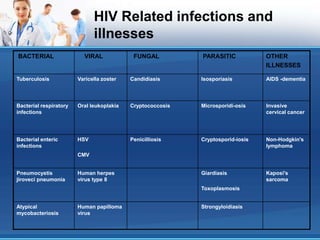
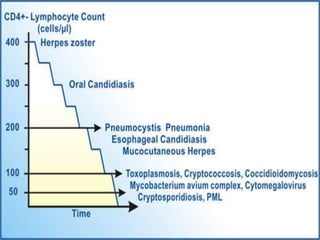
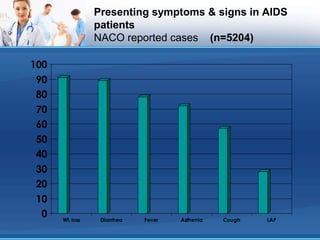
This document discusses opportunistic infections (OIs) that occur in patients with AIDS. It defines AIDS according to CDC and NACO criteria involving OIs or low CD4 counts. Common OIs seen in India are described such as tuberculosis, candidiasis, cryptosporidiosis, herpes zoster, toxoplasmosis, and Pneumocystis pneumonia. Symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of these OIs are outlined. The role of patient education in prevention and treatment adherence is also discussed.