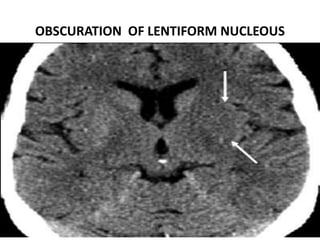
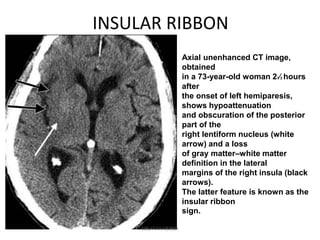
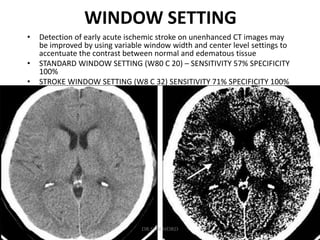
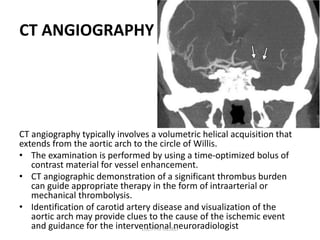
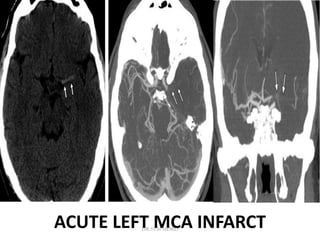
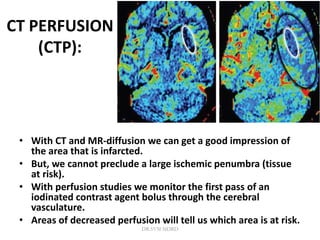
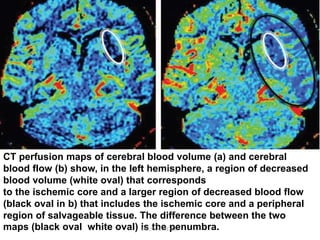
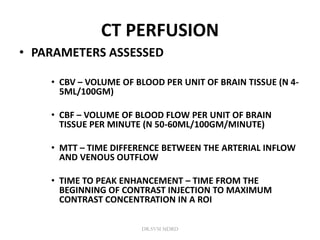
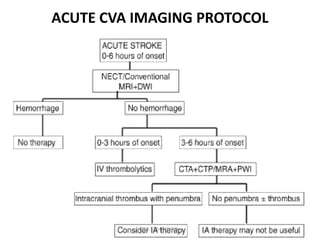
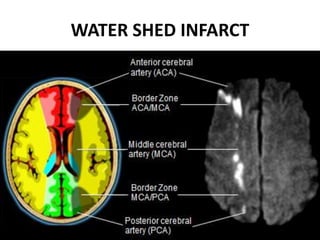
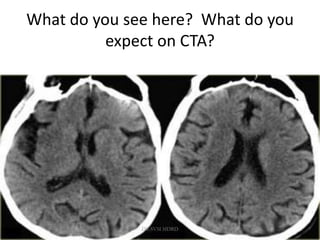
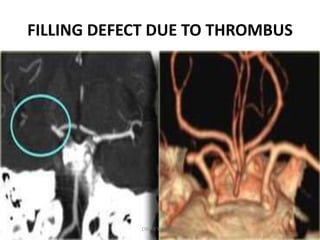
1. Imaging plays an important role in the evaluation and management of patients with acute stroke.
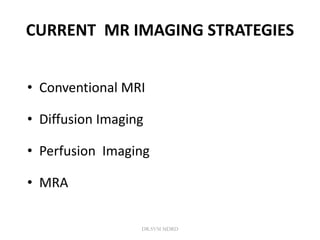
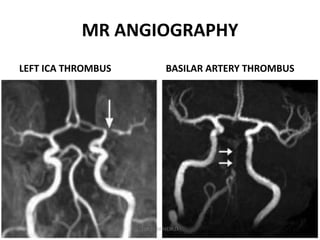
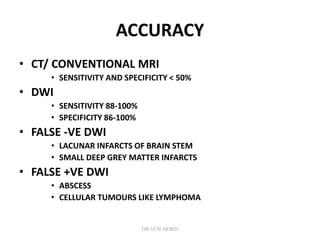
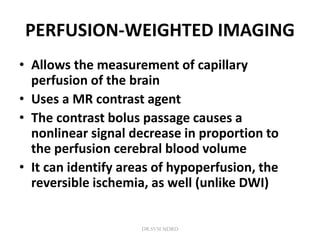
2. Different imaging modalities such as CT, CT angiography, CT perfusion, MRI, MR angiography, and MR perfusion have benefits for assessing the brain parenchyma, vasculature, perfusion, and identifying potentially salvageable penumbral tissue.
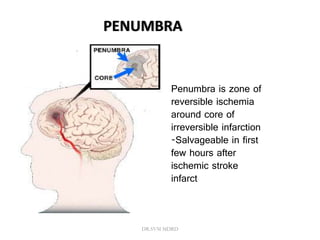
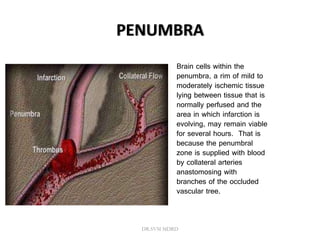
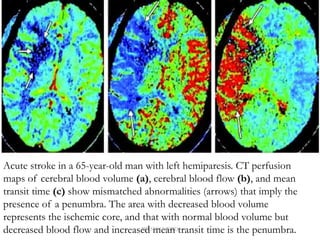
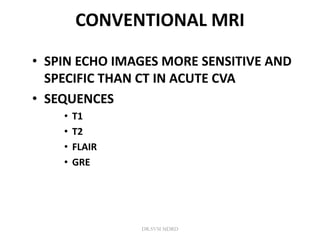
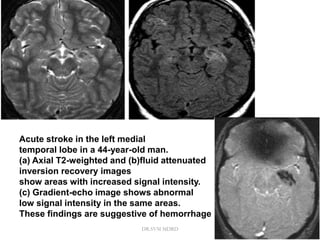
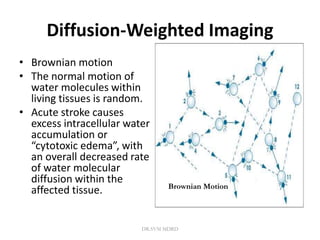
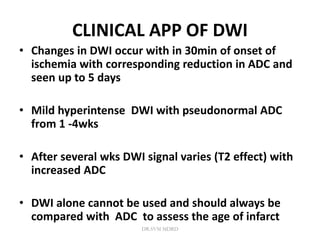
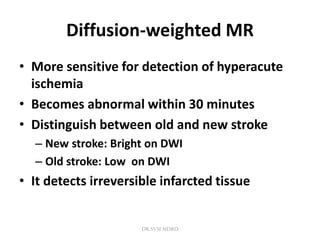
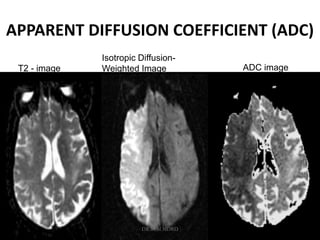
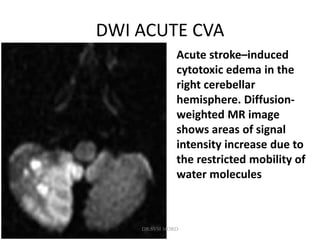
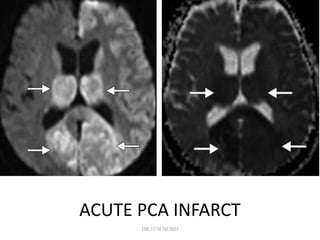
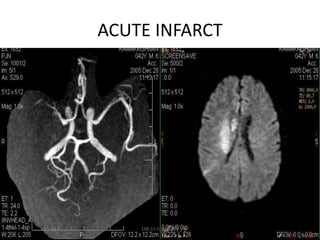
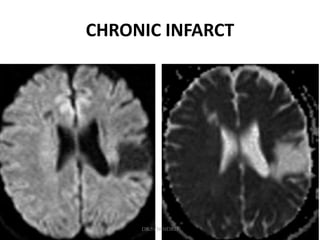
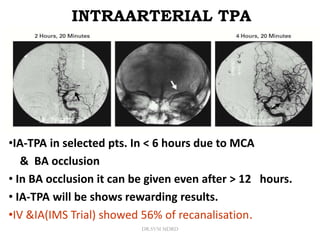
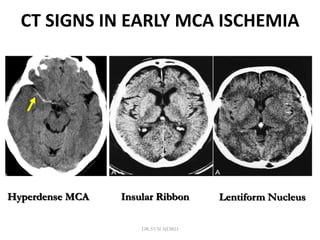
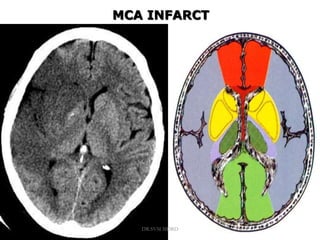
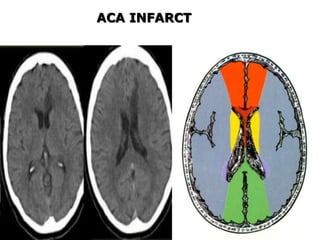
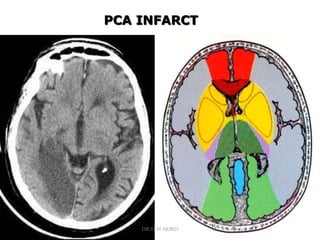
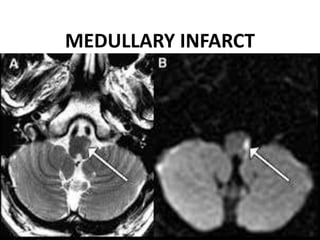
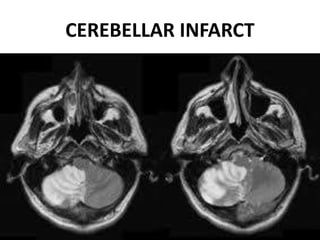
3. Diffusion-weighted MRI is the most sensitive method for detecting acute ischemia within the first few hours, while perfusion imaging can identify tissue at risk of infarction in the ischemic penumbra that may be rescued with reperfusion therapy.