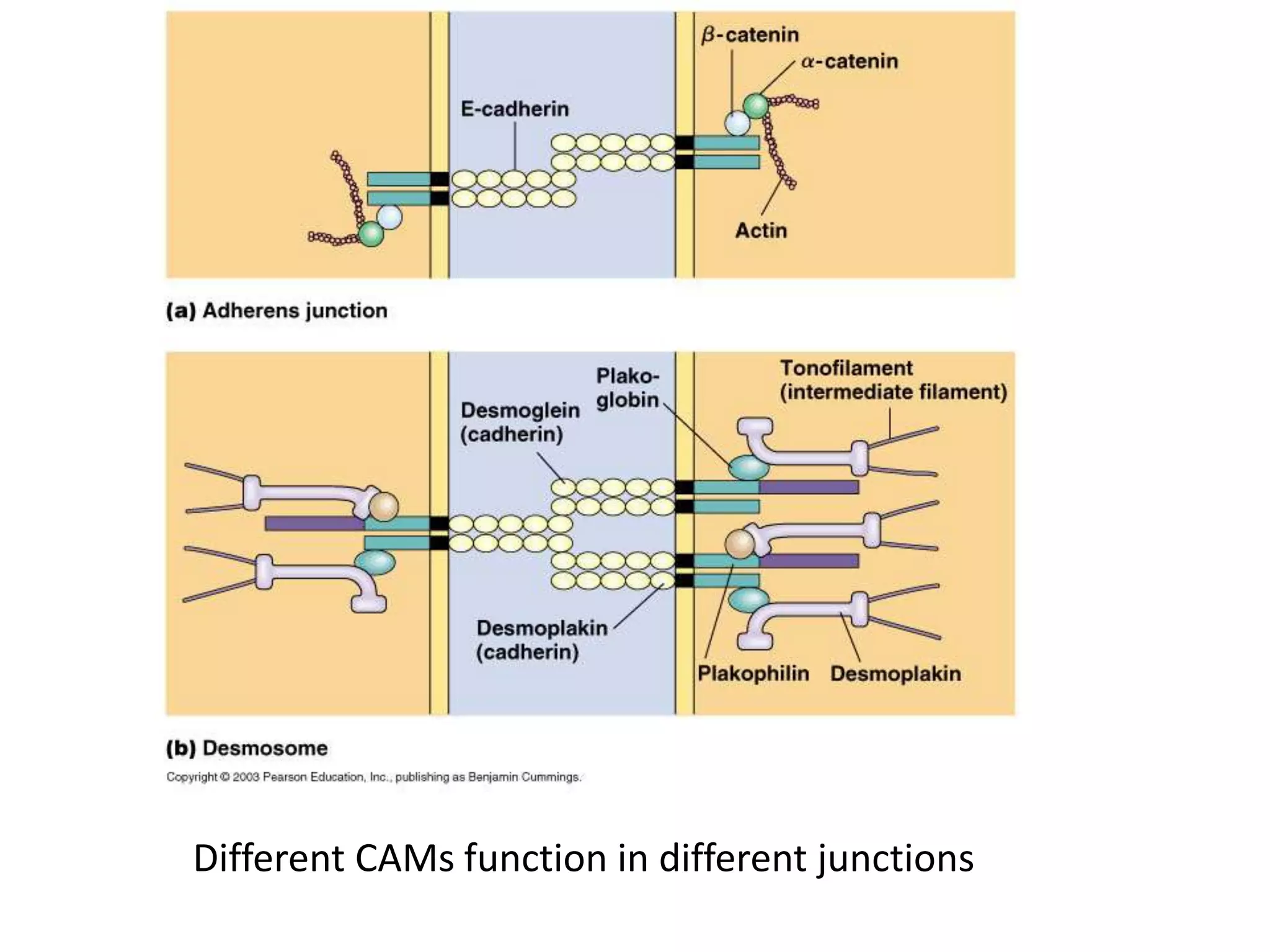
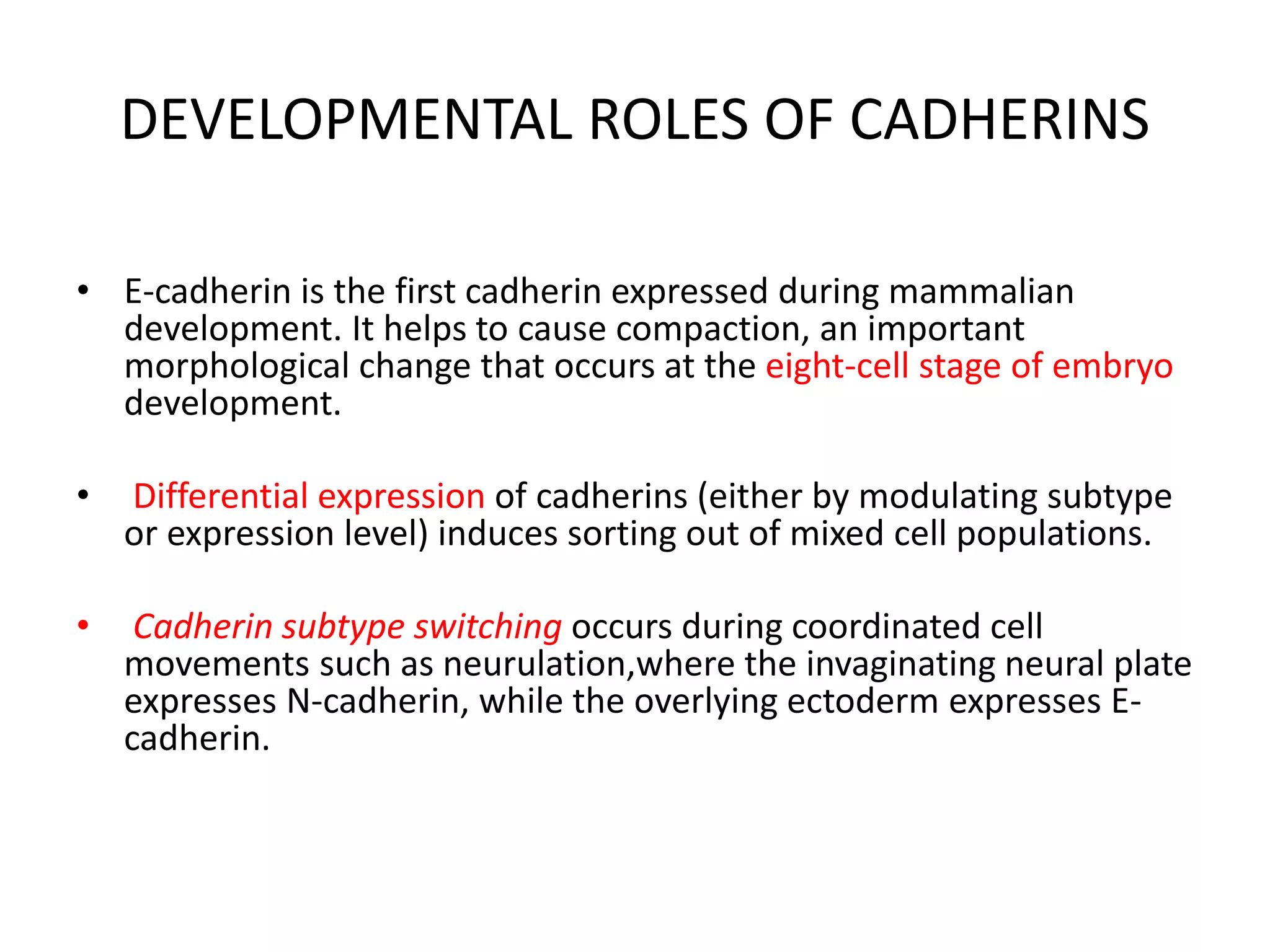
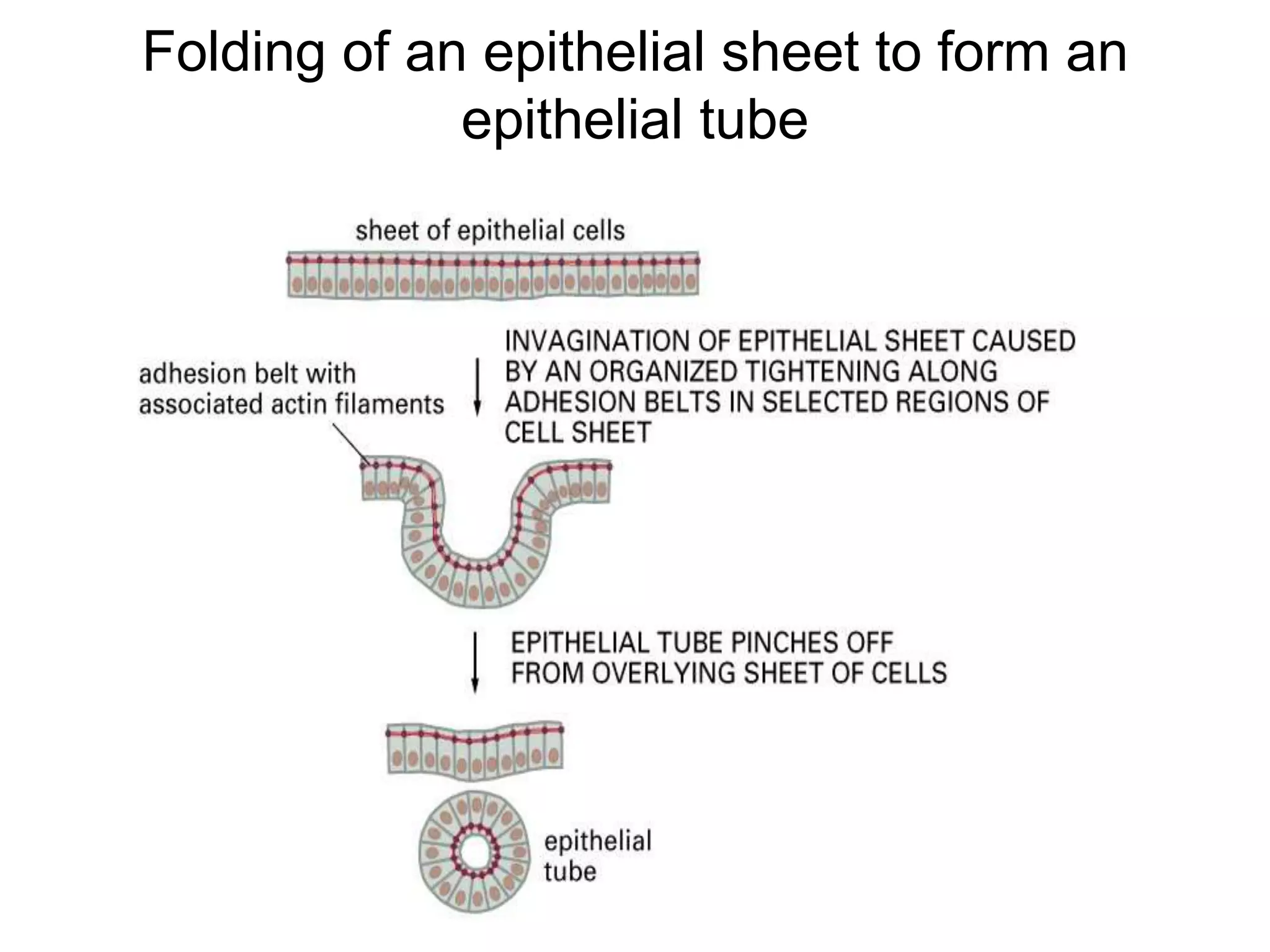
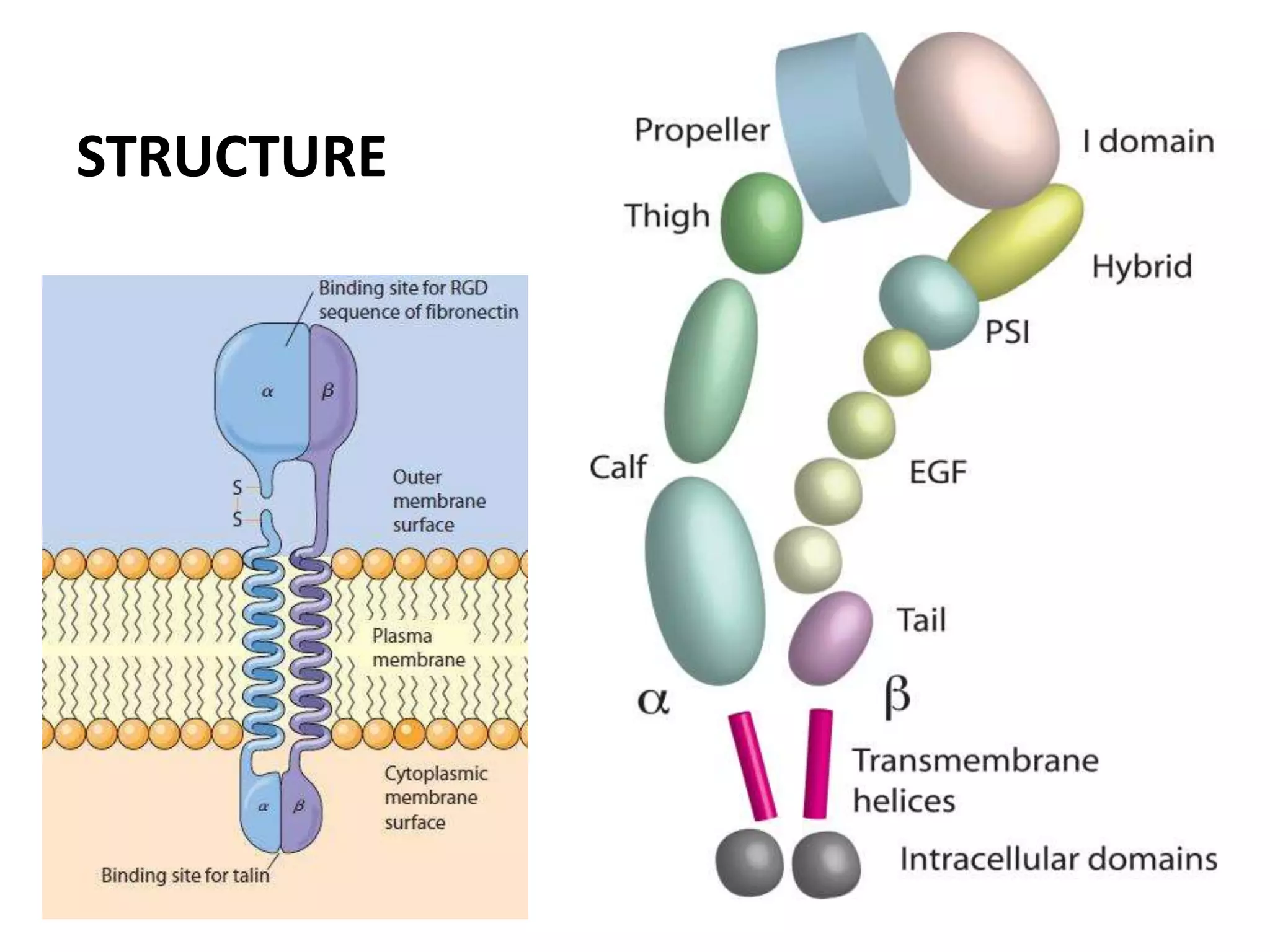
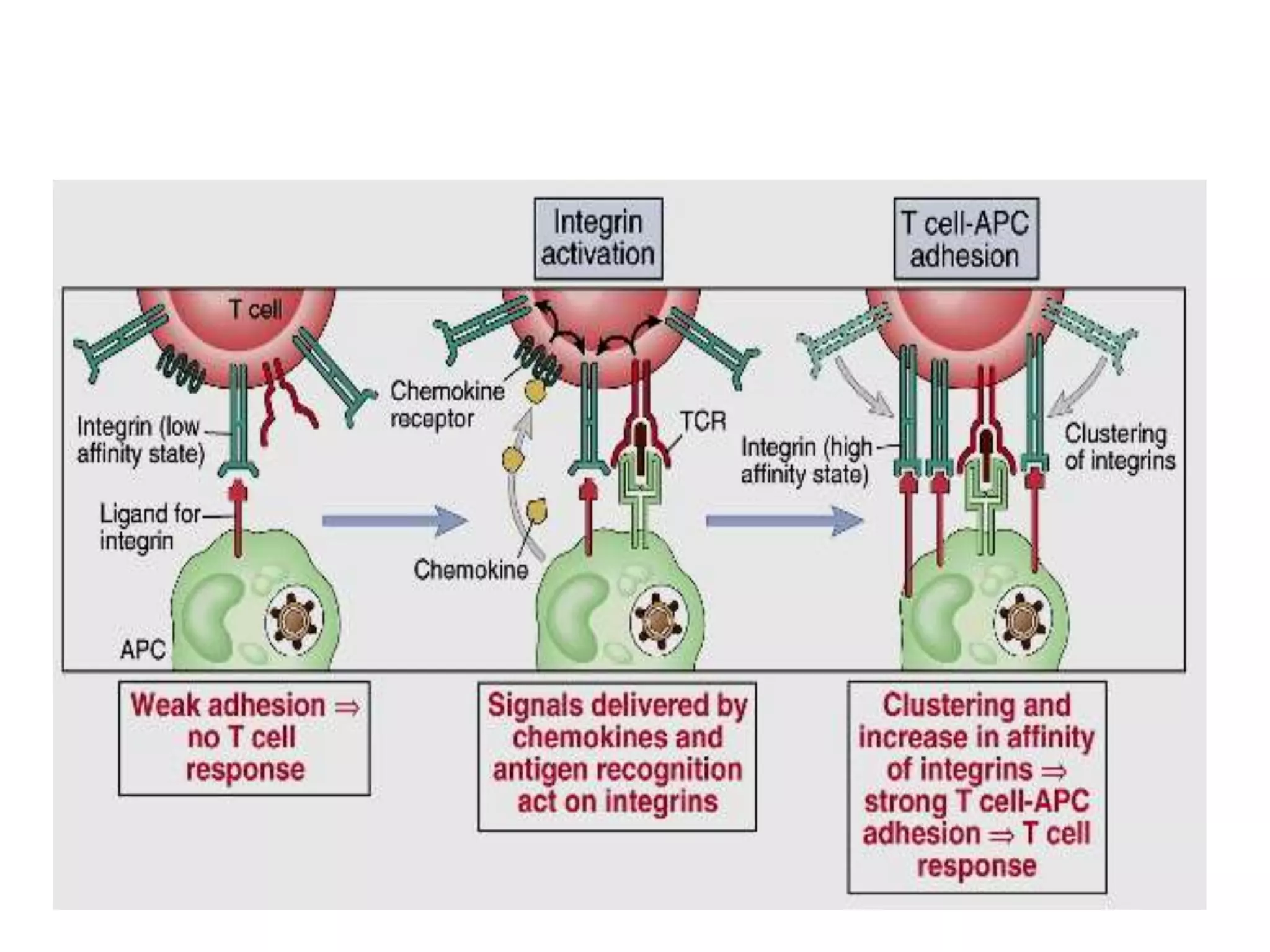
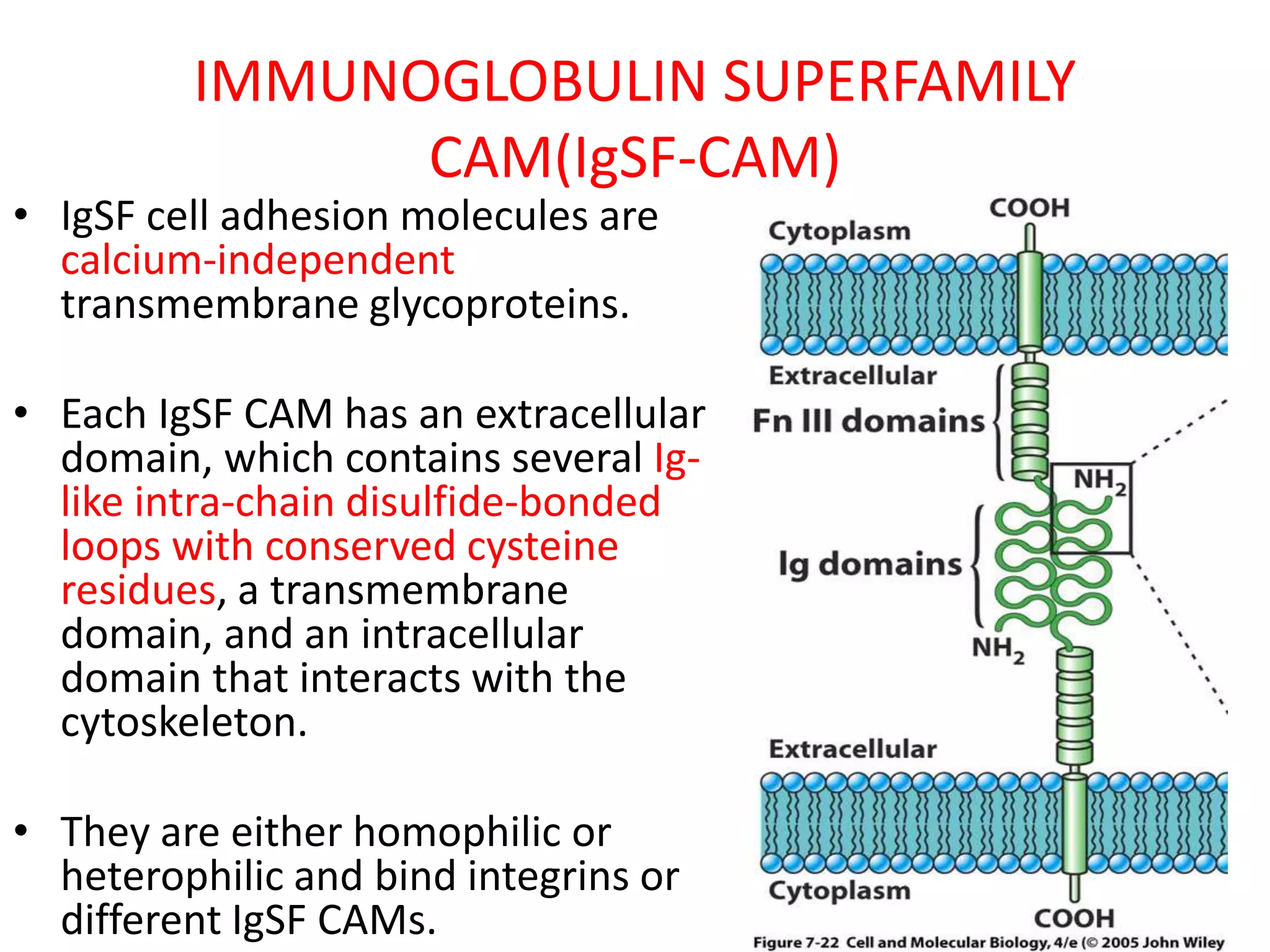
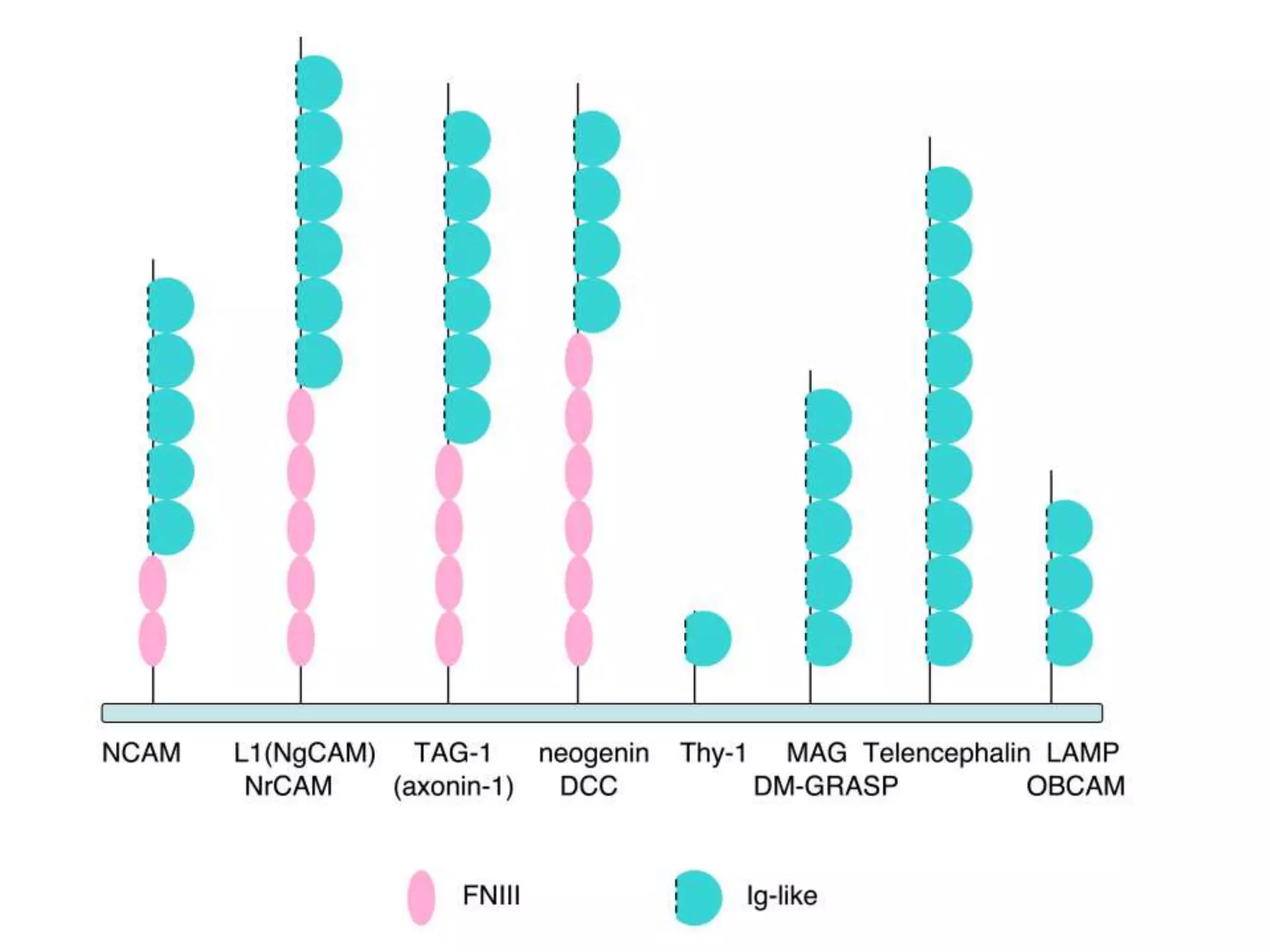
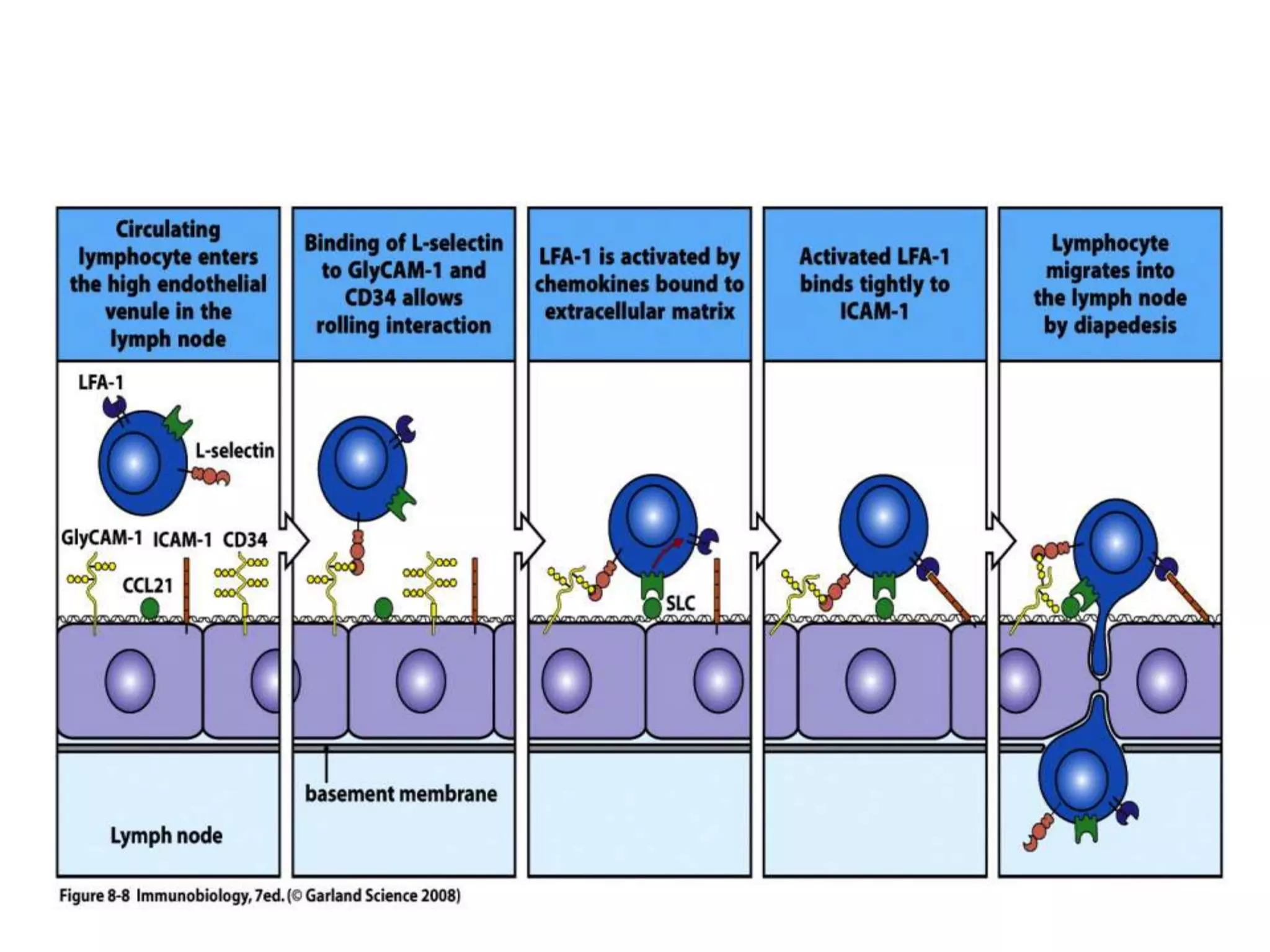
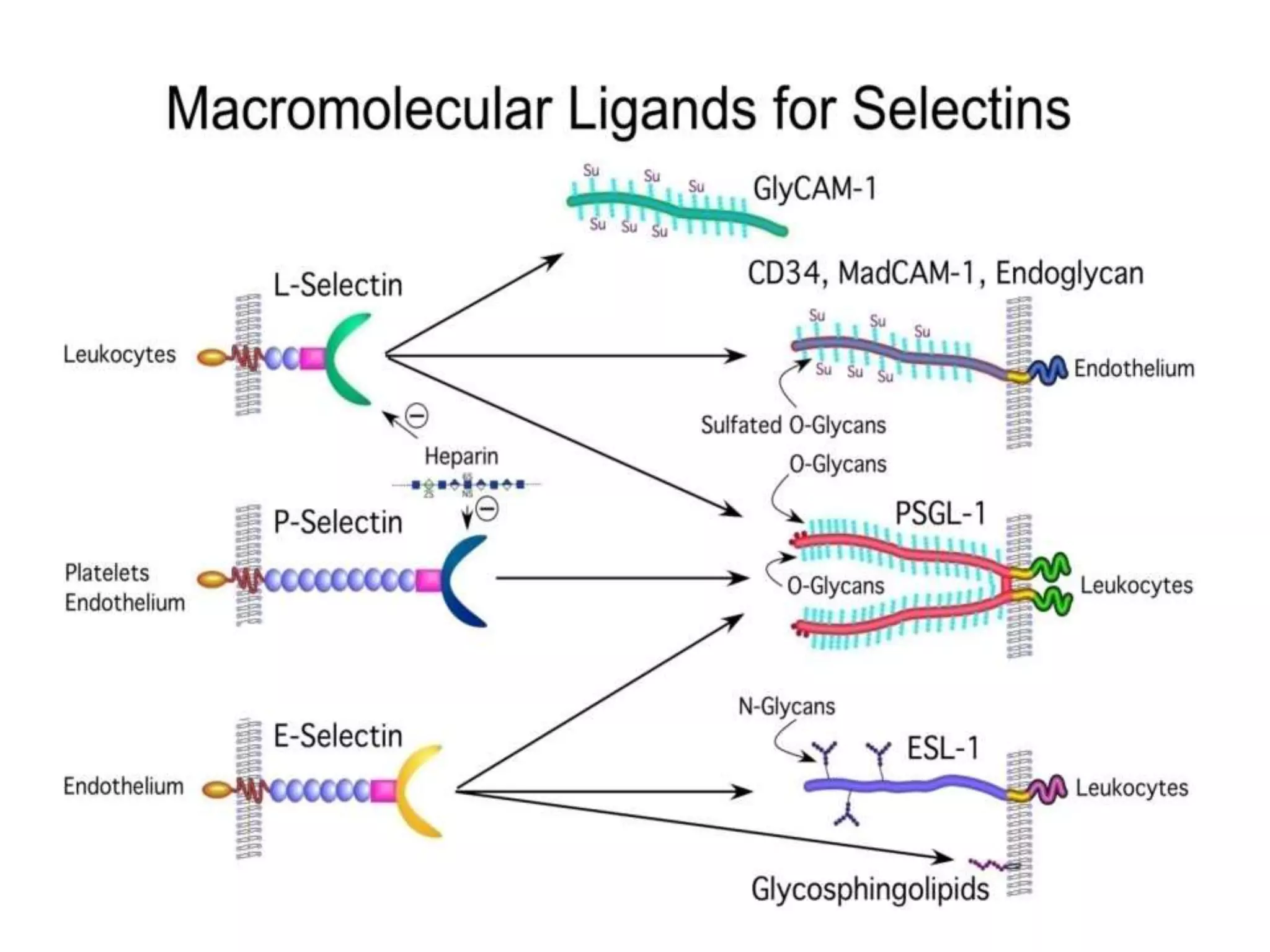
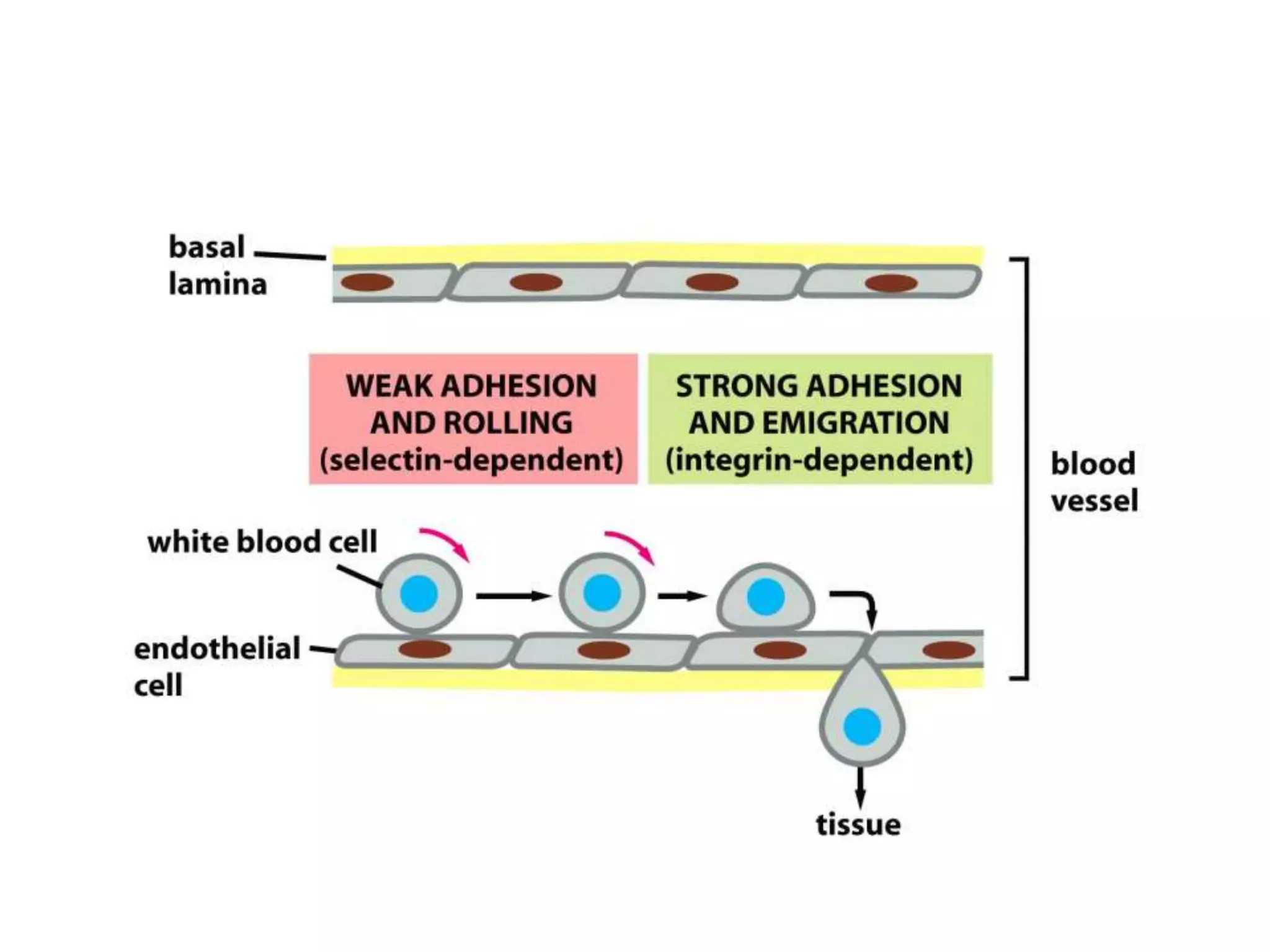
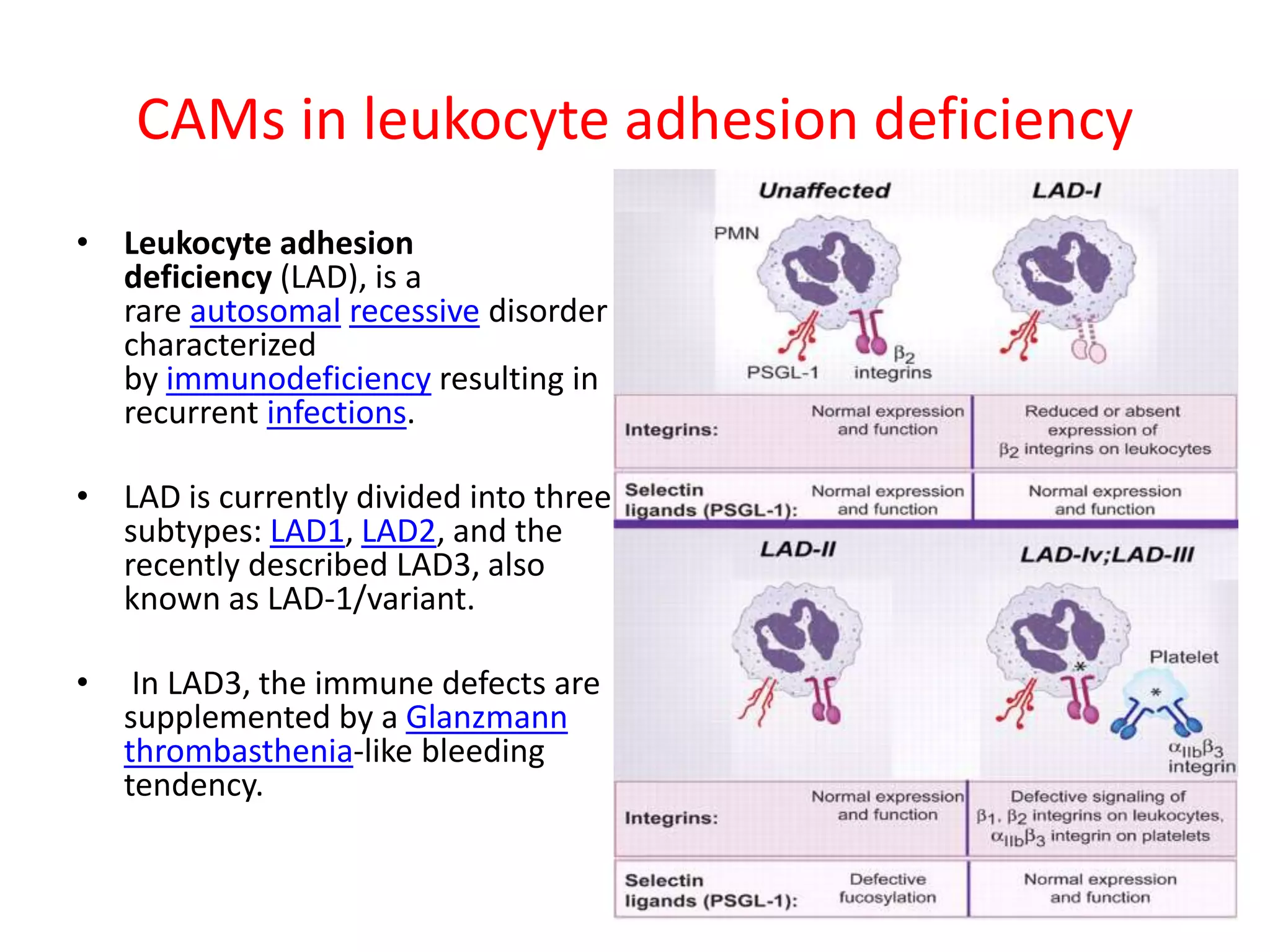
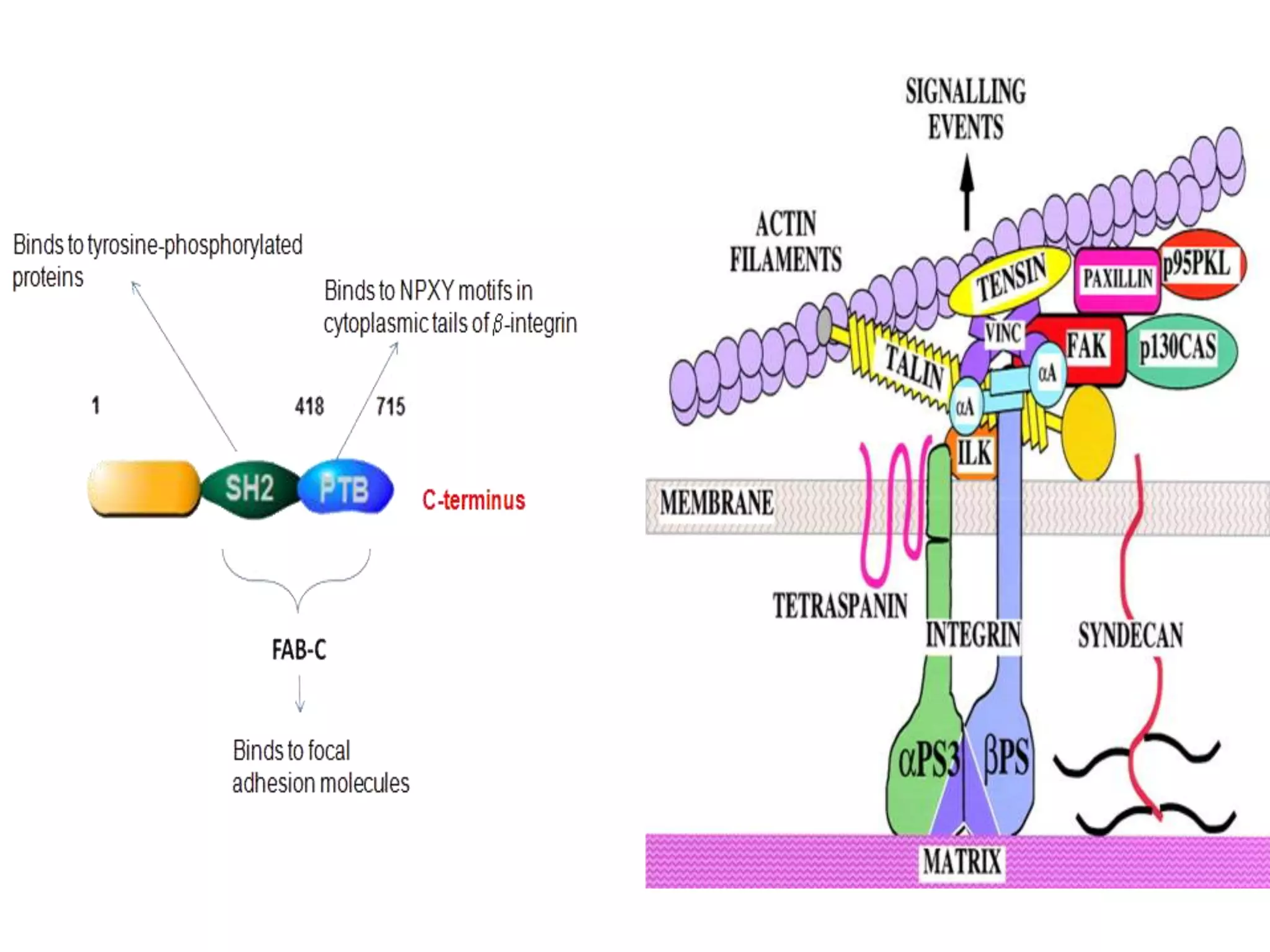
This document summarizes different types of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). It discusses cadherins, which are the primary CAMs in adherens junctions and desmosomes. Integrins are heterodimeric receptors that connect the intracellular and extracellular environments and are involved in cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix. The immunoglobulin superfamily of CAMs are calcium-independent transmembrane proteins with immunoglobulin-like domains. Selectins mediate the initial tethering of leukocytes to endothelial cells during inflammation. Cell adhesion molecules play important roles in processes like embryogenesis, immunity, tissue development, and cancer metastasis.