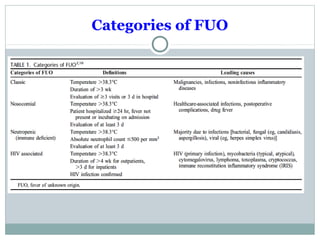
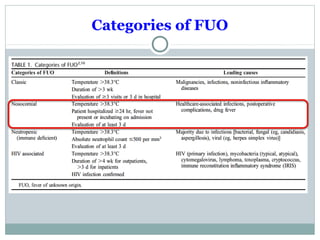
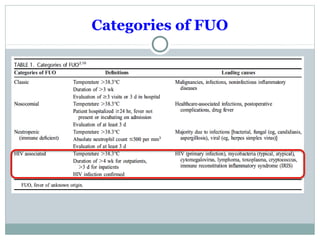
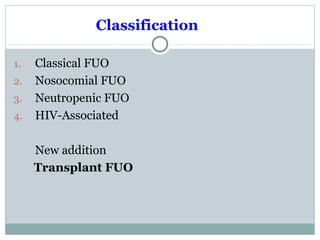
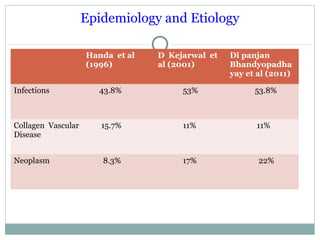
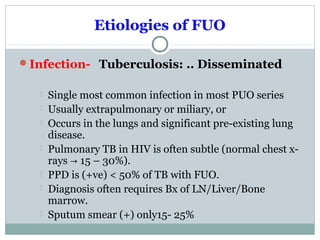
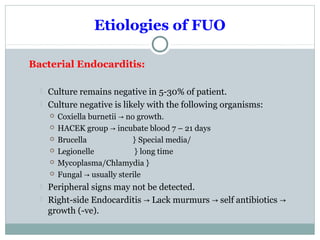
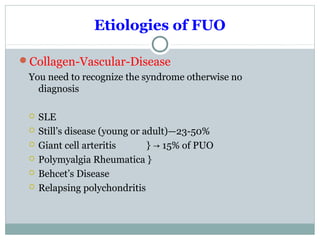
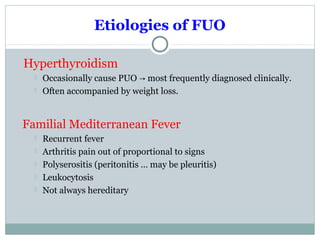
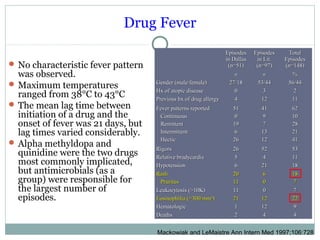
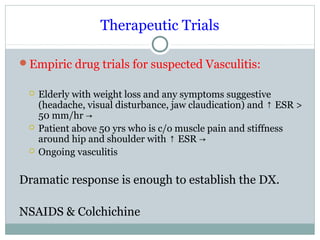
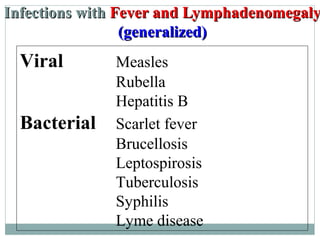
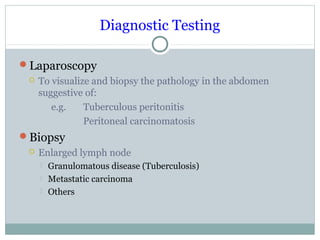
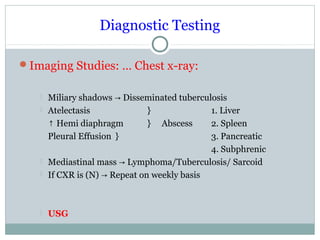
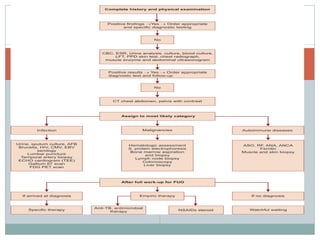
This document discusses fever of unknown origin (FUO). It begins by classifying FUO into categories like classical FUO and nosocomial FUO. It then discusses the epidemiology and common etiologies of FUO, which include infections, collagen vascular diseases, and malignancies. The diagnostic approach involves a thorough history, repeated physical exams, and diagnostic testing like blood tests, imaging, and biopsies. Empirical therapeutic drug trials can help diagnose certain conditions but have limitations. The prognosis depends on the underlying cause, with poorer outcomes seen in elderly patients or those with neoplasms or diagnostic delays.