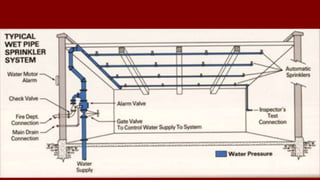
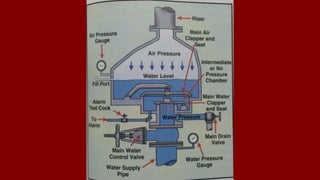
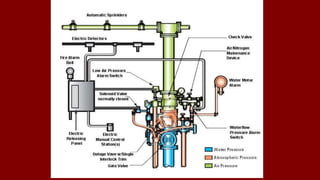
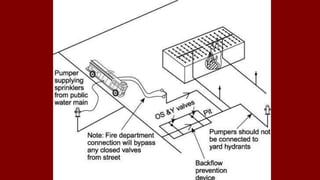
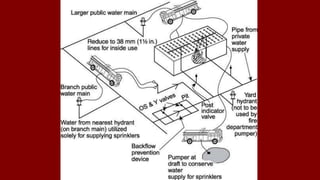
The document outlines various types of sprinkler systems used in buildings, including wet-pipe, dry-pipe, preaction, and deluge systems, along with their operational mechanisms. It also discusses common reasons for sprinkler failure and emphasizes the importance of pre-incident planning and proper fireground operations to mitigate these risks. Additionally, it details post-fire operations and reporting requirements related to sprinkler performance and restoration.