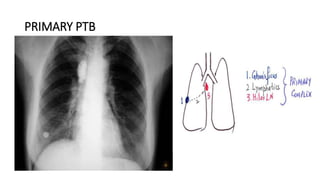
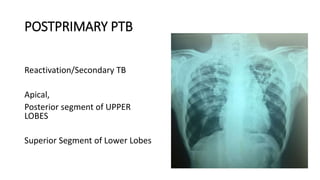
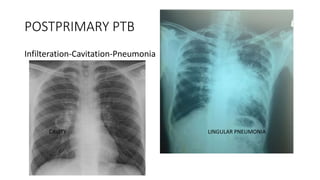
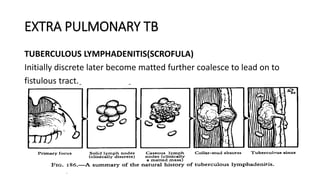
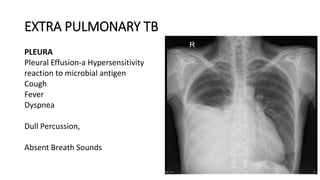
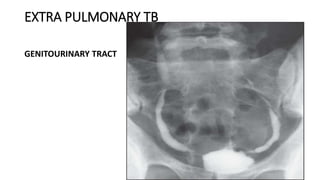
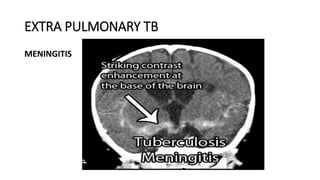
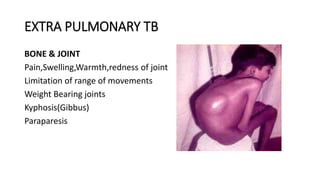
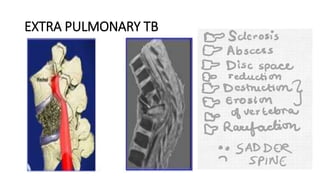
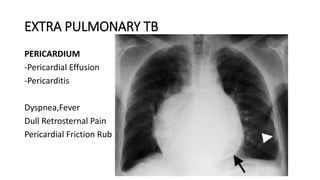
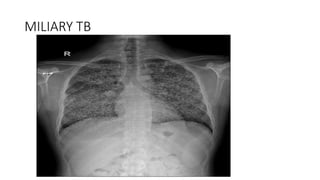
Tuberculosis can manifest as either pulmonary or extra-pulmonary disease. Pulmonary TB, which accounts for over 78% of cases, is divided into primary TB occurring after initial infection and reactivation post-primary TB. Extra-pulmonary TB involves sites outside the lungs, with lymph nodes, pleura, and the genitourinary tract being most commonly affected. Symptoms vary depending on the infected site but may include cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.