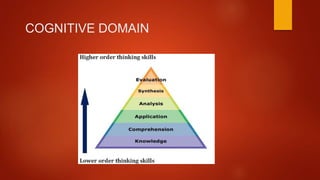
Bloom's Taxonomy, developed by Benjamin Bloom and others in 1956, is a classification system for educational objectives that helps define different levels of human cognition like thinking and understanding. It includes three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor, each with distinct categories that guide educators in curriculum development and assessment. The revised taxonomy by Lorin Anderson in 2001 updated the cognitive domain's categories and emphasizes skills over content, serving as a foundational tool in educational philosophy and teaching methodologies.