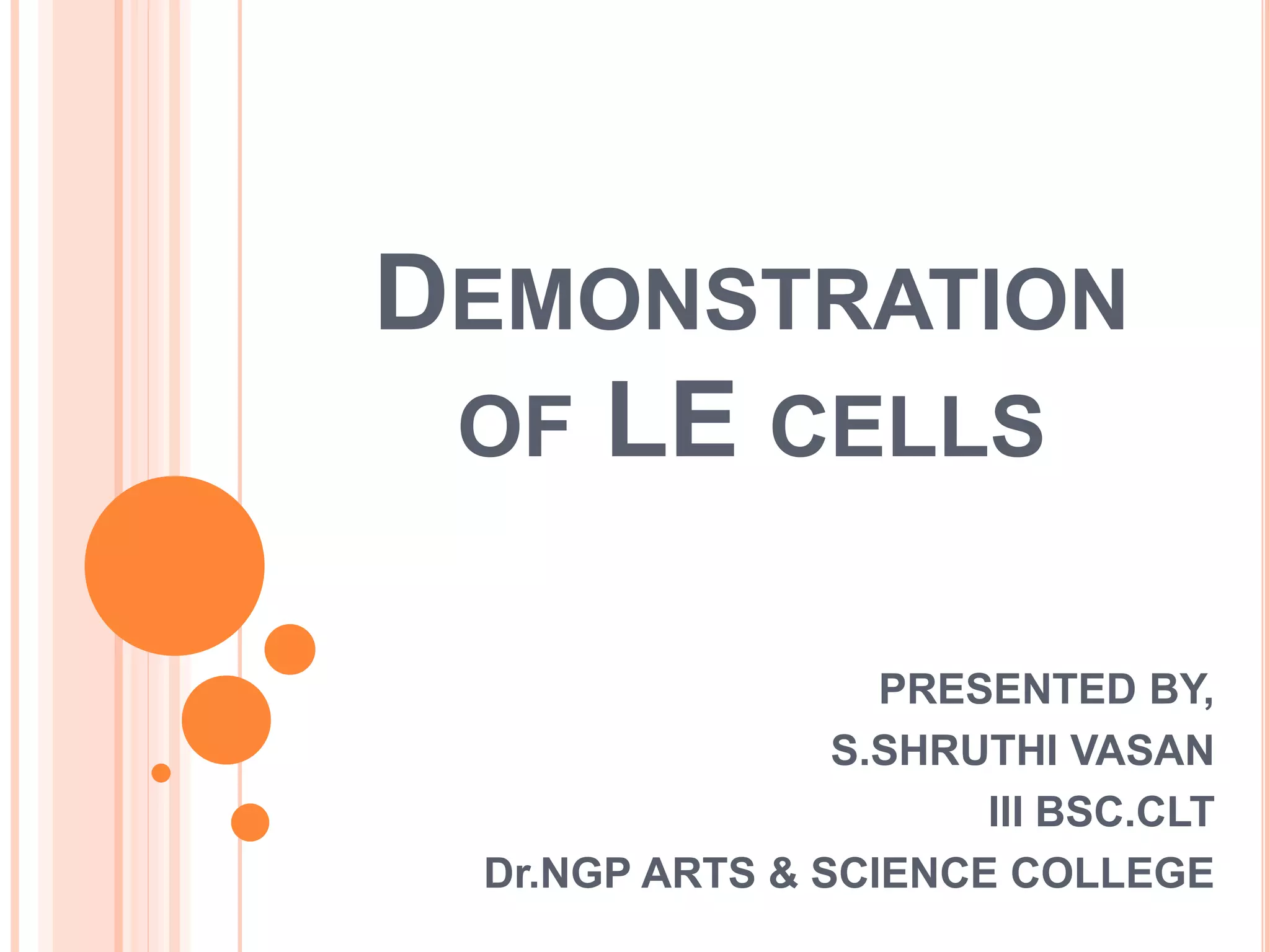
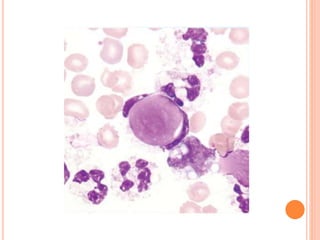
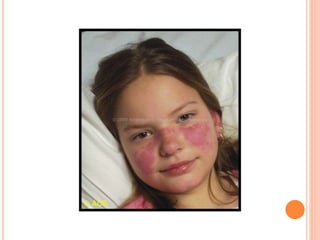
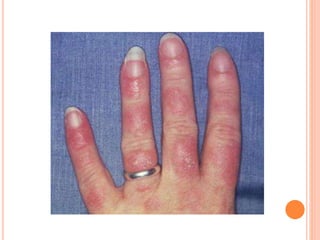
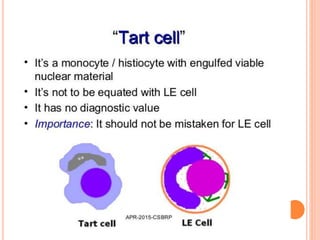
L.E. cells are neutrophils or macrophages that have engulfed denatured nuclear material, primarily associated with lupus erythematosus and similar connective tissue disorders. The presence of L.E. cells is indicative of lupus, while diagnostic testing methods include the rotary bead and fluorescent antibody methods. Although L.E. cell testing has largely been replaced by antinuclear antibody testing for diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus, it remains a relevant aspect in the evaluation of related conditions.






![ Obtaining bone marrow is usually distressing for the
patient; therefore, the buffy coat from venous blood is
an adequate substitute.
If the equipment for buffy coat is unavailable, an
untreated venous blood sample is left to clot (from 20-
120 minutes) and the plasma removed. The residual
clot is passed through a wire mesh and centrifuged
for 5 minutes to obtain a buffy coat. This buffy coat is
then smeared on glass slides to search for LE cells. [2]
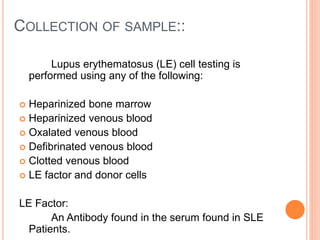
The test may be performed by mixing the patient's
plasma, serum, or serous effusions as a source of LE
factor with bone marrow from a donor subject.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/demonstrationoflecells-171122095514/85/Demonstration-of-le-cells-14-320.jpg)




