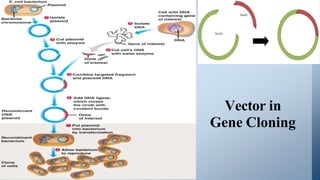
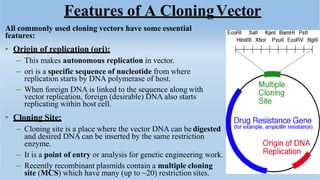
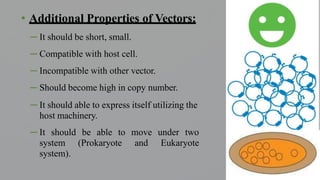
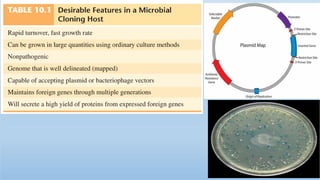
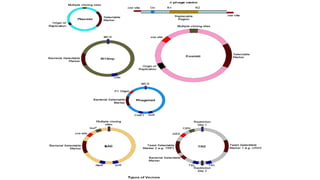
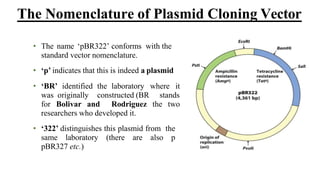
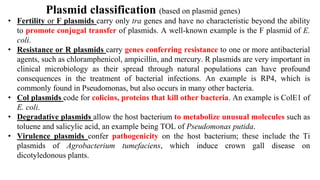
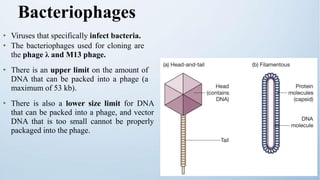
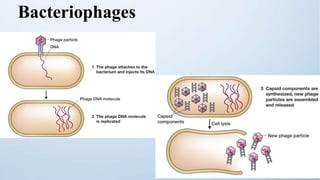
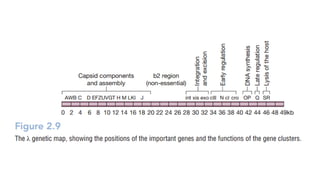
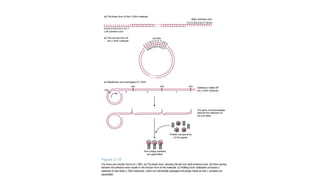
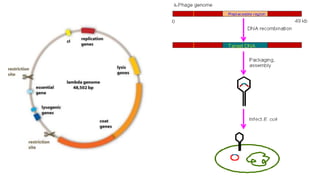
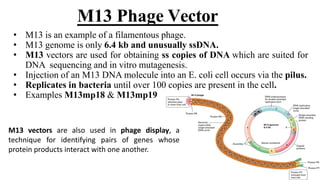
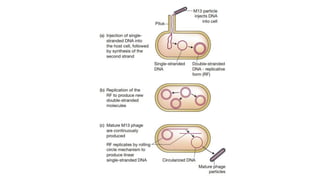
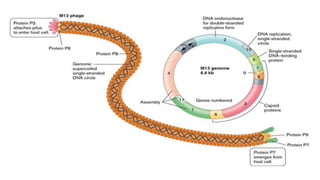
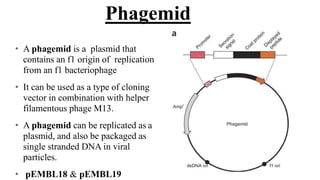
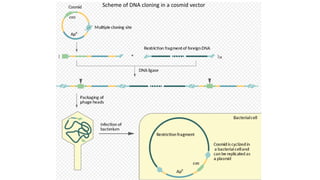
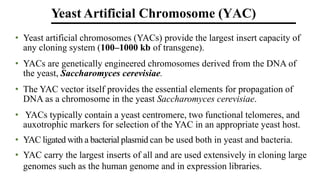
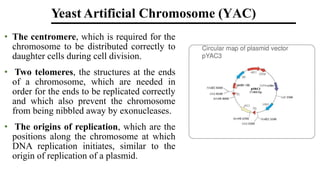
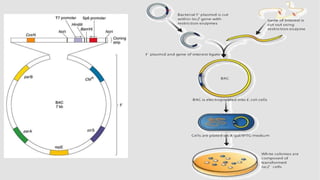
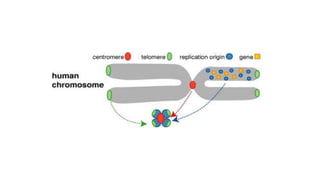
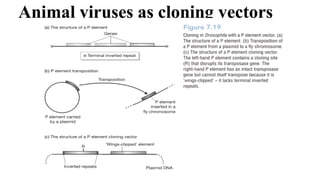
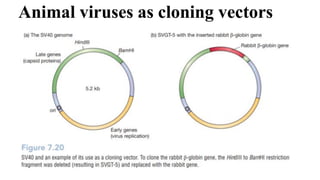
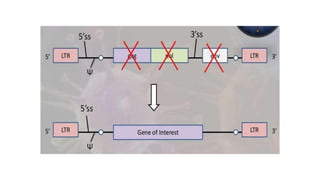
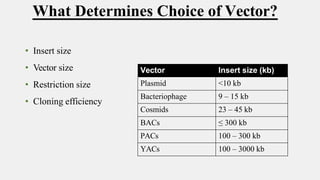
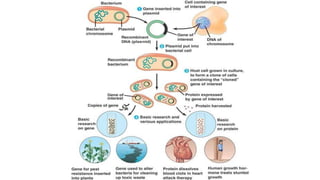
The document discusses cloning vectors. It describes what a cloning vector is, including that it is a small piece of DNA that can stably maintain foreign DNA for cloning purposes. Common types of cloning vectors are described in detail, including plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, yeast artificial chromosomes, bacterial artificial chromosomes, and plant virus vectors. Key features of cloning vectors like origins of replication, antibiotic resistance genes, and cloning sites are also summarized.