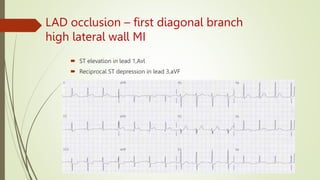
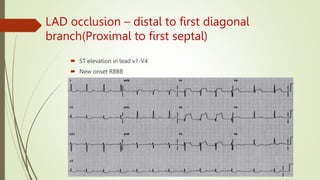
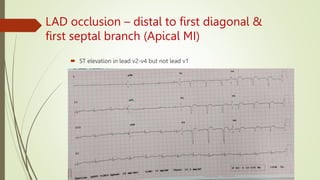
A 46-year-old male presented with sudden onset of chest pain radiating to the left arm and shortness of breath. He has risk factors of smoking but no other medical history. On examination, his vitals were stable and heart and lung sounds were normal. The document discusses the arterial supply of the heart and how electrocardiogram leads correspond to different areas of the heart muscle. It provides detailed descriptions of ST segment changes that would indicate occlusions or blocks in different coronary arteries and the regions of the heart affected.