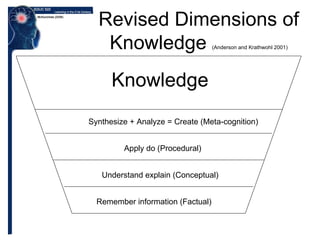
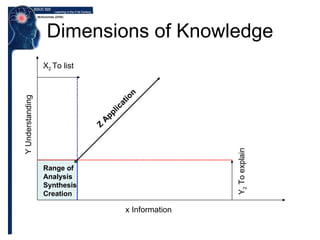
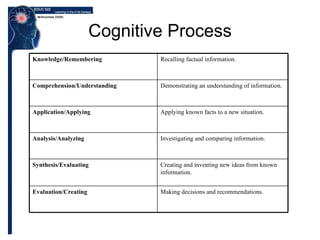
Benjamin Bloom created a taxonomy of cognitive processes and knowledge dimensions in 1956. The taxonomy outlines six levels of cognitive processes - remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. It also describes four dimensions of knowledge - factual, conceptual, procedural, and metacognitive. Bloom's taxonomy set the framework for categorizing educational goals and objectives according to their cognitive complexity and has influenced the development of educational objectives and assessments. It was later revised in 2001 to better reflect 21st century work.



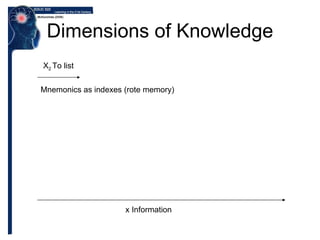
![Dimensions of Knowledge x Information “95% of the test questions students encounter requires them to think only at the lowest possible level…the recall of information.” [Bloom 1956]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bloom-091110005903-phpapp02/85/Blooms-taxonomy-Expanding-past-rote-memory-5-320.jpg)