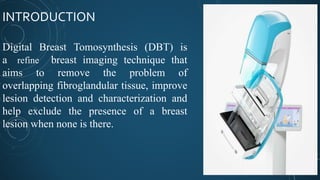
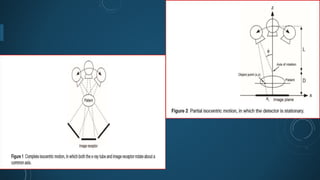
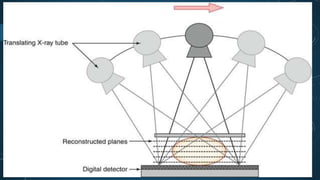
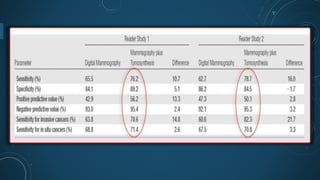
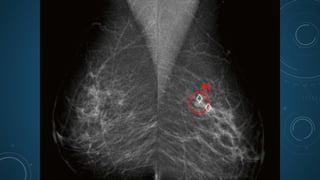
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is an advanced breast imaging technique that improves lesion detection by reducing overlapping tissue and offers benefits over traditional mammography, including higher sensitivity and specificity. The technology involves capturing a three-dimensional volume of breast tissue using modified digital mammography units and has been shown to reduce recall rates and overdiagnosis. However, challenges remain, including cost, time investment, and concerns about radiation dosage, despite DBT being within safety parameters.