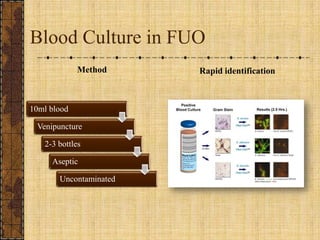
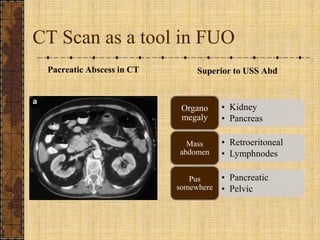
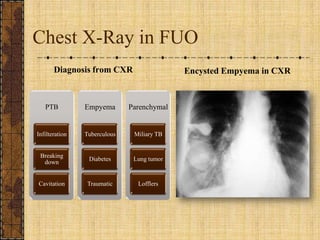
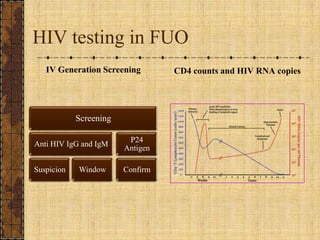
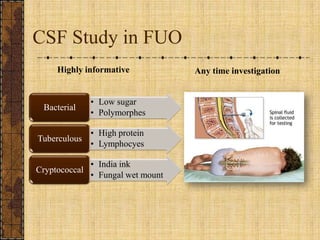
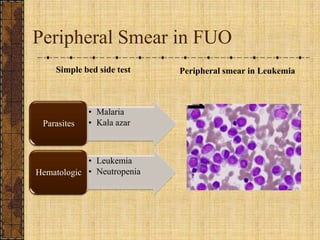
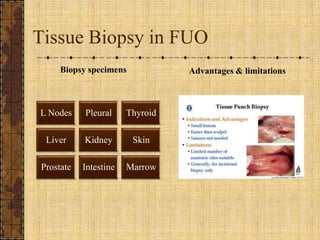
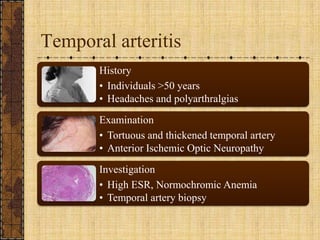
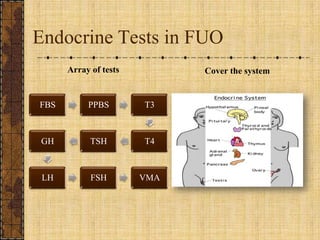
The document discusses fever of unknown origin (FUO), defining it and outlining a new classification system. It presents case studies from various patients, detailing their symptoms, examination results, and diagnostic challenges across different categories of FUO, such as classic FUO, nosocomial FUO, and neutropenic FUO. Additionally, it includes the diagnostic approaches for identifying potential causes and links various diseases to FUO presentations.