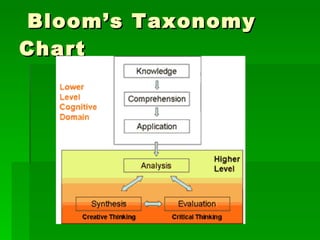
1) Bloom's Taxonomy is a hierarchical model that classifies thinking into six levels of complexity: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create.
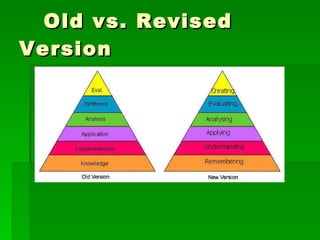
2) Originally developed in the 1950s, Bloom's Taxonomy was revised in the 1990s to change nouns into verbs to illustrate thinking as an active process.
3) The revised taxonomy defines each level using key verbs and provides examples of questions and activities for each level.