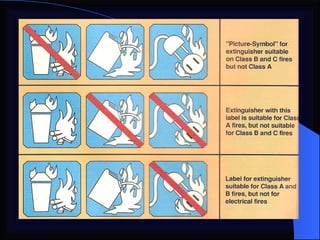
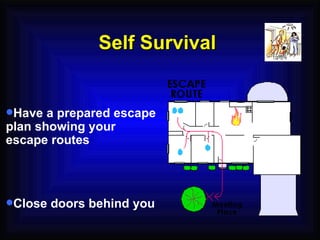
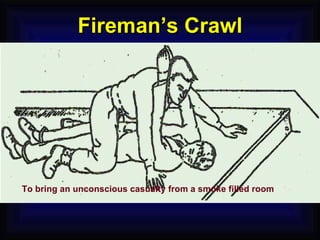
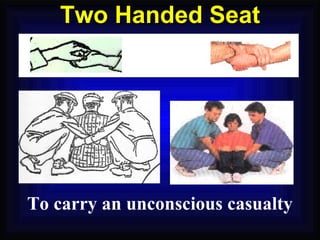
1. The document provides an overview of fire safety training, including definitions of fire, fire classifications, fire extinguishers, and emergency response procedures.
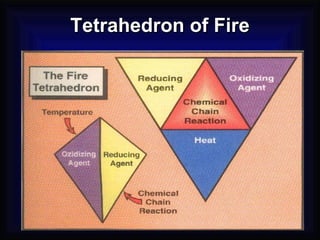
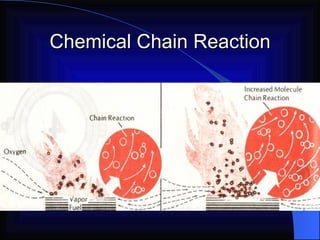
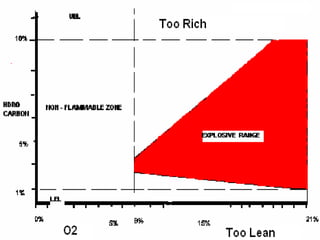
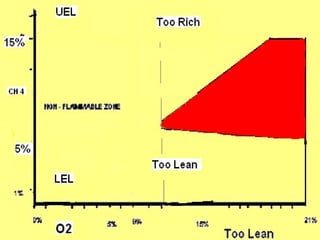
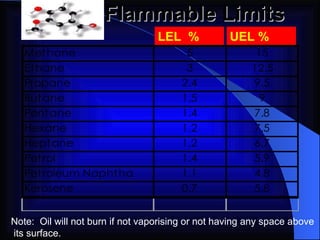
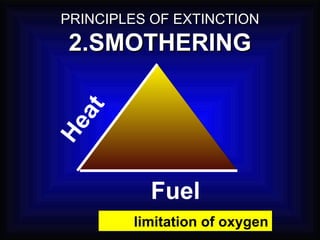
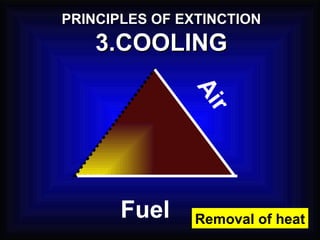
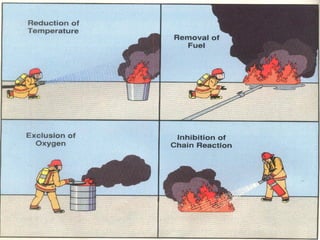
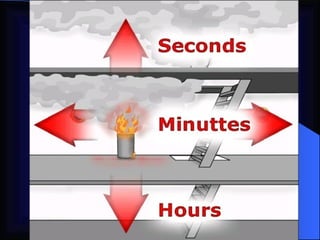
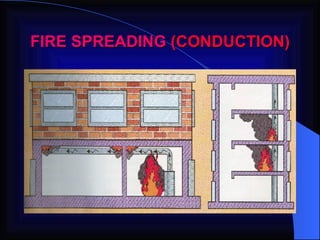
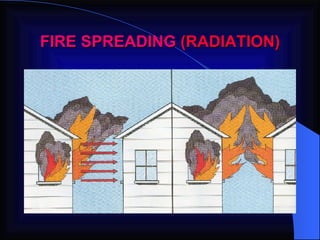
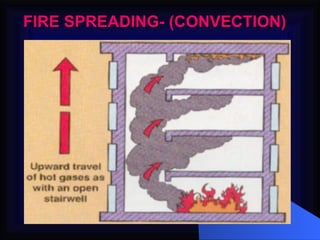
2. It details the principles of fire extinction through starvation, smothering, and cooling. Methods of fire spreading through conduction, radiation, and convection are also explained.
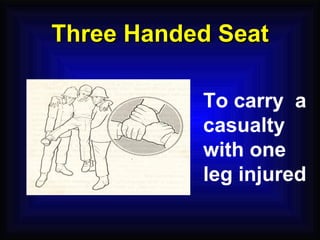
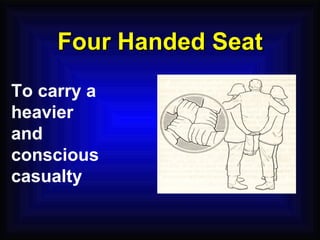
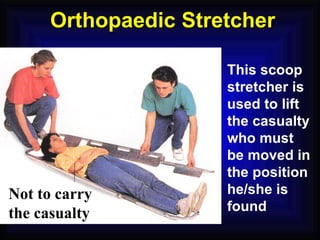
3. Proper firefighting techniques and safety procedures in the event of a fire are outlined, such as following the PASS method for using a fire extinguisher and RACE for fire emergency response.