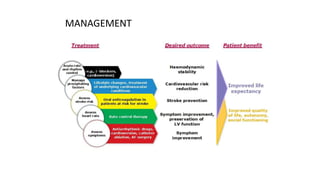
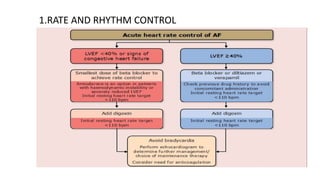
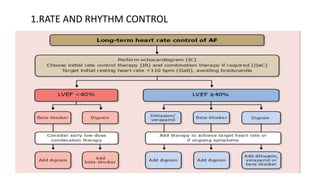
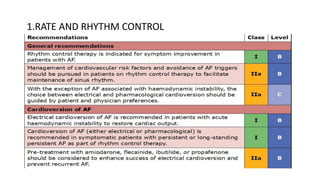
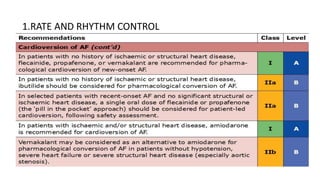
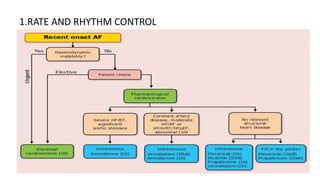
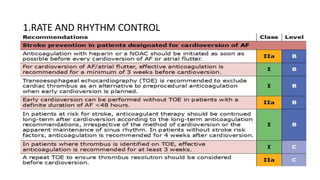
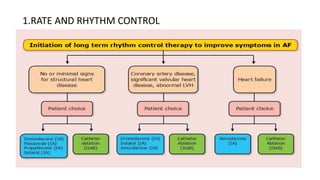
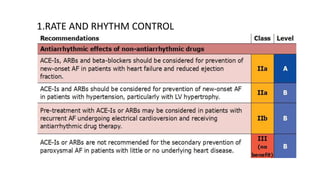
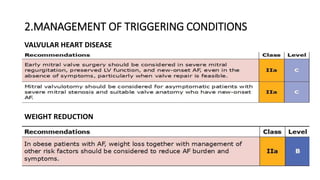
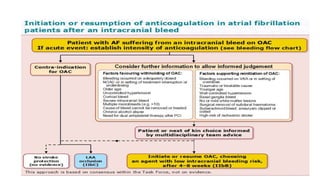
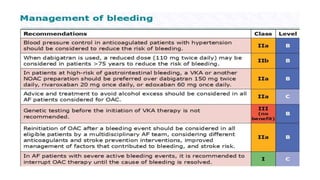
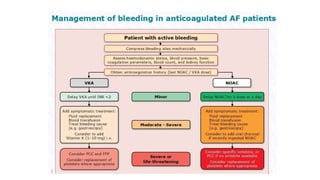
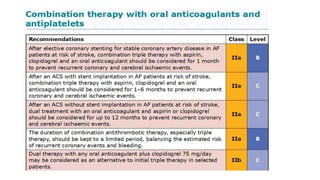
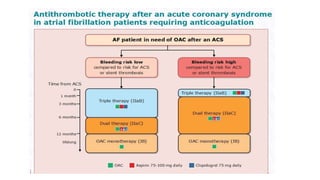
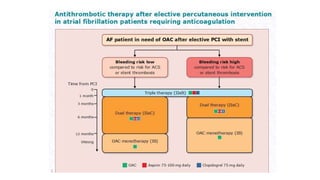
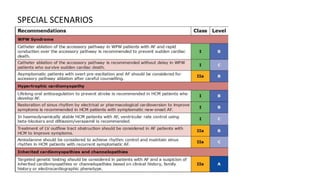
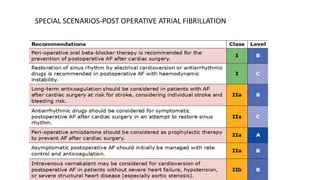
This document provides an overview of atrial fibrillation (AF), including its pathogenesis, types, diagnosis, and management. Some key points:
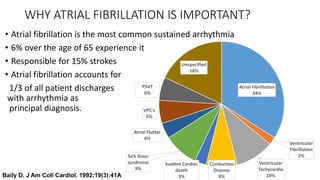
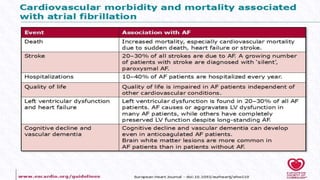
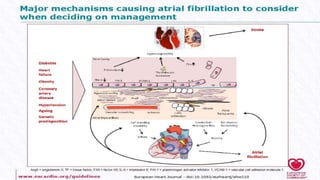
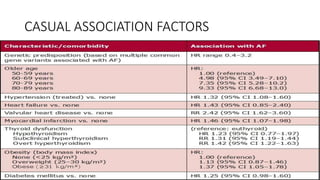
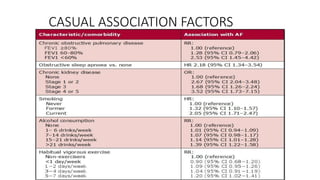
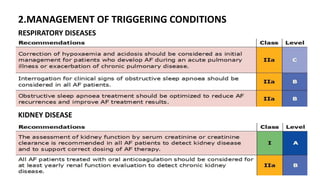
- AF is the most common cardiac arrhythmia, affecting around 6% of those over 65. It increases the risk of stroke.
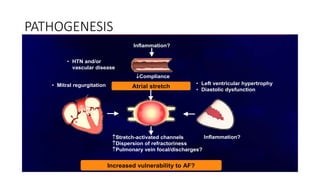
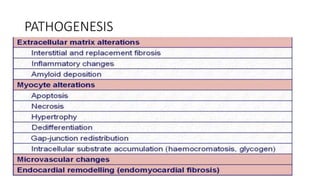
- It occurs when the normal sinus rhythm is overridden by disorganized electrical impulses, usually originating in the lungs.
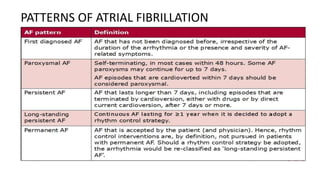
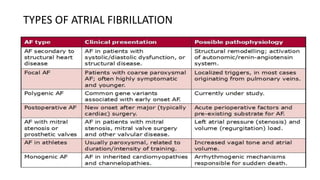
- Types include paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent. Symptoms range from none to palpitations, dyspnea, chest pain, and neurological issues.
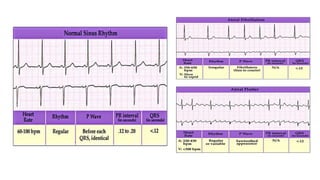
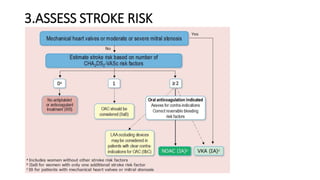
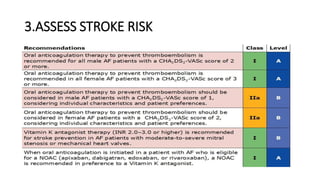
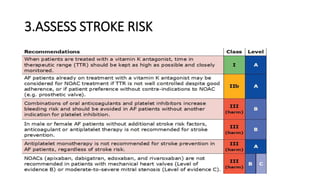
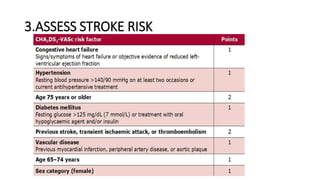
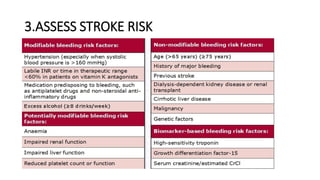
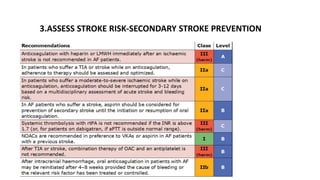
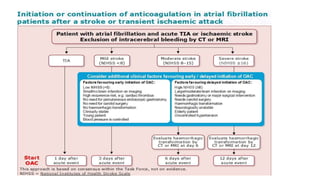
- Diagnosis is made via ECG showing irregular rhythm without P waves. Workup evaluates for underlying causes and stroke risk factors.