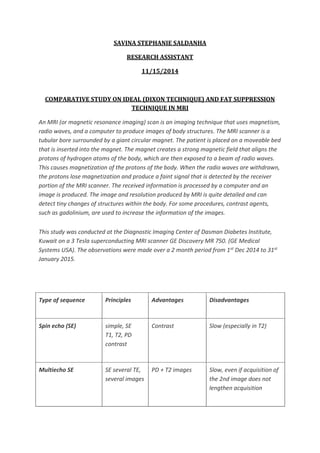
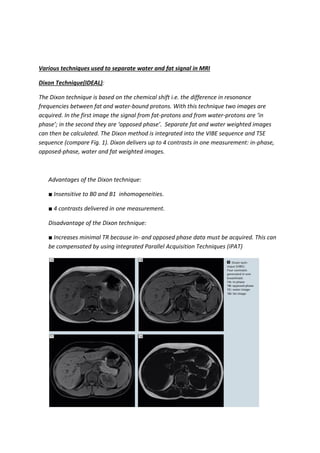
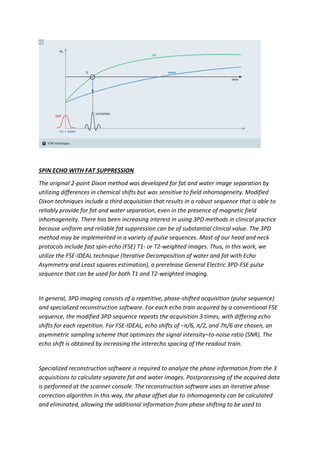
This study compares different MRI techniques for fat suppression and water-fat separation, including Dixon, spectral fat saturation, water excitation, and inversion recovery techniques. Dixon technique uses chemical shift to generate in-phase and opposed-phase images from which water and fat images can be calculated. It is insensitive to B0 and B1 inhomogeneities but increases minimum TR. Spectral fat saturation selectively excites and destroys fat signal, while water excitation uses a special pulse to maximize water excitation. Both are sensitive to inhomogeneities. Inversion recovery techniques like STIR use different tissue relaxation times to suppress fat. The study also examines a 3-point Dixon method for fat suppression in fast spin echo sequences, which uses echo shifting