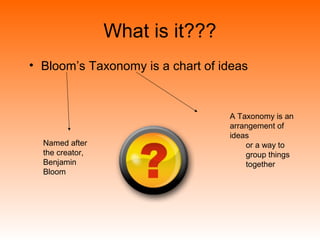
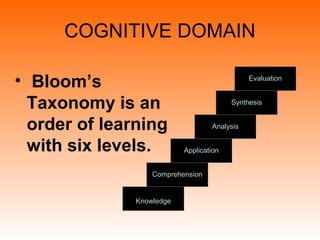
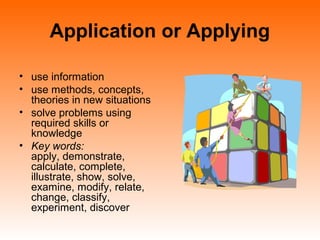
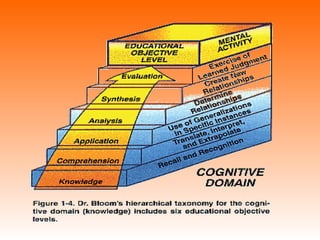
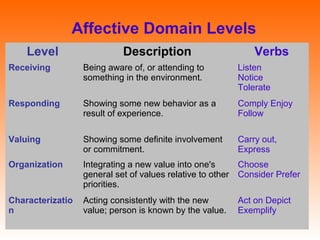
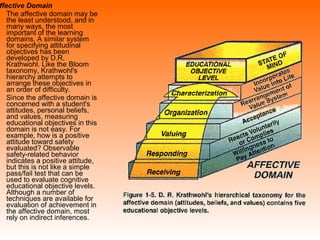
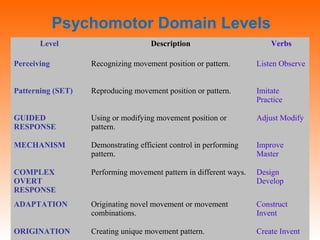
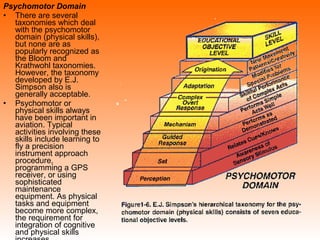
Bloom's Taxonomy is a framework for classifying educational goals and objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. It was created in 1956 by education psychologist Benjamin Bloom and revised in 2001. The taxonomy categorizes learning objectives into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain involves knowledge and intellectual skills and has six levels - remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The affective domain deals with attitudes, values, and emotions and also has five levels. The psychomotor domain involves physical skills and manipulations and its levels range from perception to complex overt responses. Bloom's Taxonomy provides a useful guide for designing instructional objectives and assessments across different learning types and depths