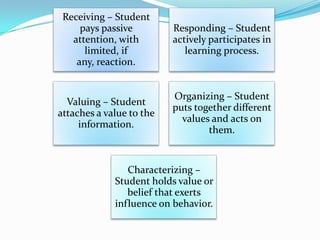
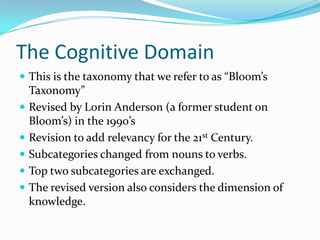
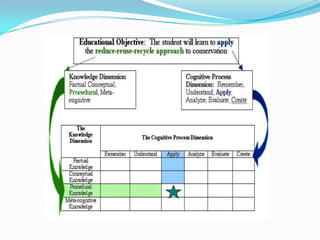
This document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which classifies educational goals into three domains: Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor. The Cognitive domain was revised by Anderson and Krathwohl in 2001 to better align with 21st century skills. The revised taxonomy has six levels within the Cognitive domain - Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. Objectives are classified based on the type of knowledge (factual, conceptual, procedural, metacognitive) and cognitive process verb used. The document provides examples of verbs to write objectives for each cognitive process level.